We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 897
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
=== Evolutionary conservations === | === Evolutionary conservations === | ||
| - | PWWP domain is only found in eukaryotes, from a yeast to a human. The number of PWWP containing protein is also varying on species; the human has 20. The loyal family has a common structural characteristic, three conserved β-strands.<ref>Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.</ref> The PWWP domain is also believed to be evolved from a common ancestor which had 3 β-strands. | + | PWWP domain is only found in eukaryotes, from a yeast to a human. The number of PWWP containing protein is also varying on species; the human has 20. The loyal family has a common structural characteristic, three conserved β-strands.<ref>Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.</ref> The PWWP domain is also believed to be evolved from a common ancestor which had 3 β-strands. Using domain-tree approach, the BRPF family was branched out from rest of PWWP domain containg proteins and evolved itself.<ref>Alvarez-Venegas R, Avramova Z. Evolution of the PWWP-domain encoding genes in the plant and animal lineages. BMC evolutionary biology. 2012 Dec 1;12(1):101.</ref> As a domain, the PWWP presents in both unicellular and multicellular organisms. However, proteins of unicellular organisms are not found in multicellular creatures. Therefore, the PWWP domain was transmitted as a conserved linear arrangement alone, not the whole protein.<ref>Alvarez-Venegas R, Avramova Z. Evolution of the PWWP-domain encoding genes in the plant and animal lineages. BMC evolutionary biology. 2012 Dec 1;12(1):101.</ref> |
== Therapheutic features == | == Therapheutic features == | ||
Revision as of 19:01, 28 April 2020
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 13 through July 31, 2020 for use in the course Protein Structure in Drug Discovery taught by Karen C. Glass at the ACPHS, Colchester, United States. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 895 through Sandbox Reserved 901. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
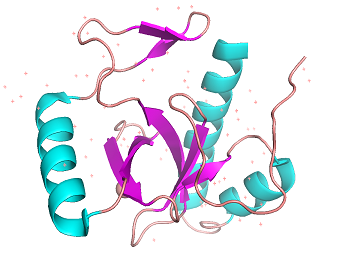
BRPF3 PWWP binding domain 3PFS
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.
- ↑ Vermeulen M, Eberl HC, Matarese F, Marks H, Denissov S, Butter F, Lee KK, Olsen JV, Hyman AA, Stunnenberg HG, Mann M. Quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling of epigenetic histone marks and their readers. Cell. 2010 Sep 17;142(6):967-80.
- ↑ Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.
- ↑ Hung YL, Lee HJ, Jiang I, Lin SC, Lo WC, Lin YJ, Sue SC. The first residue of the PWWP motif modulates HATH domain binding, Stability, and Protein–Protein Interaction. Biochemistry. 2015 Jul 7;54(26):4063-74.
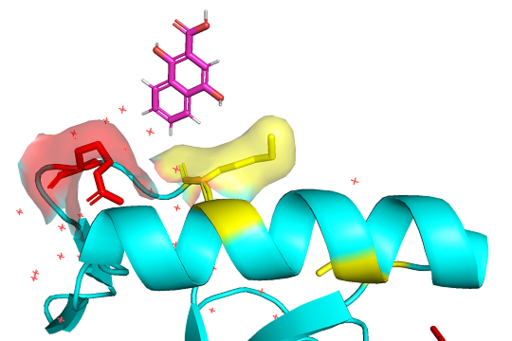
- ↑ Vezzoli A, Bonadies N, Allen MD, Freund SM, Santiveri CM, Kvinlaug BT, Huntly BJ, Göttgens B, Bycroft M. Molecular basis of histone H3K36me3 recognition by the PWWP domain of Brpf1. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2010 May;17(5):617-9.
- ↑ Vermeulen M, Eberl HC, Matarese F, Marks H, Denissov S, Butter F, Lee KK, Olsen JV, Hyman AA, Stunnenberg HG, Mann M. Quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling of epigenetic histone marks and their readers. Cell. 2010 Sep 17;142(6):967-80.
- ↑ Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.
- ↑ Qiu Y, Zhang W, Zhao C, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Li G, Shi Y, Tu X, Wu J. Solution structure of the Pdp1 PWWP domain reveals its unique binding sites for methylated H4K20 and DNA. Biochemical Journal. 2012 Mar 15;442(3):527-38.
- ↑ Qiu C, Sawada K, Zhang X, Cheng X. The PWWP domain of mammalian DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3b defines a new family of DNA-binding folds. Nature structural biology. 2002 Mar;9(3):217-24.
- ↑ Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.
- ↑ Alvarez-Venegas R, Avramova Z. Evolution of the PWWP-domain encoding genes in the plant and animal lineages. BMC evolutionary biology. 2012 Dec 1;12(1):101.
- ↑ Alvarez-Venegas R, Avramova Z. Evolution of the PWWP-domain encoding genes in the plant and animal lineages. BMC evolutionary biology. 2012 Dec 1;12(1):101.
- ↑ Vezzoli A, Bonadies N, Allen MD, Freund SM, Santiveri CM, Kvinlaug BT, Huntly BJ, Göttgens B, Bycroft M. Molecular basis of histone H3K36me3 recognition by the PWWP domain of Brpf1. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2010 May;17(5):617-9.
- ↑ Bjarkam CR, Corydon TJ, Olsen IM, Pallesen J, Nyegaard M, Fryland T, Mors O, Børglum AD. Further immunohistochemical characterization of BRD1 a new susceptibility gene for schizophrenia, and bipolar affective disorder. Brain Structure and Function. 2009 Dec 1;214(1):37.