Journal:Acta Cryst D:S2059798320008475
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
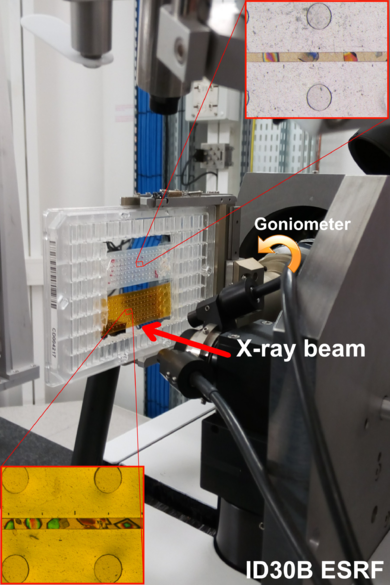
Furthermore, RT diffraction data can reveal motions crucial for catalysis, ligand binding, and allosteric regulation, not always accessible under standard cryogenic data collection.The chips are fabricated by a combination of either OSTEMER-Kapton or OSTEMER-Mylar materials, both produce a sufficiently low scattering background to permit atomic resolution diffraction data collection at room temperature. The proposed system can be easily incorporated into a fully automatized workflow at any synchrotron beamline facilitating the collection of users' data with no-intervention required of the end-user. | Furthermore, RT diffraction data can reveal motions crucial for catalysis, ligand binding, and allosteric regulation, not always accessible under standard cryogenic data collection.The chips are fabricated by a combination of either OSTEMER-Kapton or OSTEMER-Mylar materials, both produce a sufficiently low scattering background to permit atomic resolution diffraction data collection at room temperature. The proposed system can be easily incorporated into a fully automatized workflow at any synchrotron beamline facilitating the collection of users' data with no-intervention required of the end-user. | ||
*<scene name='85/853720/Cv/7'>Test</scene>. | *<scene name='85/853720/Cv/7'>Test</scene>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='85/853720/Cv/8'>Test1</scene> | ||
Revision as of 14:55, 8 July 2020
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.