We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Sumit Kamat/Sandbox Reserved 901
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) known as acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1 (ALL-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KMT2A gene. KMT2A gene is a histone methyltransferase which are histone modifying enzymes which catalyze the transfer of methyl groups to lysine and arginine residues of histone proteins. The KMT2A gene is a positive global regulator of gene transcription and comprises of transactivation domain 9aaTAD which is involved in the epigenetic maintenance of transcriptional memory <ref>PMID 1720549</ref>. The KMT2 family can mono-, di- and trimethylates histone H3K4. This family of enzymes is found within a macromolecular complex known as the COMPASS family and are highly conserved from yeast to human <ref>PMC3711870</ref>. | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) known as acute lymphoblastic leukemia 1 (ALL-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KMT2A gene. KMT2A gene is a histone methyltransferase which are histone modifying enzymes which catalyze the transfer of methyl groups to lysine and arginine residues of histone proteins. The KMT2A gene is a positive global regulator of gene transcription and comprises of transactivation domain 9aaTAD which is involved in the epigenetic maintenance of transcriptional memory <ref>PMID 1720549</ref>. The KMT2 family can mono-, di- and trimethylates histone H3K4. This family of enzymes is found within a macromolecular complex known as the COMPASS family and are highly conserved from yeast to human <ref>PMC3711870</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:|thumb|1000px|center|Figure 1. Schematic representation of ATAD2 with the two separate domains shown in yellow (AAA Domain) and blue (Bromodomain).]] | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 10: | Line 13: | ||
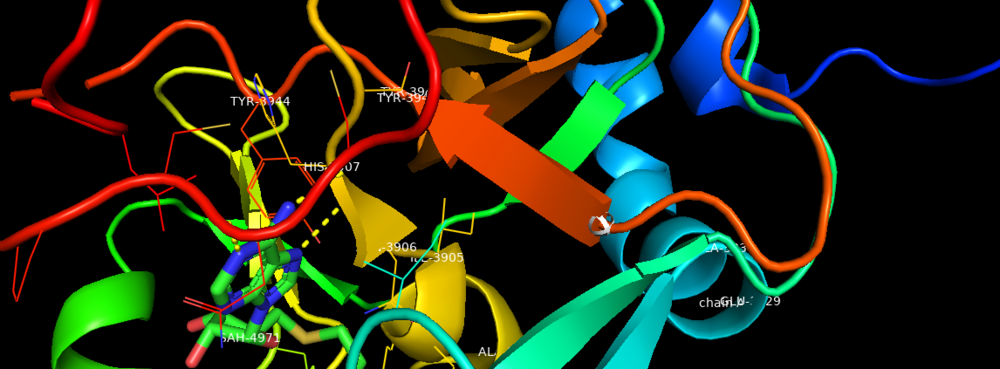
The KMT2A gene encodes a protein which is contains multiple conserved domains. KMT2A gene encodes a transcriptional coactivator that plays an important role in regulating gene expression during early development and hematopoiesis. Out of the many domains, SET domain is responsible for its histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase activity which mediates chromatin modifications associated with epigenetic transcriptional activation <ref> PMC 3225774 </ref>.The SET1 and MLL (KMT2) methyltransferases are conserved from yeast through humans. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome encodes a single H3K4 methyltransferase, Set1, whereas humans possess at least six homologs: SET1a, SET1b and MLL1-4. Unlike many SET domain enzymes, SET1 and MLL KMTs display very weak activity toward H3K4 and require additional subunits to attain maximal activity <ref>PMC3711867</ref>. MLL1 was found to be involved in chromosomal translocations in a variety of acute lymphoid and myeloid leukaemias <ref> Eissenberg JC, Shilatifard A. Histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation in development and differentiation. Dev Biol. 2010 Mar 15;339(2):240-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.08.017. Epub 2009 Aug 21. PMID: 19703438; PMCID: PMC3711867 </ref>. | The KMT2A gene encodes a protein which is contains multiple conserved domains. KMT2A gene encodes a transcriptional coactivator that plays an important role in regulating gene expression during early development and hematopoiesis. Out of the many domains, SET domain is responsible for its histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase activity which mediates chromatin modifications associated with epigenetic transcriptional activation <ref> PMC 3225774 </ref>.The SET1 and MLL (KMT2) methyltransferases are conserved from yeast through humans. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome encodes a single H3K4 methyltransferase, Set1, whereas humans possess at least six homologs: SET1a, SET1b and MLL1-4. Unlike many SET domain enzymes, SET1 and MLL KMTs display very weak activity toward H3K4 and require additional subunits to attain maximal activity <ref>PMC3711867</ref>. MLL1 was found to be involved in chromosomal translocations in a variety of acute lymphoid and myeloid leukaemias <ref> Eissenberg JC, Shilatifard A. Histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methylation in development and differentiation. Dev Biol. 2010 Mar 15;339(2):240-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.08.017. Epub 2009 Aug 21. PMID: 19703438; PMCID: PMC3711867 </ref>. | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Binding Pocket.png|thumb|1000px|center|Figure 1. Binding Domain pocket of KMT2A SET Domain with the cofactor product S-Adenosylhomocysteine. |
| + | ]] | ||
Revision as of 17:23, 28 April 2020
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A KMT2A
| |||||||||||