We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox GGC2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
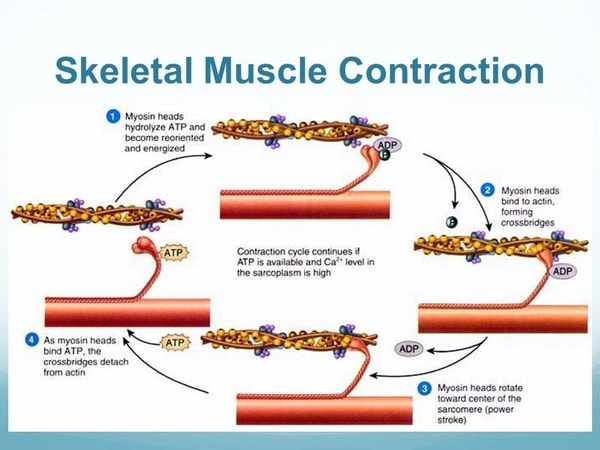
Actin is a family of globular proteins that form microfilaments. It is the most abundant protein in eukaryotes <ref>DOI: 10.1073/pnas.122126299</ref>. They can be found in virtually all eukaryotic cells and come in two main forms, F-actin and G actin. Actin is responsible for many contraction properties in muscles. | Actin is a family of globular proteins that form microfilaments. It is the most abundant protein in eukaryotes <ref>DOI: 10.1073/pnas.122126299</ref>. They can be found in virtually all eukaryotic cells and come in two main forms, F-actin and G actin. Actin is responsible for many contraction properties in muscles. | ||
Vertebrates have 3 main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta, and gamma. Alpha actins play a major role in muscle contraction mechanism. Beta and gamma actins are involved in the regulation of cell motility. Actin has the capability to bind with other molecules, most notably myosin and ATP, in order to carry out its function. | Vertebrates have 3 main groups of actin isoforms, alpha, beta, and gamma. Alpha actins play a major role in muscle contraction mechanism. Beta and gamma actins are involved in the regulation of cell motility. Actin has the capability to bind with other molecules, most notably myosin and ATP, in order to carry out its function. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:C.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 06:11, 16 November 2020
Actin, alpha skeletal muscle (ACTA1)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Otterbein LR, Cosio C, Graceffa P, Dominguez R. Crystal structures of the vitamin D-binding protein and its complex with actin: structural basis of the actin-scavenger system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jun 11;99(12):8003-8. Epub 2002 Jun 4. PMID:12048248 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.122126299
- ↑ Nowak KJ, Wattanasirichaigoon D, Goebel HH, Wilce M, Pelin K, Donner K, Jacob RL, Hubner C, Oexle K, Anderson JR, Verity CM, North KN, Iannaccone ST, Muller CR, Nurnberg P, Muntoni F, Sewry C, Hughes I, Sutphen R, Lacson AG, Swoboda KJ, Vigneron J, Wallgren-Pettersson C, Beggs AH, Laing NG. Mutations in the skeletal muscle alpha-actin gene in patients with actin myopathy and nemaline myopathy. Nat Genet. 1999 Oct;23(2):208-12. PMID:10508519 doi:10.1038/13837
- ↑ Laing NG, Clarke NF, Dye DE, Liyanage K, Walker KR, Kobayashi Y, Shimakawa S, Hagiwara T, Ouvrier R, Sparrow JC, Nishino I, North KN, Nonaka I. Actin mutations are one cause of congenital fibre type disproportion. Ann Neurol. 2004 Nov;56(5):689-94. PMID:15468086 doi:10.1002/ana.20260
- ↑ Ilkovski B, Nowak KJ, Domazetovska A, Maxwell AL, Clement S, Davies KE, Laing NG, North KN, Cooper ST. Evidence for a dominant-negative effect in ACTA1 nemaline myopathy caused by abnormal folding, aggregation and altered polymerization of mutant actin isoforms. Hum Mol Genet. 2004 Aug 15;13(16):1727-43. Epub 2004 Jun 15. PMID:15198992 doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh185
- ↑ Laing NG, Dye DE, Wallgren-Pettersson C, Richard G, Monnier N, Lillis S, Winder TL, Lochmuller H, Graziano C, Mitrani-Rosenbaum S, Twomey D, Sparrow JC, Beggs AH, Nowak KJ. Mutations and polymorphisms of the skeletal muscle alpha-actin gene (ACTA1). Hum Mutat. 2009 Sep;30(9):1267-77. doi: 10.1002/humu.21059. PMID:19562689 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/humu.21059
- ↑ Otterbein LR, Cosio C, Graceffa P, Dominguez R. Crystal structures of the vitamin D-binding protein and its complex with actin: structural basis of the actin-scavenger system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jun 11;99(12):8003-8. Epub 2002 Jun 4. PMID:12048248 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.122126299