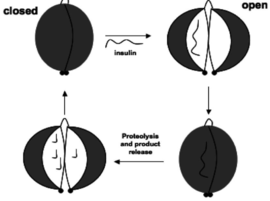
Human Insulin Degrading Enzyme (Hebrew)
From Proteopedia
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=3416 | 1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=3416 | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
2. https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P14735 | 2. https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P14735 | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
3. Affholter JA, Fried VA, Roth RA (December 1988). "Human insulin-degrading enzyme shares structural and functional homologies with E. coli protease III". Science. 242 (4884): 1415–8. | 3. Affholter JA, Fried VA, Roth RA (December 1988). "Human insulin-degrading enzyme shares structural and functional homologies with E. coli protease III". Science. 242 (4884): 1415–8. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
4. Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, et al. (April 2003). "Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (7): 4162–7. | 4. Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, et al. (April 2003). "Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (7): 4162–7. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
5. Hulse RE, Ralant LA, Tang WJ (February 2009). "Structure, Function, and Regulation of Insulin-Degrading Enzyme". Vitamins & Hormones 80:635-48. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(08)00622-5 | 5. Hulse RE, Ralant LA, Tang WJ (February 2009). "Structure, Function, and Regulation of Insulin-Degrading Enzyme". Vitamins & Hormones 80:635-48. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(08)00622-5 | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
6. Kerr ML, Small DH (April 2005). "Cytoplasmic domain of the beta-amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease: function, regulation of proteolysis, and implications for drug development". Journal of Neuroscience Research. 80 (2): 151–9. doi:10.1002/jnr.20408. PMID 15672415. | 6. Kerr ML, Small DH (April 2005). "Cytoplasmic domain of the beta-amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease: function, regulation of proteolysis, and implications for drug development". Journal of Neuroscience Research. 80 (2): 151–9. doi:10.1002/jnr.20408. PMID 15672415. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
7. Kurochkin IV, Goto S (May 1994). "Alzheimer's beta-amyloid peptide specifically interacts with and is degraded by insulin degrading enzyme". FEBS Letters. 345 (1): 33–7. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)00387-4. PMID 8194595. | 7. Kurochkin IV, Goto S (May 1994). "Alzheimer's beta-amyloid peptide specifically interacts with and is degraded by insulin degrading enzyme". FEBS Letters. 345 (1): 33–7. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)00387-4. PMID 8194595. | ||
| - | 8. Mirsky IA, Broh-Kahn RH (January 1949). "The inactivation of insulin by tissue extracts; the distribution and properties of insulin inactivating extracts". Archives of Biochemistry. 20 (1): 1–9. PMID 18104389 | + | <br> |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 8. Mirsky IA, Broh-Kahn RH (January 1949). "The inactivation of insulin by tissue extracts; the distribution and properties of insulin inactivating extracts". Archives of Biochemistry. 20 (1): 1–9. PMID 18104389. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
9.Wang DS, Dickson DW, Malter JS (2006). "beta-Amyloid degradation and Alzheimer's disease". Journal of Biomedicine & Biotechnology. 2006 (3): 58406. doi:10.1155/JBB/2006/58406. PMC 1559921. PMID 17047308. | 9.Wang DS, Dickson DW, Malter JS (2006). "beta-Amyloid degradation and Alzheimer's disease". Journal of Biomedicine & Biotechnology. 2006 (3): 58406. doi:10.1155/JBB/2006/58406. PMC 1559921. PMID 17047308. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 09:37, 14 July 2020
| |||||||||||
References
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=3416
2. https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P14735
3. Affholter JA, Fried VA, Roth RA (December 1988). "Human insulin-degrading enzyme shares structural and functional homologies with E. coli protease III". Science. 242 (4884): 1415–8.
4. Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, et al. (April 2003). "Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 100 (7): 4162–7.
5. Hulse RE, Ralant LA, Tang WJ (February 2009). "Structure, Function, and Regulation of Insulin-Degrading Enzyme". Vitamins & Hormones 80:635-48. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(08)00622-5
6. Kerr ML, Small DH (April 2005). "Cytoplasmic domain of the beta-amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease: function, regulation of proteolysis, and implications for drug development". Journal of Neuroscience Research. 80 (2): 151–9. doi:10.1002/jnr.20408. PMID 15672415.
7. Kurochkin IV, Goto S (May 1994). "Alzheimer's beta-amyloid peptide specifically interacts with and is degraded by insulin degrading enzyme". FEBS Letters. 345 (1): 33–7. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)00387-4. PMID 8194595.
8. Mirsky IA, Broh-Kahn RH (January 1949). "The inactivation of insulin by tissue extracts; the distribution and properties of insulin inactivating extracts". Archives of Biochemistry. 20 (1): 1–9. PMID 18104389.
9.Wang DS, Dickson DW, Malter JS (2006). "beta-Amyloid degradation and Alzheimer's disease". Journal of Biomedicine & Biotechnology. 2006 (3): 58406. doi:10.1155/JBB/2006/58406. PMC 1559921. PMID 17047308.