|
Overview
Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2A (KMT2A) known as mixed-lineage leukemia 1 (MLL-1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KMT2A gene. KMT2A gene is a histone methyltransferase which are histone modifying enzymes which catalyze the transfer of methyl groups to lysine and arginine residues of histone proteins. The KMT2A gene is a positive global regulator of gene transcription and comprises of transactivation domain 9aaTAD which is involved in the epigenetic maintenance of transcriptional memory [1]. The KMT2 family can mono-, di- and trimethylates histone H3K4. This family of enzymes is found within a macromolecular complex known as the COMPASS family and are highly conserved from yeast to human [2].
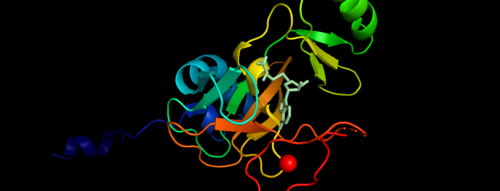 .Figure 1. Showing the Binary Complex of the Mixed Lineage Leukaemia (MLL1) SET Domain with the cofactor product S-Adenosylhomocysteine. Function
The KMT2A gene encodes a protein which is contains multiple conserved domains. KMT2A gene encodes a transcriptional coactivator that plays an important role in regulating gene expression during early development and hematopoiesis. Out of the many domains, SET domain is responsible for its histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4) methyltransferase activity which mediates chromatin modifications associated with epigenetic transcriptional activation [3].The SET1 and MLL (KMT2) methyltransferases are conserved from yeast through humans. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome encodes a single H3K4 methyltransferase, Set1, whereas humans possess at least six homologs: SET1a, SET1b and MLL1-4. Unlike many SET domain enzymes, SET1 and MLL KMTs display very weak activity toward H3K4 and require additional subunits to attain maximal activity [4].MLL-1 has a defined role in mammalian development, where it has been shown to be required for the regulation of important homeobox (Hox) genes and therefore is essential for early patterning in the embryo. In acute myeloid and lymphoid leukemia the MLL1 gene is frequently targeted in oncogenic gene translocations, leading to the expression of chimeric fusions between the amino-terminal 1400 residues of MLL1 and one of over 50 partner genes. MLL1 translocations are more prevalent in childhood leukemias and in therapy-related cases, where they are associated with a poor prognosis [5].
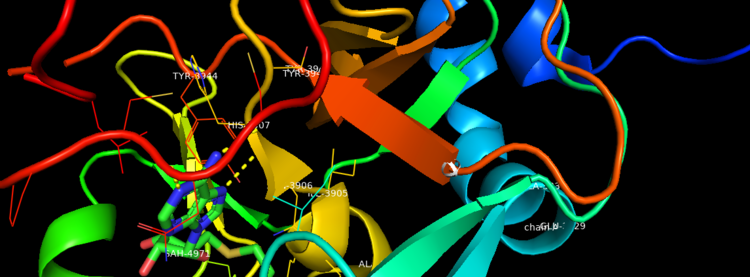 Figure 2. Binding Domain pocket of KMT2A SET Domain with the cofactor product S-Adenosylhomocysteine.
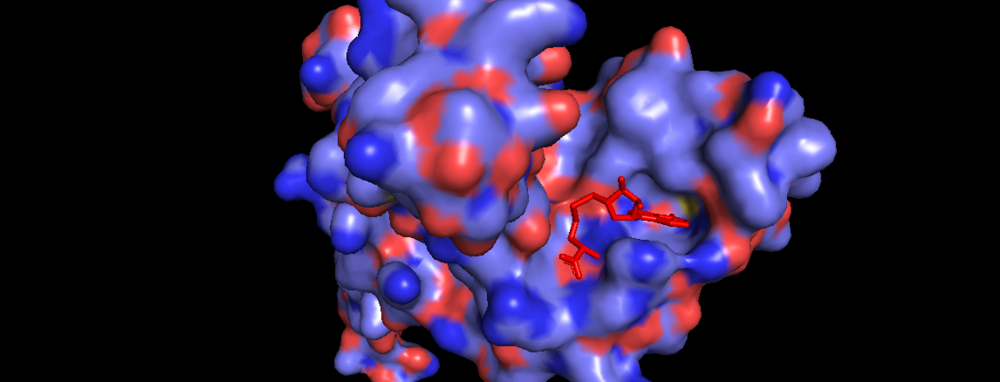 Figure 3. Surface of Binding Domain pocket of KMT2A SET Domain with the cofactor product S-Adenosylhomocysteine.
Structural Analysis
MLL-1 is a 431-kDa protein to be a structural and functional homolog of the Drosophila trithorax (TRX) protein. Two domains are highly conserved between MLL and TRX consist of a carboxy-terminal SET (Su(var)3-9, enhancer-of-zeste, and trithorax) domain and internal plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers. Both domains are found in many chromatin-associated transcriptional regulators and are thought to function either directly in chromatin modification or as protein-protein interaction surfaces for the recruitment of chromatin-modifying machinery [6].There are no significant changes in the structure of the SET domain of the binary complex with the cofactor binding in the surface pocket. It has been determined at the essential active site residues (Phe3884, Tyr3942, Tyr3944, and Phe3946 and the main chain of the tetrapeptide, residues Cys3882 to Phe3885) have a similar arrangement to other SET domains earlier characterized. In the absence of substrate, the electron density for the side chain of Tyr3942 suggests two orientations, but upon substrate binding it becomes ordered and assumes the rotamer equivalent to other structures [7].
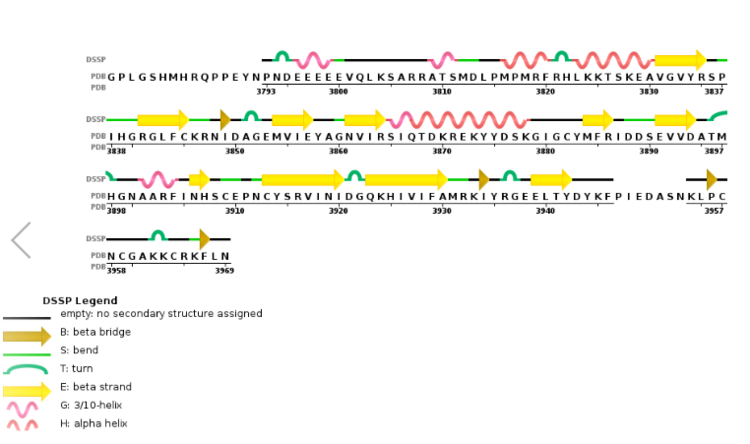 Figure 4. Secondary structure of KMT2A SET Domain with the cofactor product S-Adenosylhomocysteine. [8]
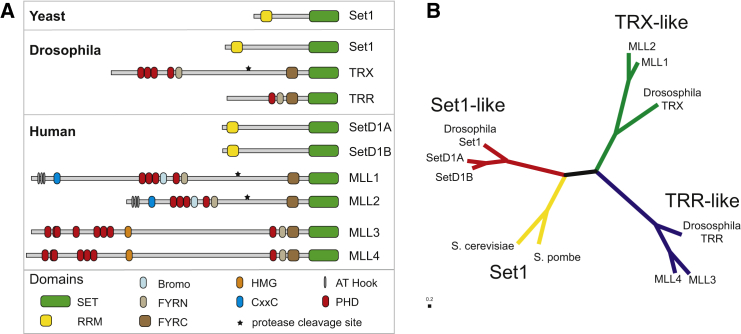 Figure 5. Phylogenetic analysis based on the sequence of only the SET domains of KMT2 proteins in yeast and Humans [9]
Conservation
KMT2A alone has over a dozen of binding partners and is cleaved into two pieces, a larger N-terminal fragment, involved in gene repression, and a smaller C-terminal fragment, which is a transcriptional activator. The cleavage, followed by the association of the two fragments, is necessary for KMT2A to be fully active. KMT2A-E can be distinguished through the catalytic Su(var)3–9, Enhancer of Zeste, Trithorax (SET) domain, however the number of PHD fingers found in these proteins differs considerably. Four PHD fingers are present in KMT2A and KMT2B, whereas KMT2C, KMT2D and KMT2E have eight, seven, and one, respectively [10].
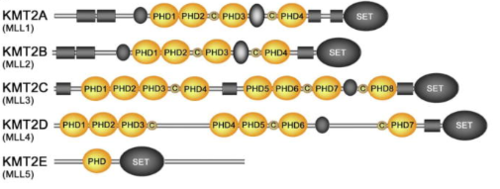 Figure 6.Schematic representation of the KMT2A-E subfamily 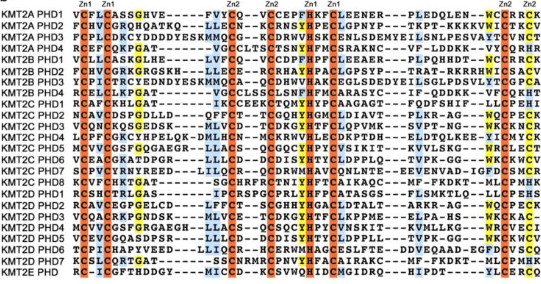 Figure 7. Alignment of the KMT2A-E PHD finger sequences: absolutely, moderately and weakly conserved residues are colored orange, yellow and blue, respectively. Zinc-coordinating cysteine/histidine residues are labeled. [11]
Clinical Significance
KMT2A is an important gene because of its association with cognition and development. Epigenetic dysregulation of DNA methylation which leads to abnormal H3K4 trimethylation has been implicated in several neurological disorders such as autism [12]. In schizophrenia MLL-1 participates in the process of GAD67 downregulation resulting in decreased H3K4 methylation at GABAergic gene promoters [13]. Rearrangements of the MLL1 gene are associated with aggressive acute leukemias, both lymphoblastic and myeloid.native MLL1 regulates Hox genes in hematopoietic cells to establish cellular identity. Disruption of MLL1 function by chromosomal translocation results in Hox misregulation coupled with the onset of leukemic phenotypes. Despite being an aggressive leukemia, the MLL1 rearranged sub-type had the lowest mutation rates reported for any cancer [14], [15].
Wiedemann–Steiner syndrome results from mutations in the MLL-1 gene which encodes a histone modification enzyme on the long arm of chromosome 11. The leukemia cells of up to 80 percent of infants with ALL-1 have a chromosomal rearrangement that fuses the MLL1 gene to a gene on a different chromosome [16] .
References
- ↑ Ziemin-van der Poel S, McCabe NR, Gill HJ, Espinosa R 3rd, Patel Y, Harden A, Rubinelli P, Smith SD, LeBeau MM, Rowley JD, et al.. Identification of a gene, MLL, that spans the breakpoint in 11q23 translocations associated with human leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10735-9. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10735. PMID:1720549 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.23.10735
- ↑ PMC3711870
- ↑ PMC 3225774
- ↑ PMC3711867
- ↑ Guenther, M. G., Jenner, R. G., Chevalier, B., Nakamura, T., Croce, C. M., Canaani, E., & Young, R. A. (2005). Global and Hox-specific roles for the MLL1 methyltransferase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(24), 8603–8608. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0503072102
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-04-1015
- ↑ https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2008.12.029
- ↑ Kabsch W, Sander C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2577-637. PMID:6667333 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bip.360221211
- ↑ Zhang, Y., Mittal, A., Reid, J., Reich, S., Gamblin, S. J., & Wilson, J. R. (2015). Evolving Catalytic Properties of the MLL Family SET Domain. Structure (London, England : 1993), 23(10), 1921–1933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.07.018
- ↑ Hsieh JJ, Ernst P, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Korsmeyer SJ. Proteolytic cleavage of MLL generates a complex of N- and C-terminal fragments that confers protein stability and subnuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(1):186–194. doi:10.1128/mcb.23.1.186-194.2003
- ↑
AMA Ali M, Hom RA, Blakeslee W, Ikenouye L, Kutateladze TG. Diverse functions of PHD fingers of the MLL/KMT2 subfamily. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1843(2):366–371. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.11.016
- ↑ Shulha HP, Cheung I, Whittle C, et al. Epigenetic Signatures of Autism: Trimethylated H3K4 Landscapes in Prefrontal Neurons. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(3):314–324. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.151
- ↑ Huang, H. S., Matevossian, A., Whittle, C., Kim, S. Y., Schumacher, A., Baker, S. P., & Akbarian, S. (2007). Prefrontal dysfunction in schizophrenia involves mixed-lineage leukemia 1-regulated histone methylation at GABAergic gene promoters. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 27(42), 11254–11262. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3272-07.2007
- ↑ Guenther MG, Jenner RG, Chevalier B, et al. Global and Hox-specific roles for the MLL1 methyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(24):8603–8608. doi:10.1073/pnas.0503072102
- ↑ Andersson AK, Ma J, Wang J, et al. The landscape of somatic mutations in infant MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Nat Genet. 2015;47(4):330–337. doi:10.1038/ng.3230
- ↑ Andersson AK, Ma J, Wang J, et al. The landscape of somatic mutations in infant MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Nat Genet. 2015;47(4):330–337. doi:10.1038/ng.3230
|







