This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 897
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
===Methyl-lysine reader=== | ===Methyl-lysine reader=== | ||
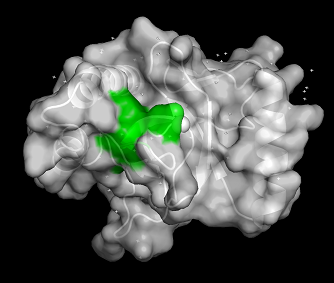
PWWP domains are one of epigenetic regulators which recognize specific lysine residues which are methylated. Even though there is no detailed research on 3pfs, it may be assumed to have similar function with BRPF1 PWWP domain which is shown to have methylated histone binding activity.<ref>Vezzoli A, Bonadies N, Allen MD, Freund SM, Santiveri CM, Kvinlaug BT, Huntly BJ, Göttgens B, Bycroft M. Molecular basis of histone H3K36me3 recognition by the PWWP domain of Brpf1. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2010 May;17(5):617-9.</ref> With a high-throughput mass spectrometry screening, this motif is suggested as an essential motif of histone 3 lysine 36 trimethylation binding.<ref>Vermeulen M, Eberl HC, Matarese F, Marks H, Denissov S, Butter F, Lee KK, Olsen JV, Hyman AA, Stunnenberg HG, Mann M. Quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling of epigenetic histone marks and their readers. Cell. 2010 Sep 17;142(6):967-80.</ref> The β-strands and Pro-Trp-Trp-Pro motif form hydrophobic cavity, which is the binding site of methylated lysines.<ref>Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.</ref> Since the aromatic cage is a common structure in the Royal family, it can be a common tool for methylated lysine binding.<ref>Qiu Y, Zhang W, Zhao C, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Li G, Shi Y, Tu X, Wu J. Solution structure of the Pdp1 PWWP domain reveals its unique binding sites for methylated H4K20 and DNA. Biochemical Journal. 2012 Mar 15;442(3):527-38.</ref> | PWWP domains are one of epigenetic regulators which recognize specific lysine residues which are methylated. Even though there is no detailed research on 3pfs, it may be assumed to have similar function with BRPF1 PWWP domain which is shown to have methylated histone binding activity.<ref>Vezzoli A, Bonadies N, Allen MD, Freund SM, Santiveri CM, Kvinlaug BT, Huntly BJ, Göttgens B, Bycroft M. Molecular basis of histone H3K36me3 recognition by the PWWP domain of Brpf1. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2010 May;17(5):617-9.</ref> With a high-throughput mass spectrometry screening, this motif is suggested as an essential motif of histone 3 lysine 36 trimethylation binding.<ref>Vermeulen M, Eberl HC, Matarese F, Marks H, Denissov S, Butter F, Lee KK, Olsen JV, Hyman AA, Stunnenberg HG, Mann M. Quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling of epigenetic histone marks and their readers. Cell. 2010 Sep 17;142(6):967-80.</ref> The β-strands and Pro-Trp-Trp-Pro motif form hydrophobic cavity, which is the binding site of methylated lysines.<ref>Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.</ref> Since the aromatic cage is a common structure in the Royal family, it can be a common tool for methylated lysine binding.<ref>Qiu Y, Zhang W, Zhao C, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Li G, Shi Y, Tu X, Wu J. Solution structure of the Pdp1 PWWP domain reveals its unique binding sites for methylated H4K20 and DNA. Biochemical Journal. 2012 Mar 15;442(3):527-38.</ref> | ||
| + | [[Image:PWWP surface.png|thumb|center|512 px| '''Figure 2:''' Surface of 3PFS with PWWP motif(green) is indicated. generated in PyMOL using PDB: ''3PFS'']] | ||
===Nonspecific binding=== | ===Nonspecific binding=== | ||
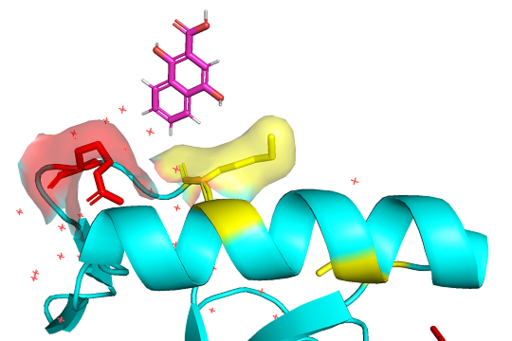
The PWWP domains have a significant amount of basic residues which gives ability of nonspecific binding on DNA strands.<ref>Qiu C, Sawada K, Zhang X, Cheng X. The PWWP domain of mammalian DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3b defines a new family of DNA-binding folds. Nature structural biology. 2002 Mar;9(3):217-24.</ref> BRPF3 3pfs protein has 11 lysine residues and 12 arginine residues. These residues' sidechains remain being positively charged on in vivo pH. The DNA strand phosphate backbone, which is negatively charged, would be attracted to PWWP domain surface due to the nature of attraction between the opposite charges. | The PWWP domains have a significant amount of basic residues which gives ability of nonspecific binding on DNA strands.<ref>Qiu C, Sawada K, Zhang X, Cheng X. The PWWP domain of mammalian DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3b defines a new family of DNA-binding folds. Nature structural biology. 2002 Mar;9(3):217-24.</ref> BRPF3 3pfs protein has 11 lysine residues and 12 arginine residues. These residues' sidechains remain being positively charged on in vivo pH. The DNA strand phosphate backbone, which is negatively charged, would be attracted to PWWP domain surface due to the nature of attraction between the opposite charges. | ||
| - | [[Image:3pfs non-selective model.png|thumb|center|512 px| '''Figure | + | [[Image:3pfs non-selective model.png|thumb|center|512 px| '''Figure 3:''' Lysine(yellow) and Arginine(red) residues on 3PFS surface interacting with DNA backbone generated in PyMOL using PDB: ''3PFS'']] |
Revision as of 19:48, 28 April 2020
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 13 through July 31, 2020 for use in the course Protein Structure in Drug Discovery taught by Karen C. Glass at the ACPHS, Colchester, United States. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 895 through Sandbox Reserved 901. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
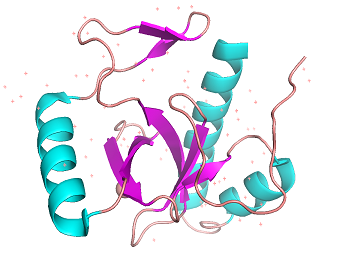
BRPF3 PWWP binding domain 3PFS
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.
- ↑ Vermeulen M, Eberl HC, Matarese F, Marks H, Denissov S, Butter F, Lee KK, Olsen JV, Hyman AA, Stunnenberg HG, Mann M. Quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling of epigenetic histone marks and their readers. Cell. 2010 Sep 17;142(6):967-80.
- ↑ Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.
- ↑ Hung YL, Lee HJ, Jiang I, Lin SC, Lo WC, Lin YJ, Sue SC. The first residue of the PWWP motif modulates HATH domain binding, Stability, and Protein–Protein Interaction. Biochemistry. 2015 Jul 7;54(26):4063-74.
- ↑ Vezzoli A, Bonadies N, Allen MD, Freund SM, Santiveri CM, Kvinlaug BT, Huntly BJ, Göttgens B, Bycroft M. Molecular basis of histone H3K36me3 recognition by the PWWP domain of Brpf1. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2010 May;17(5):617-9.
- ↑ Vermeulen M, Eberl HC, Matarese F, Marks H, Denissov S, Butter F, Lee KK, Olsen JV, Hyman AA, Stunnenberg HG, Mann M. Quantitative interaction proteomics and genome-wide profiling of epigenetic histone marks and their readers. Cell. 2010 Sep 17;142(6):967-80.
- ↑ Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.
- ↑ Qiu Y, Zhang W, Zhao C, Wang Y, Wang W, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Li G, Shi Y, Tu X, Wu J. Solution structure of the Pdp1 PWWP domain reveals its unique binding sites for methylated H4K20 and DNA. Biochemical Journal. 2012 Mar 15;442(3):527-38.
- ↑ Qiu C, Sawada K, Zhang X, Cheng X. The PWWP domain of mammalian DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3b defines a new family of DNA-binding folds. Nature structural biology. 2002 Mar;9(3):217-24.
- ↑ Rona GB, Eleutherio EC, Pinheiro AS. PWWP domains and their modes of sensing DNA and histone methylated lysines. Biophysical reviews. 2016 Mar 1;8(1):63-74.
- ↑ Alvarez-Venegas R, Avramova Z. Evolution of the PWWP-domain encoding genes in the plant and animal lineages. BMC evolutionary biology. 2012 Dec 1;12(1):101.
- ↑ Alvarez-Venegas R, Avramova Z. Evolution of the PWWP-domain encoding genes in the plant and animal lineages. BMC evolutionary biology. 2012 Dec 1;12(1):101.
- ↑ Vezzoli A, Bonadies N, Allen MD, Freund SM, Santiveri CM, Kvinlaug BT, Huntly BJ, Göttgens B, Bycroft M. Molecular basis of histone H3K36me3 recognition by the PWWP domain of Brpf1. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2010 May;17(5):617-9.
- ↑ Bjarkam CR, Corydon TJ, Olsen IM, Pallesen J, Nyegaard M, Fryland T, Mors O, Børglum AD. Further immunohistochemical characterization of BRD1 a new susceptibility gene for schizophrenia, and bipolar affective disorder. Brain Structure and Function. 2009 Dec 1;214(1):37.