Sandbox Reserved 1649
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Structure and Function == | == Structure and Function == | ||
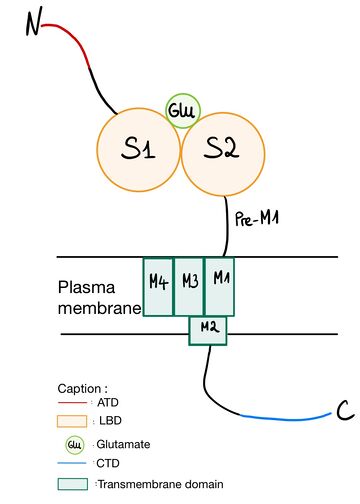
| - | NR2A (GluN2A) is composed of Amino-terminal domain (ATD), segments S1 and S2 which formed ligand binding domain of glutamate, three transmembrane helices (M1, M3,and M4), cytoplasmic re-entrant pore loop (M2), and an intracellular C-terminal domain (CTD). [[Image:StructureNR2A4.jpg#filehistory| thumb |left| | + | NR2A (GluN2A) is composed of Amino-terminal domain (ATD), segments S1 and S2 which formed ligand binding domain of glutamate, three transmembrane helices (M1, M3,and M4), cytoplasmic re-entrant pore loop (M2), and an intracellular C-terminal domain (CTD). [[Image:StructureNR2A4.jpg#filehistory| thumb |left|360px| upright=10|'''NR2A submit structure''']] |
'''Amino-terminal domain (ATD)''' | '''Amino-terminal domain (ATD)''' | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 13 January 2021
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 26/11/2020, through 26/11/2021 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1643 through Sandbox Reserved 1664. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
NR2A (2A5S)
NR2A is a protein which forms an heterodimers channel with NR1 protein , the gathering of this two subnits formed NMDA receptors which is essential for Ca2+ influx in synapses thanks to glutamate and glycine binding essential for learning and memory. Variety of NR2 allows modulation of NMDAr.In the other hand, NMDA receptor is related to AMPA receptor in the same synapse.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Zhu S, Stroebel D, Yao CA, Taly A, Paoletti P. Allosteric signaling and dynamics of the clamshell-like NMDA receptor GluN1 N-terminal domain. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Apr;20(4):477-85. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2522. Epub 2013 Mar, 3. PMID:23454977 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2522
- ↑ Paoletti P, Perin-Dureau F, Fayyazuddin A, Le Goff A, Callebaut I, Neyton J. Molecular organization of a zinc binding n-terminal modulatory domain in a NMDA receptor subunit. Neuron. 2000 Dec;28(3):911-25. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00163-x. PMID:11163276 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00163-x
- ↑ Yuan H, Hansen KB, Vance KM, Ogden KK, Traynelis SF. Control of NMDA receptor function by the NR2 subunit amino-terminal domain. J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 30;29(39):12045-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1365-09.2009. PMID:19793963 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1365-09.2009
- ↑ Gielen M. [Molecular operation of ionotropic glutamate receptors: proteins that mediate the excitatory synaptic neurotransmission]. Med Sci (Paris). 2010 Jan;26(1):65-72. doi: 10.1051/medsci/201026165. PMID:20132777 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1051/medsci/201026165
- ↑ Furukawa H, Singh SK, Mancusso R, Gouaux E. Subunit arrangement and function in NMDA receptors. Nature. 2005 Nov 10;438(7065):185-92. PMID:16281028 doi:10.1038/nature04089
- ↑ Krupp JJ, Vissel B, Heinemann SF, Westbrook GL. N-terminal domains in the NR2 subunit control desensitization of NMDA receptors. Neuron. 1998 Feb;20(2):317-27. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80459-6. PMID:9491992 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80459-6
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Franchini L, Carrano N, Di Luca M, Gardoni F. Synaptic GluN2A-Containing NMDA Receptors: From Physiology to Pathological Synaptic Plasticity. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 24;21(4). pii: ijms21041538. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041538. PMID:32102377 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041538
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Ronald KM, Mirshahi T, Woodward JJ. Ethanol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors is reduced by site-directed mutagenesis of a transmembrane domain phenylalanine residue. J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 30;276(48):44729-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102800200. Epub 2001, Sep 25. PMID:11572853 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M102800200
- ↑ Sprengel R, Suchanek B, Amico C, Brusa R, Burnashev N, Rozov A, Hvalby O, Jensen V, Paulsen O, Andersen P, Kim JJ, Thompson RF, Sun W, Webster LC, Grant SG, Eilers J, Konnerth A, Li J, McNamara JO, Seeburg PH. Importance of the intracellular domain of NR2 subunits for NMDA receptor function in vivo. Cell. 1998 Jan 23;92(2):279-89. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80921-6. PMID:9458051 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80921-6
- ↑ DeGiorgio LA, Konstantinov KN, Lee SC, Hardin JA, Volpe BT, Diamond B. A subset of lupus anti-DNA antibodies cross-reacts with the NR2 glutamate receptor in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Med. 2001 Nov;7(11):1189-93. doi: 10.1038/nm1101-1189. PMID:11689882 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nm1101-1189