Proteopedia:Featured SEL/5
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
</imagemap> | </imagemap> | ||
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
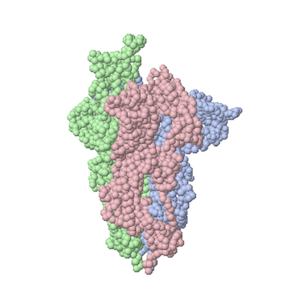
| - | <tr><td><div class='scrolling '>''' | + | <tr><td><div class='scrolling '>'''Coronavirus Spike Protein Priming'''<br> |
''by Eric Martz''<br> | ''by Eric Martz''<br> | ||
| - | Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (responsible for COVID-19) has a spike protein on its surface enabling it to infect host cells. Initially, proteases in the lungs clip the spike protein at a <font color="red">'''unique sequence'''</font>. This primes it, causing it to extend its <font color="magenta">'''receptor binding surface'''</font>, optimizing binding to the ACE2 receptor on the host cell. In a subsequent step (not shown) the virus RNA | + | Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (responsible for COVID-19) has a spike protein on its surface enabling it to infect host cells. Initially, proteases in the lungs clip the spike protein at a <font color="red">'''unique sequence'''</font>. This primes it, causing it to extend its <font color="magenta">'''receptor binding surface'''</font>, optimizing binding to the ACE2 receptor on the host cell. In a subsequent step (not shown) spike protein fuses with the host cell membrane, enabling the virus RNA to enter the cell and initiate production of new virions. Knowledge of spike protein's molecular structure and function is crucial to developing effective therapies and vaccines. |
>>> [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_S_priming_by_furin|Visit this page]] >>> | >>> [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_S_priming_by_furin|Visit this page]] >>> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 19:27, 28 July 2020
Coronavirus Spike Protein Priming
by Eric Martz |