This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Sumit Kamat/Sandbox Reserved 901
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== Clinical Significance == | == Clinical Significance == | ||
| - | KMT2A is an important gene because of its association with cognition and development. Epigenetic dysregulation of DNA methylation which leads to abnormal H3K4 trimethylation has been implicated in several neurological disorders such as autism <ref> Shulha HP, Cheung I, Whittle C, et al. Epigenetic Signatures of Autism: Trimethylated H3K4 Landscapes in Prefrontal Neurons. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(3):314–324. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.151 </ref>. In schizophrenia MLL-1 participates in the process of GAD67 downregulation resulting in decreased H3K4 methylation at GABAergic gene promoters <ref> Huang, H. S., Matevossian, A., Whittle, C., Kim, S. Y., Schumacher, A., Baker, S. P., & Akbarian, S. (2007). Prefrontal dysfunction in schizophrenia involves mixed-lineage leukemia 1-regulated histone methylation at GABAergic gene promoters. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 27(42), 11254–11262. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3272-07.2007 </ref>. Rearrangements of the MLL1 gene are associated with aggressive acute leukemias, both lymphoblastic and myeloid.native MLL1 regulates Hox genes in hematopoietic cells to establish cellular identity | + | KMT2A is an important gene because of its association with cognition and development. Epigenetic dysregulation of DNA methylation which leads to abnormal H3K4 trimethylation has been implicated in several neurological disorders such as autism <ref> Shulha HP, Cheung I, Whittle C, et al. Epigenetic Signatures of Autism: Trimethylated H3K4 Landscapes in Prefrontal Neurons. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(3):314–324. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.151 </ref>. In schizophrenia MLL-1 participates in the process of GAD67 downregulation resulting in decreased H3K4 methylation at GABAergic gene promoters <ref> Huang, H. S., Matevossian, A., Whittle, C., Kim, S. Y., Schumacher, A., Baker, S. P., & Akbarian, S. (2007). Prefrontal dysfunction in schizophrenia involves mixed-lineage leukemia 1-regulated histone methylation at GABAergic gene promoters. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 27(42), 11254–11262. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3272-07.2007 </ref>. Rearrangements of the MLL1 gene are associated with aggressive acute leukemias, both lymphoblastic and myeloid.native MLL1 regulates Hox genes in hematopoietic cells to establish cellular identity. Disruption of MLL1 function by chromosomal translocation results in Hox misregulation coupled with the onset of leukemic phenotypes. Despite being an aggressive leukemia, the MLL1 rearranged sub-type had the lowest mutation rates reported for any cancer <ref> Guenther MG, Jenner RG, Chevalier B, et al. Global and Hox-specific roles for the MLL1 methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(24):8603–8608. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503072102 </ref>, <ref> Andersson AK, Ma J, Wang J, et al. The landscape of somatic mutations in infant MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Nat Genet. 2015;47(4):330–337. doi:10.1038/ng.3230 </ref>. |
| + | Wiedemann–Steiner syndrome results from mutations in the MLL-1 gene which encodes a histone modification enzyme on the long arm of chromosome 11. The leukemia cells of up to 80 percent of infants with ALL-1 have a chromosomal rearrangement that fuses the MLL1 gene to a gene on a different chromosome <ref> Andersson AK, Ma J, Wang J, et al. The landscape of somatic mutations in infant MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Nat Genet. 2015;47(4):330–337. doi:10.1038/ng.3230 </ref> . | ||
| - | Mutations in MLL1 cause Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome and Acute lymphoblastic leukemia.[23] The leukemia cells of up to 80 percent of infants with ALL-1 have a chromosomal rearrangement that fuses the MLL1 gene to a gene on a different chromosome. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 19:53, 28 April 2020
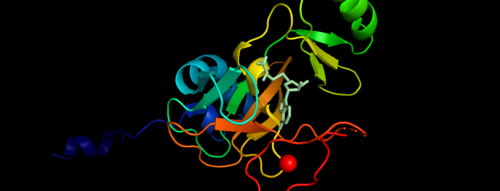
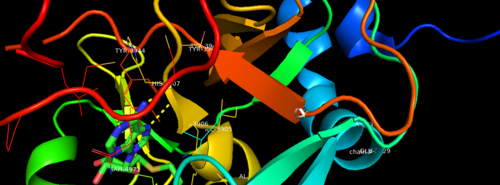
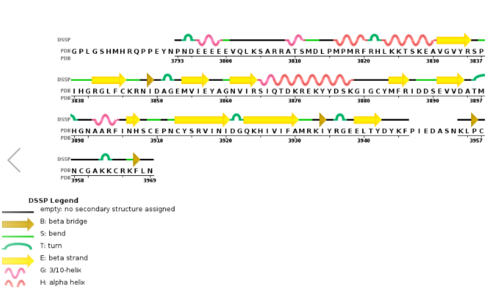
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A KMT2A
| |||||||||||