Overview
The mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) complex is the main source of entry for calcium ions into the mitochondrial matrix from the intermembrane space. MCU channels exist in most eukaryotic life, but activity is regulated differently in each clade.[1] The precise identity of the MCU wasn't discovered until 2011 and was discovered using a combination of NMR spectroscopy, cryo-electron microscopy, and x-ray crystallography.[2] Cryoelectron microscopy (Cryo-EM) was instrumental in understanding the complete structure of the MCU. Cryo-EM analysis provided a structural framework for understanding the mechanism by with the MCU functions.[3] Prior modeling of the structure was difficult because it has no apparent sequence similarity to other ion channels.[1] However, like other ion channels, the MCU is highly selective and efficient. The MCU has the ability to only allow calcium ions into the mitochondrial matrix at a rate of 5,000,000 ions per second even though potassium ions are over 100,000 times more abundant in the intermembrane space.[1]
Under resting conditions, the calcium concentration in the mitochondria is about the same as in the cytoplasm, but when stimulated, it can increase calcium concentration 10-20-fold.[3] Mitochondria-associated ER membranes (MAMs) exist between mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum, the two largest cellular stores of calcium, to allow for efficient transport of calcium ions.[4] The transfer of electrons through respiratory complexes I-IV produces the energy to pump hydrogen ions into the intermembrane space (IMS) and create the proton electrochemical gradient potential.[3] This negative electrochemical potential is the driving force that moves positively charged calcium ions into the mitochondrial matrix.[3]
Regulation of the uptake and efflux of calcium is important to increase calcium levels enough to activate certain enzymes, but also avoid calcium overload and apoptosis.[4] Mitochondrial calcium increases ATP production by activating pyruvate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and isocitrate dehydrogenase in the Krebs cycle.[4] Therefore, deficiency of MCU leads to decrease of enzyme activity and of oxidative phosphorylation.
Structure
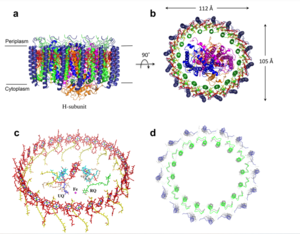
Figure 1: Structure of mitochondrial calcium uniporter colored by functional domain. The transmembrane domain is highlighted in salmon, the matrix domain in light cyan, coiled-coil domain in dark violet, and the N-terminal domain in slate blue.
PDB 6DT0 Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter Complex
The mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex exists as a large complex (around 480 kDa in humans) made up of both pore-forming and regulatory subunits.[4] The MCU is a complex composed of regulatory subunits including mitochondrial calcium uptake (MICU), essential MICU regulator (EMRE), MCU regulatory subunit b (MCUb), and MCU regulator 1 (MCUR1). [5] The mitochondrial uptake proteins (MICU1 and MICU2) are regulatory proteins in the MCU complex that exist in the IMS and contain EF hand domains for calcium binding to control transport through the channel of the MCU complex.[4] When calcium ion concentration in the IMS is low, MICU1 and 2 block the MCU to prevent uptake of calcium.[4] In the presence of high calcium concentrations, more calcium binds to these regulatory proteins and they undergo a conformational change to allow calcium ions through the MCU and into the matrix.[4] In fact, when calcium levels are below 500 nM, MICU1 can block movement of calcium by itself, calcium levels between 500 nM and 1,500 nM require both MICU1 and MICU2 to block ion entry, and any concentration over 1,500 nM is sufficient for calcium entry.[3] Another regulatory protein, MCUR1 is a cofactor in the assembly of the respiratory chain rather than an essential part of the uniporter.[3] Though the MCU is able to take up calcium independently, there are two other pore-forming subunits, the MCUb and the essential MCU regulator (EMRE).[4] MCUb is similar to MCU, but certain amino acids differ and make it an inhibitory subunit.[4] The EMRE is located in the IMS and connects MICU1 and MICU2 to the MCU.[3] It also contributes to regulation of calcium intake in the MCU.[4]
Mitochondrial Calcium Uniporter
The is the ion channel component (Figure 1). The MCU was originally thought to be composed of pentamer of five identical subunits, but it is now known to exist as a dimer of (Figure 2).[2] The organization of the MCU is described as a . The protein is composed of a , a , and a (NTD) (Figure 1).[2] The hydrophobic is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) and the hydrophilic coiled-coil domain exists in the mitochondrial matrix.[1]
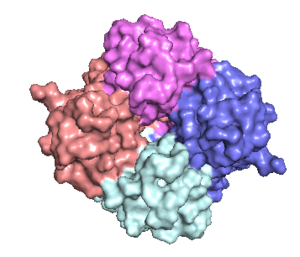
Figure 2: Symmetry and organization of subunits from looking down into the uniporter from the inner mitochondrial membrane
PDB 6DT0 Transmembrane Domain
The is on the inner mitochondrial membrane open to the inner membrane space (Figure 1). The consists of eight separate helices (TM1 and TM2 from each subunit) that are connected by mostly hydrophobic amino acids in the IMS and has symmetry (Figure 4).[1] The small pore, highly specific for calcium binding is located in (TM2) while (TM1) surrounds the pore. packs tightly against from the neighboring subunit which conveys a sense of domain-swapping.[5] The transmembrane domain of MCU can be roughly divided into a narrow outer leaflet portion with a , which is lined by the helices and a wide inner leaflet.[1]
Coiled-coil domain
Past the transmembrane domain, the N-terminal domains of the helices extend into the matrix and form coiled-coils with a C-terminal helix.[1] These "legs" are separated from each other which allows enough space for calcium ions to diffuse out into the matrix.[1] The domain is the first subsection of the soluble domain, which resides in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The coiled coil functions as the joints of the uniporter, providing flexibility to promote transport of Ca2+ions down their concentration gradient.[5] When Ca2+ ions binds to the selectivity pore, the coiled-coil swings approximately 8° around its end near the . This movement propagates to the top of the transmembrane domain, where the pore is located about 85 Å away. The largest displacement triggered by the movement of the coiled-coil is in the transmembrane domain, where the coil bends 20°, moving the transmembrane domain further apart. The junction between the transmembrane domain and the coiled coil's flexibility can be attributed to the disordered packing between subunits. Subunits A and C adopt different conformations than the B and D subunits, although they superimpose closely.[5] The coiled-coil domain is also responsible for assembly of the MCU and is post-translationally modified.[5]
N-terminal Domain
Finally, each leg ends in a (NTD).[1] While the MCU can intake calcium without the NTD, the NTD has regulatory functions, including bending to constrict the pore.[1][5] Reorganization in the NTD due to shifts in the The domain alters membrane packing, facilitating a rotamer switch between a pair of tyrosine residues controlling calcium flow through the pore. The soluble domain is wider than the transmembrane domain (Figure 1), allowing calcium ions to rehydrate and increasing the conductivity of ions through the uniporter into the mitochondrial matrix.[5]
Selectivity Filter
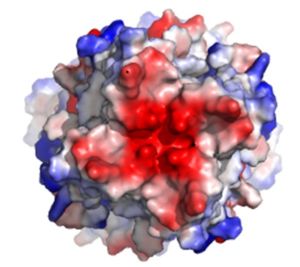
Figure3: Electronegativity of the MCU viewed from outside the channel. The high concentration of negative charge (shown in red) attracts the positive calcium ions.
PDB 6DT0The of the MCU is composed by many acidic amino acids near the narrow mouth of the channel which leads to high affinity for calcium (dissociation constant of less than 2nM) (Figure 3).[1] Negatively charged aspartates at the mouth of the MCU congregate positively charged at the entrance of the channel.[1] A highly conserved motif in the TM2 helices form the selectivity pore which selects for calcium transport over other similar ions.[1]
The motif consists of at the N-terminal end, , , and .[1] The negatively charged side chains of Asp225 and point towards the pore.[1] The of the carboxyl ring is about 4Å, allowing only a dehydrated Ca2+ ion to bind. The combination of these radii and high negative charge (Figure 3) account for the selectivity of the MCU. For example, potassium has an ionic radius of 1.38Å which is much larger than the 1.00Å ionic radius of calcium and potassium cannot fit into the negatively charged ring formed by .[1] Additionally, even though sodium ions have a similar ionic radius, the +2 charge on calcium is better matched to coordination with the glutamate residues.[1]
scene name='83/832952/Tryptophan_proline/2'>Trp224 and Pro229</scene> pack against each other and are oriented towards the pore, but only serve to stabilize and not interact with calcium ions.[1][5] Trp224 stabilizes the carbonyl side chains through and anion pi interactions. These Trp residues also form stacking interactions with Pro229, which orientate the Glu carboxyl side chains towards the middle of the pore to interact with Ca2+ ions.[6] Approximately one helical turn below the glutamate ring of the selectivity filter, there is a tyrosine ring coming a 12Å wide pore allowing high conductivity. [5] The wider opening allows calcium to rehydrate once they pass the selectivity pore.
Calcium Uniporter Structure The X residues ( in this case) face away from the pore and are exposed to the membrane.[1]
Movement of Calcium
Cryo-EM showed three in the MCU channel of roughly spherical density equally spaced 6Å apart.[1] Sites 1 and 2 lie within the and likely contain calcium, but site 3 could be calcium or some other small molecule.[1] Site 1 is positioned in the ring formed by residues and there is a distance of 4Å between the center of the site and each carboxylate group indicating presence of water.[1] The second site is positioned in the ring formed by and there is a distance of 2.8Å between the carboxylate group of each residue and the middle of the site indicating absence of water.[1] For transporting calcium, it is proposed that one calcium ion coordinated with water positioned in site 1 loses its water and moves to site 2 and a calcium ion moves from the IMS into site 1.[1] Meanwhile, a different calcium ion moves from site 2 to site 3 or the mitochondrial matrix.[1]
Mutations
A number of mutations completely eliminate calcium uptake by the MCU. For example, mutation of Trp224, Asp225, Glu228, or Pro229 of the WDXXEP motif altered the highly conserved selectivity filter and completely eliminated calcium uptake.[1][5] Even mutating Glu228 to an aspartate significantly changed the dimensions of the pore and inhibited uptake of calcium.[1] However, mutation of either X residue was not detrimental to calcium uptake.[1] Furthermore, mutation of the tyrosine residue directly below the selectivity filter substantially impaired calcium intake and proper protein folding.[5] The residue on TM1 that affected calcium uptake the most in human MCU was Trp317 (analogous to in C. europaea) which has a side chain constituting a primary contact point between TM1 and TM2.[5] Mutation of human MCU Phe326 (analogous to in C. europaea) or Gly331 of the TM1-TM2 linker ( in C. europaea) affected the linker conformation and configuration of the pore entrance and impaired calcium intake.[5]
Regulation and Inhibition
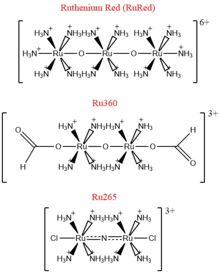
Figure 4: Structures of the ruthenium-based inhibitors of the MCU. Created using ChemDraw Professional 16.0
The most well-known and commonly used inhibitor of the MCU is ruthenium red (RuRed).[2] RuRed is a trinuclear, oxo-bridged complex that effectively inhibits calcium uptake without affecting mitochondrial respiration or calcium efflux.[2] The disadvantage of ruthenium red is its challenging purification.[2] Interestingly, an impure version of RuRed, termed Ru360, was found to be the active component of RuRed and thus another good inhibitor of the MCU (Figure 4).[2] Ru360 is a binuclear, oxo-bridged complex with a similar structure to that of RuRed.[2] The only flaw with Ru360 was that it showed low cell permeability, so Ru265 was developed and had twice the cell permeability of Ru360.[2] Ru265 possesses two bridged Ru centers bridged by a nitride ligand (Figure 4).[2]
Recent experiments suggest that Ru360 inhibits calcium uptake through interactions with the motif.[2] However, not much is known about the mode of inhibition. Mutations of Asp261 and Ser259 in human MCU were shown to maintain calcium uptake into the matrix, but reduce the inhibitory effect of Ru360 but not Ru265.[2] A mutation in a cysteine residue in the had the opposite effect as it reduced the inhibitory effects of Ru265, but not Ru360 (Figure 4).[2]
Medical Relevance
The MCU has a large role in disease because of its effect on apoptosis and cell signaling. The overload of the mitochondrial matrix with calcium leads to release of cytochrome c, overproduction of reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial swelling, and the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) which all lead to apoptotic cell death.[2] This connection between mitochondrial calcium and apoptosis makes the MCU dysregulation a large contributor to cell death and disease. Calcium machinery in the mitochondria are targets for proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressors for this very reason.[3] Apoptosis can either be induced or repressed. Furthermore, external stimuli can activate receptors in the endoplasmic reticulum that release calcium and activate signal transductions.[4] Sequestration of calcium in the mitochondria is vital to shut down these activations, so any impact in movement of calcium ions can cause a wide variety of diseases.[4]
Neurodegenerative Disorders
Disruption in calcium homeostasis leads to a wide range of neurodegenerative disorders. The MCU complex has been identified to play a large role in neuromuscular disease because of a loss or mutation of MICU1.[2] This causes myopathy, learning difficulties, and progressive movement disorders which can be lethal.[2] In Alzheimer's disease, the buildup of amyloid-β plaques in the brain leads to increased calcium uptake in neurons and cell death.[2] Similarly, in early onset Parkinson's disease, degradation of MICU1 by the protein ligase Parkin leads to increased mitochondrial calcium uptake, overload, and death.[2] Finally, disrupted glutamate homeostasis in astrocytes and neurons leads to calcium overload and cell death via excitotoxicity in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).[2]
Diabetes
Calcium homeostasis misregulation has also been proven to be instrumental in obesity, insulin resistance, and type-II diabetes.[4] The intracellular calcium concentrations in primary adipocytes from obese human subjects has been found to be elevated.[4] Any inhibition of downstream calcium signaling could decrease movement of the GLUT4 glucose transporter and glucose uptake.[4] Additionally, ablation of MCU in β-cells in the pancreas demonstrated a decrease in cellular ATP concentration following glucose stimulation which resulted in decreased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.[4] Furthermore, MAMs have been shown to cause glucose intolerance and mitochondrial dysfunction in primary hepatocytes in mice.[4] Subsequent reinforcement of these MAMs has been shown to increase insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.[4]
Heart Failure
Calcium overload in the mitochondria of cardiac cells lead to apoptotic cardiac cell death. Calcium governs excitation contraction coupling (EC coupling) of the cardiac muscles, which creates the ATP needed to power the contraction during heart beats. The increase in mitochondrial Ca2+ concentration is essential for the functioning of this muscle contraction. Mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, though, leads to necrotic cardiac cell death and can be targeted with regulation of the MCU. An example of treatment would be with the use of Ru360 to inhibit the uptake of Ca2+ ions into the mitochondria.[3]




