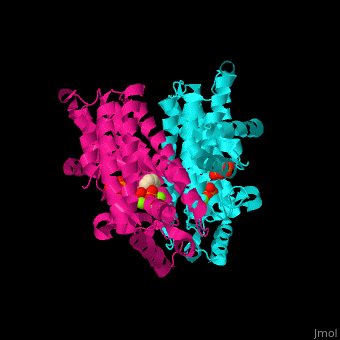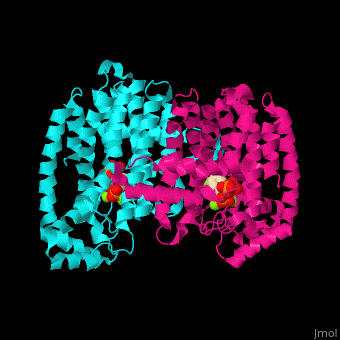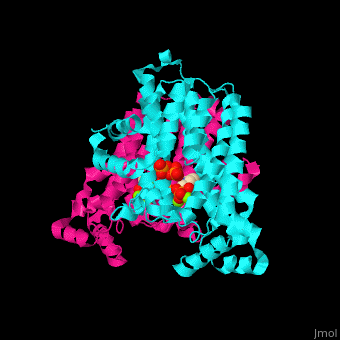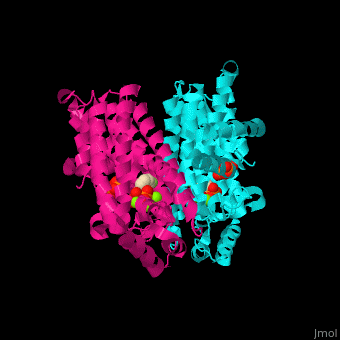We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Farnesyl diphosphate synthase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | == Introduction == | + | == Introduction == |
<StructureSection load='2opm' size='350' side='right' scene='48/485622/Cv/15' caption='Human farnesyl diphosphate synthase complex with lipophylic bisphosphonate inhibitor and Mg+2 ions (green) (PDB code [[2opm]]) '> | <StructureSection load='2opm' size='350' side='right' scene='48/485622/Cv/15' caption='Human farnesyl diphosphate synthase complex with lipophylic bisphosphonate inhibitor and Mg+2 ions (green) (PDB code [[2opm]]) '> | ||
'''Farnesyl pyrophospate synthase''' (FPPS), also named '''Farnesyl diphosphate synthase''' (FPS), is a chain elongation enzyme that catalyzes carbon-carbon formation in two consecutive condensation reactions that convert one equivalent of dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) and two equivalents of isopentyl diphosphates (IPP) into one equivalent of Farnesyl pyrophospate (FPP).<ref>PMID:11152452</ref> | '''Farnesyl pyrophospate synthase''' (FPPS), also named '''Farnesyl diphosphate synthase''' (FPS), is a chain elongation enzyme that catalyzes carbon-carbon formation in two consecutive condensation reactions that convert one equivalent of dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) and two equivalents of isopentyl diphosphates (IPP) into one equivalent of Farnesyl pyrophospate (FPP).<ref>PMID:11152452</ref> | ||
| - | == Function == | + | == Function == |
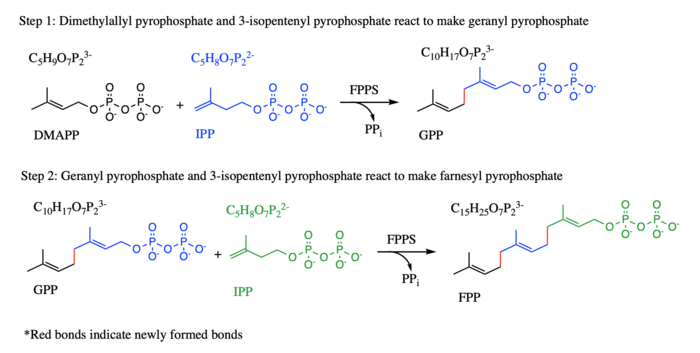
In the first condensation reaction, IPP and its isomer DMAPP react to form a ten-carbon geranyl diphosphate (GPP), while in the second condensation reaction, the product geranyl diphosphate from the first step and an additional IPP molecule react to make FPP (see diagram). FPP is an essential enzyme in the biosynthesis of mevalonate, isoprenoids, and sterols in a variety of organisms. FPPS has been studied in conjunction with different parasites. TcFPPS refers to FPPS in the Typanosoma cruzi parasite while LmFPPS refers to FPPS in the Leishmania major parasite. Bisphosphonates have been shown to inhibit FPPS and are currently being used as antiparasitic drugs as well as a treatment for various bone diseases. | In the first condensation reaction, IPP and its isomer DMAPP react to form a ten-carbon geranyl diphosphate (GPP), while in the second condensation reaction, the product geranyl diphosphate from the first step and an additional IPP molecule react to make FPP (see diagram). FPP is an essential enzyme in the biosynthesis of mevalonate, isoprenoids, and sterols in a variety of organisms. FPPS has been studied in conjunction with different parasites. TcFPPS refers to FPPS in the Typanosoma cruzi parasite while LmFPPS refers to FPPS in the Leishmania major parasite. Bisphosphonates have been shown to inhibit FPPS and are currently being used as antiparasitic drugs as well as a treatment for various bone diseases. | ||
[[Image:FPPSynthesisDiagram.png|700x750px]] | [[Image:FPPSynthesisDiagram.png|700x750px]] | ||
| - | == Structure == | + | == Structure == |
FPPS exists as a homodimer, with each monomer having an active site. The monomers have the characteristic FPPS fold of a ten-helix bundle and four other helices that run perpendicular to the bundle. There are two substrate sites, one is allylic and the other is homoallylic. GPP and DMAPP bind to the allylic site, while IPP binds to the homoallylic site. These two sites are connected to the top of the bundle and exist as part of a cavity<ref>PMID:24598749</ref>. Another characteristic feature of all FPPS enzymes are two highly conserved aspartate rich motifs. These motifs are called <scene name='48/485622/Lmfpps_rbs/5'>First Aspartate Rich Motif (FARM) and Second Aspartate Rich Motif (SARM)</scene>, and have sequences of DDXX(XX)D and DDXXD respectively. FARM and SARM are found on opposite sides on the active site cavity facing one another<ref>DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00432</ref>. | FPPS exists as a homodimer, with each monomer having an active site. The monomers have the characteristic FPPS fold of a ten-helix bundle and four other helices that run perpendicular to the bundle. There are two substrate sites, one is allylic and the other is homoallylic. GPP and DMAPP bind to the allylic site, while IPP binds to the homoallylic site. These two sites are connected to the top of the bundle and exist as part of a cavity<ref>PMID:24598749</ref>. Another characteristic feature of all FPPS enzymes are two highly conserved aspartate rich motifs. These motifs are called <scene name='48/485622/Lmfpps_rbs/5'>First Aspartate Rich Motif (FARM) and Second Aspartate Rich Motif (SARM)</scene>, and have sequences of DDXX(XX)D and DDXXD respectively. FARM and SARM are found on opposite sides on the active site cavity facing one another<ref>DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00432</ref>. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
FPS <scene name='48/485622/Cv/12'>active site</scene> contains <scene name='48/485622/Cv/13'>Mg+2 ions coordination sites</scene> and binds <scene name='48/485622/Cv/11'>bisphosphonate inhibitors</scene>; see also <scene name='48/485622/Cv/14'>phosphates coordination sites</scene>, (PDB code [[2opm]])<ref>PMID:19309137</ref>, water molecules are shown as red spheres. | FPS <scene name='48/485622/Cv/12'>active site</scene> contains <scene name='48/485622/Cv/13'>Mg+2 ions coordination sites</scene> and binds <scene name='48/485622/Cv/11'>bisphosphonate inhibitors</scene>; see also <scene name='48/485622/Cv/14'>phosphates coordination sites</scene>, (PDB code [[2opm]])<ref>PMID:19309137</ref>, water molecules are shown as red spheres. | ||
| - | == Relevance == | + | == Relevance == |
FPS bisphosphonate inhibitors (like zoledronic acid) are used as drugs for treatment of bone resorption diseases<ref>PMID:24369118</ref>. FPS inhibitor [[Alendronate]] or Fosamax is used in treatment of osteoporosis<ref>PMID:9116385</ref>. Bisphosphonates have been explored as antiparasitic drugs with FPPS because current treatments are expensive, have low efficacy, and have dangerous side effects. FPPS is important in the lengthening of hydrophobic chains and determination of their specificity. | FPS bisphosphonate inhibitors (like zoledronic acid) are used as drugs for treatment of bone resorption diseases<ref>PMID:24369118</ref>. FPS inhibitor [[Alendronate]] or Fosamax is used in treatment of osteoporosis<ref>PMID:9116385</ref>. Bisphosphonates have been explored as antiparasitic drugs with FPPS because current treatments are expensive, have low efficacy, and have dangerous side effects. FPPS is important in the lengthening of hydrophobic chains and determination of their specificity. | ||
Revision as of 17:30, 27 July 2020
Introduction
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Schulbach MC, Mahapatra S, Macchia M, Barontini S, Papi C, Minutolo F, Bertini S, Brennan PJ, Crick DC. Purification, enzymatic characterization, and inhibition of the Z-farnesyl diphosphate synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biol Chem. 2001 Apr 13;276(15):11624-30. Epub 2001 Jan 4. PMID:11152452 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M007168200
- ↑ Aripirala S, Gonzalez-Pacanowska D, Oldfield E, Kaiser M, Amzel LM, Gabelli SB. Structural and thermodynamic basis of the inhibition of Leishmania major farnesyl diphosphate synthase by nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Mar;70(Pt 3):802-10. doi:, 10.1107/S1399004713033221. Epub 2014 Feb 22. PMID:24598749 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1107/S1399004713033221
- ↑ Maheshwari S, Kim YS, Aripirala S, Murphy M, Amzel LM, Gabelli SB. Identifying Structural Determinants of Product Specificity in Leishmania major Farnesyl Diphosphate Synthase. Biochemistry. 2020 Jul 12. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00432. PMID:32584028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00432
- ↑ Zhang Y, Cao R, Yin F, Hudock MP, Guo RT, Krysiak K, Mukherjee S, Gao YG, Robinson H, Song Y, No JH, Bergan K, Leon A, Cass L, Goddard A, Chang TK, Lin FY, Van Beek E, Papapoulos S, Wang AH, Kubo T, Ochi M, Mukkamala D, Oldfield E. Lipophilic bisphosphonates as dual farnesyl/geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase inhibitors: an X-ray and NMR investigation. J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Apr 15;131(14):5153-62. PMID:19309137 doi:10.1021/ja808285e
- ↑ Das S, Edwards PA, Crockett JC, Rogers MJ. Upregulation of endogenous farnesyl diphosphate synthase overcomes the inhibitory effect of bisphosphonate on protein prenylation in Hela cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Apr 4;1841(4):569-73. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.12.010. Epub 2013 Dec 22. PMID:24369118 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.12.010
- ↑ Selby P. Alendronate treatment for osteoporosis: a review of the clinical evidence. Osteoporos Int. 1996;6(6):419-26. doi: 10.1007/bf01629572. PMID:9116385 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/bf01629572
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Hannah Campbell, Michal Harel, Tihitina Y Aytenfisu, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Sandra B. Gabelli