This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox GGC5
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== '''Function''' == | == '''Function''' == | ||
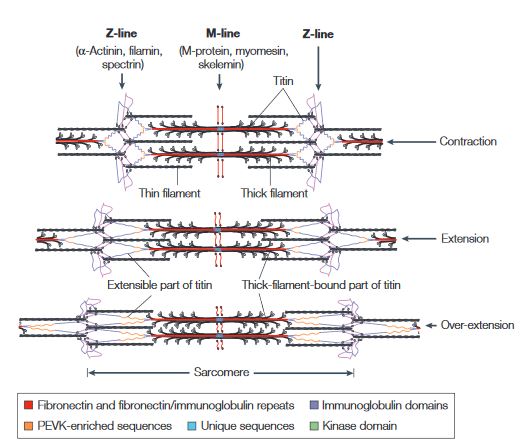
| - | Titin is a key component in the assembly and | + | Titin is a highly complex protein responsible for a variety of functions including the key component in the assembly and operation of vertebrate striated muscles. Titin provides connections at the level of individual micro-filaments and contributes to the fine balance of forces between the two halves of the sarcomere. |
Titin plays a vital role in the highly ordered macromolecular complex of the sarcomere structures and functions requiring the controlled integration of striated myofibrils in differentiating myocytes. The giant titin protein extends over on half of the sarcomeric unit. | Titin plays a vital role in the highly ordered macromolecular complex of the sarcomere structures and functions requiring the controlled integration of striated myofibrils in differentiating myocytes. The giant titin protein extends over on half of the sarcomeric unit. | ||
Revision as of 02:07, 13 November 2020
Titin
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Chatziefthimiou SD, Hornburg P, Sauer F, Mueller S, Ugurlar D, Xu ER, Wilmanns M. Structural diversity in the atomic resolution 3D fingerprint of the titin M-band segment. PLoS One. 2019 Dec 19;14(12):e0226693. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226693., eCollection 2019. PMID:31856237 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0226693
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J. Giant proteins: sensing tension with titin kinase. Curr Biol. 2008 Dec 23;18(24):R1141-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2008.10.035. PMID:19108772 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2008.10.035
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Mayans O, van der Ven PF, Wilm M, Mues A, Young P, Furst DO, Wilmanns M, Gautel M. Structural basis for activation of the titin kinase domain during myofibrillogenesis. Nature. 1998 Oct 29;395(6705):863-9. PMID:9804419 doi:10.1038/27603
- ↑ Lange S, Xiang F, Yakovenko A, Vihola A, Hackman P, Rostkova E, Kristensen J, Brandmeier B, Franzen G, Hedberg B, Gunnarsson LG, Hughes SM, Marchand S, Sejersen T, Richard I, Edstrom L, Ehler E, Udd B, Gautel M. The kinase domain of titin controls muscle gene expression and protein turnover. Science. 2005 Jun 10;308(5728):1599-603. Epub 2005 Mar 31. PMID:15802564 doi:1110463
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Satoh M, Takahashi M, Sakamoto T, Hiroe M, Marumo F, Kimura A. Structural analysis of the titin gene in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: identification of a novel disease gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Aug 27;262(2):411-7. PMID:10462489 doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1221
- ↑ Itoh-Satoh M, Hayashi T, Nishi H, Koga Y, Arimura T, Koyanagi T, Takahashi M, Hohda S, Ueda K, Nouchi T, Hiroe M, Marumo F, Imaizumi T, Yasunami M, Kimura A. Titin mutations as the molecular basis for dilated cardiomyopathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Feb 22;291(2):385-93. PMID:11846417 doi:10.1006/bbrc.2002.6448
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Hackman P, Vihola A, Haravuori H, Marchand S, Sarparanta J, De Seze J, Labeit S, Witt C, Peltonen L, Richard I, Udd B. Tibial muscular dystrophy is a titinopathy caused by mutations in TTN, the gene encoding the giant skeletal-muscle protein titin. Am J Hum Genet. 2002 Sep;71(3):492-500. Epub 2002 Jul 26. PMID:12145747 doi:S0002-9297(07)60330-9
- ↑ Carmignac V, Salih MA, Quijano-Roy S, Marchand S, Al Rayess MM, Mukhtar MM, Urtizberea JA, Labeit S, Guicheney P, Leturcq F, Gautel M, Fardeau M, Campbell KP, Richard I, Estournet B, Ferreiro A. C-terminal titin deletions cause a novel early-onset myopathy with fatal cardiomyopathy. Ann Neurol. 2007 Apr;61(4):340-51. PMID:17444505 doi:10.1002/ana.21089
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Hu LF, Chen F, Altiok E, Winberg G, Klein G, Ernberg I. Cell phenotype-dependent splicing reflecting differential promoter usage for EBNA transcripts in EBV-carrying cells. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2000 May;27 Suppl 2:248-60. PMID:10895161
- ↑ Improta S, Politou AS, Pastore A. Immunoglobulin-like modules from titin I-band: extensible components of muscle elasticity. Structure. 1996 Mar 15;4(3):323-37. PMID:8805538