We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox GGC6
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
This is the <scene name='78/781192/3ghg/3'>structure of fibrinogen</scene>. It is composed of one pairs of alpha, beta, and gamma polypeptides. the polypeptides are oriented to <scene name='78/781192/N-c_terms/3'>N-terms</scene>ends meet to form a central E domain which is showed in blue. Both domain on the side of E domain called D domain. The N terms ends of polypeptides are cleaved by thrombin to form gel forming fibrin from soluble fibrin <ref>PMID: 28101869 </ref>. | This is the <scene name='78/781192/3ghg/3'>structure of fibrinogen</scene>. It is composed of one pairs of alpha, beta, and gamma polypeptides. the polypeptides are oriented to <scene name='78/781192/N-c_terms/3'>N-terms</scene>ends meet to form a central E domain which is showed in blue. Both domain on the side of E domain called D domain. The N terms ends of polypeptides are cleaved by thrombin to form gel forming fibrin from soluble fibrin <ref>PMID: 28101869 </ref>. | ||
| - | The | + | The black line is <scene name='78/781192/Asp_364/1'>Asp 364</scene>, which is an important residue. The mutation of this residue can cause Congenital Dysfibrinogenemia. <ref>doi.org/10.1054</ref> |
This is a <scene name='78/781192/Hydrophobic_and_polar/3'>hydrophilic and hydrophobic</scene> structure. <ref>doi.org/10.1007/BF01024625(/ref> | This is a <scene name='78/781192/Hydrophobic_and_polar/3'>hydrophilic and hydrophobic</scene> structure. <ref>doi.org/10.1007/BF01024625(/ref> | ||
Revision as of 23:45, 16 November 2020
Fibrinogen
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Weisel JW, Litvinov RI. Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties. Subcell Biochem. 2017;82:405-456. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49674-0_13. PMID:28101869 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49674-0_13
- ↑ Iwaki T, Castellino FJ. Maternal fibrinogen is necessary for embryonic development. Curr Drug Targets. 2005 Aug;6(5):535-9. doi: 10.2174/1389450054546006. PMID:16026273 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1389450054546006
- ↑ Asselta R, Plate M, Robusto M, Borhany M, Guella I, Solda G, Afrasiabi A, Menegatti M, Shamsi T, Peyvandi F, Duga S. Clinical and molecular characterisation of 21 patients affected by quantitative fibrinogen deficiency. Thromb Haemost. 2015 Mar;113(3):567-76. doi: 10.1160/TH14-07-0629. Epub 2014 Nov , 27. PMID:25427968 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1160/TH14-07-0629
- ↑ de Moerloose P, Neerman-Arbez M. Congenital fibrinogen disorders. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2009 Jun;35(4):356-66. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1225758. Epub, 2009 Jul 13. PMID:19598064 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1225758
- ↑ Baker KR, Rice L. The amyloidoses: clinical features, diagnosis and treatment. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2012 Jul-Sep;8(3):3-7. doi: 10.14797/mdcj-8-3-3. PMID:23227278 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.14797/mdcj-8-3-3
- ↑ Benson MD, Liepnieks J, Uemichi T, Wheeler G, Correa R. Hereditary renal amyloidosis associated with a mutant fibrinogen alpha-chain. Nat Genet. 1993 Mar;3(3):252-5. PMID:8097946 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng0393-252
- ↑ Casini A, Blondon M, Lebreton A, Koegel J, Tintillier V, de Maistre E, Gautier P, Biron C, Neerman-Arbez M, de Moerloose P. Natural history of patients with congenital dysfibrinogenemia. Blood. 2015 Jan 15;125(3):553-61. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-06-582866. Epub 2014, Oct 15. PMID:25320241 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-06-582866
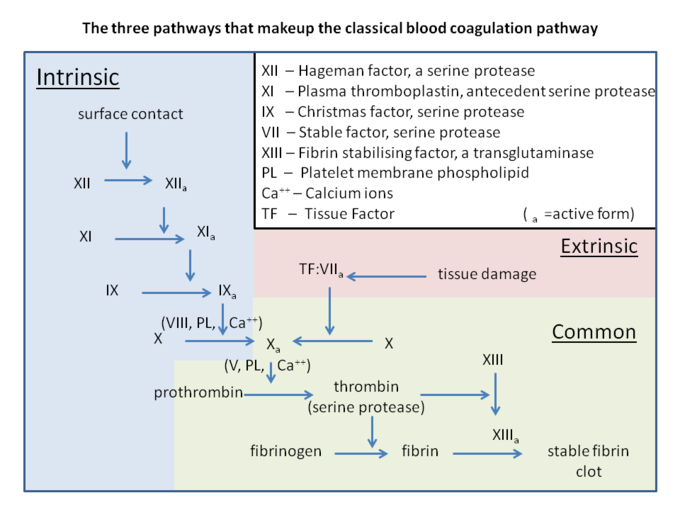
- ↑ Palta S, Saroa R, Palta A. Overview of the coagulation system. Indian J Anaesth. 2014 Sep;58(5):515-23. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.144643. PMID:25535411 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/0019-5049.144643
- ↑ Weisel JW, Litvinov RI. Fibrin Formation, Structure and Properties. Subcell Biochem. 2017;82:405-456. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49674-0_13. PMID:28101869 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49674-0_13
- ↑ doi.org/10.1054
- ↑ doi.org/10.1007/BF01024625(/ref>