We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1649
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
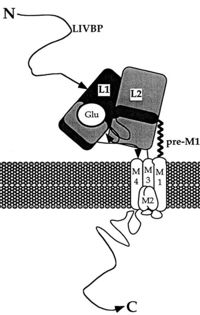
The ATD is constitued by first 383 aminoacids of NR2A. ATD is an alpha and beta protein class. Structure is bilobed and form clam-shell like structure which consists in two lobes linked by a flexible hinge region defining a central groove. <ref name="ATD clamshell">DOI 10.1038/nsmb.2522</ref> Zn2+ may insert between 2 lobes and induces closure of channel by changing conformation of ATD. Zn increase affinity of glutamate on the LBD which reminds the desensization of AMPA and Kainate receptor. <ref name="Zn">DOI 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00163-x</ref> | The ATD is constitued by first 383 aminoacids of NR2A. ATD is an alpha and beta protein class. Structure is bilobed and form clam-shell like structure which consists in two lobes linked by a flexible hinge region defining a central groove. <ref name="ATD clamshell">DOI 10.1038/nsmb.2522</ref> Zn2+ may insert between 2 lobes and induces closure of channel by changing conformation of ATD. Zn increase affinity of glutamate on the LBD which reminds the desensization of AMPA and Kainate receptor. <ref name="Zn">DOI 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00163-x</ref> | ||
ATD allow to modulate NMDA receptor. Difference between différents NR2 is mainly regulated by ATD because diversity of ATD can modulate traffic in endoplasmic reticulum ans then affect the localisation of NMDAr. ATD of NR2A increase glutamate affinity, control channel’s opening with high probability and open duration, control glutamate deactivationtime course.<ref name="ATD function">DOI 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1365-09.2009</ref> <ref name="ATD RE">DOI 10.1051/medsci/201026165</ref> | ATD allow to modulate NMDA receptor. Difference between différents NR2 is mainly regulated by ATD because diversity of ATD can modulate traffic in endoplasmic reticulum ans then affect the localisation of NMDAr. ATD of NR2A increase glutamate affinity, control channel’s opening with high probability and open duration, control glutamate deactivationtime course.<ref name="ATD function">DOI 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1365-09.2009</ref> <ref name="ATD RE">DOI 10.1051/medsci/201026165</ref> | ||
| - | ''' | + | |
| - | Ligand binding domain''' | + | '''Ligand binding domain''' |
LBD is constitued of two domains S1 (localised juste upstream M1 transmembranaire domain) and S2 and has affinity for [https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acide_glutamique glutamate] or sometime glycine. Positive charge of Amino-group of the agonist bind to negativ charges residue of the pocket D731. In GlurR, negative charge amino acid is a E731 and is able to form salt bridge with agonist. In NR2A D731 is not able to do salt bridge with amino group because aspartate is one methylene lacking to do it. Amino group of agonist is stabilised by water mediated hydrogen bonds to amino acid E413 and Y761. The high affinity for glutamate agonist may be because of van der Walls contact between γ-carboxylate group of glutamate and Y730 of S2 domain which is conserved in NR2 protein. <ref name="LBD">DOI 10.1038/nature04089</ref> | LBD is constitued of two domains S1 (localised juste upstream M1 transmembranaire domain) and S2 and has affinity for [https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acide_glutamique glutamate] or sometime glycine. Positive charge of Amino-group of the agonist bind to negativ charges residue of the pocket D731. In GlurR, negative charge amino acid is a E731 and is able to form salt bridge with agonist. In NR2A D731 is not able to do salt bridge with amino group because aspartate is one methylene lacking to do it. Amino group of agonist is stabilised by water mediated hydrogen bonds to amino acid E413 and Y761. The high affinity for glutamate agonist may be because of van der Walls contact between γ-carboxylate group of glutamate and Y730 of S2 domain which is conserved in NR2 protein. <ref name="LBD">DOI 10.1038/nature04089</ref> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
M2 loop is a channel-lining loop and located in transmembranaire domain. Two asparagines are located on N site of the domain and block Mg2+ and are permeable of Ca2+ <ref name="M2loop">DOI 10.3390/ijms21041538 | M2 loop is a channel-lining loop and located in transmembranaire domain. Two asparagines are located on N site of the domain and block Mg2+ and are permeable of Ca2+ <ref name="M2loop">DOI 10.3390/ijms21041538 | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
| + | |||
'''CTD''' | '''CTD''' | ||
Revision as of 20:37, 12 January 2021
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 26/11/2020, through 26/11/2021 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1643 through Sandbox Reserved 1664. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
NR2A (2A5S)
NR2A is a protein which forms an heterodimers channel with NR1 protein , the gathering of this two subnits formed NMDA receptors which is essential for Ca2+ influx in synapses thanks to glutamate and glycine binding essential for learning and memory. Variety of NR2 allows modulation of NMDAr.In the other hand, NMDA receptor is related to AMPA receptor in the same synapse.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Zhu S, Stroebel D, Yao CA, Taly A, Paoletti P. Allosteric signaling and dynamics of the clamshell-like NMDA receptor GluN1 N-terminal domain. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Apr;20(4):477-85. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2522. Epub 2013 Mar, 3. PMID:23454977 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2522
- ↑ Paoletti P, Perin-Dureau F, Fayyazuddin A, Le Goff A, Callebaut I, Neyton J. Molecular organization of a zinc binding n-terminal modulatory domain in a NMDA receptor subunit. Neuron. 2000 Dec;28(3):911-25. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00163-x. PMID:11163276 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00163-x
- ↑ Yuan H, Hansen KB, Vance KM, Ogden KK, Traynelis SF. Control of NMDA receptor function by the NR2 subunit amino-terminal domain. J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 30;29(39):12045-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1365-09.2009. PMID:19793963 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1365-09.2009
- ↑ Gielen M. [Molecular operation of ionotropic glutamate receptors: proteins that mediate the excitatory synaptic neurotransmission]. Med Sci (Paris). 2010 Jan;26(1):65-72. doi: 10.1051/medsci/201026165. PMID:20132777 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1051/medsci/201026165
- ↑ Furukawa H, Singh SK, Mancusso R, Gouaux E. Subunit arrangement and function in NMDA receptors. Nature. 2005 Nov 10;438(7065):185-92. PMID:16281028 doi:10.1038/nature04089
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Franchini L, Carrano N, Di Luca M, Gardoni F. Synaptic GluN2A-Containing NMDA Receptors: From Physiology to Pathological Synaptic Plasticity. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 24;21(4). pii: ijms21041538. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041538. PMID:32102377 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041538
- ↑ Sprengel R, Suchanek B, Amico C, Brusa R, Burnashev N, Rozov A, Hvalby O, Jensen V, Paulsen O, Andersen P, Kim JJ, Thompson RF, Sun W, Webster LC, Grant SG, Eilers J, Konnerth A, Li J, McNamara JO, Seeburg PH. Importance of the intracellular domain of NR2 subunits for NMDA receptor function in vivo. Cell. 1998 Jan 23;92(2):279-89. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80921-6. PMID:9458051 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80921-6
- ↑ DeGiorgio LA, Konstantinov KN, Lee SC, Hardin JA, Volpe BT, Diamond B. A subset of lupus anti-DNA antibodies cross-reacts with the NR2 glutamate receptor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Med. 2001 Nov;7(11):1189-93. doi: 10.1038/nm1101-1189. PMID:11689882 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm1101-1189