|
Huntingtin Protein
Huntingtin (HTT) is a large (350 kDa) protein essential for embryonic development and is involved in a variety of cellular functions, such as vesicular transport, endocytosis, transcription regulation and autophagy. Mutation in the associated gene — IT15 — results in an expansion of the polyQ tract found within the N-terminal region of the perspective protein. Such pathological growth, which surpasses the treshold of 36 glutamine residues, may lead to the development of Huntington disease (HD). The mutation becomes fully penetrant at ≥40 glutamine residues [1]. Huntington disease is a bit unusual, regarding the fact that there may be a progressive increase in the severity of a mutation, and sometimes in the probability that a given mutation will result in a disease, as it is passed from parents to their offspring. This may be caused due to polymerase slippage in this case. Probably the most prominent hallmark of HD is the formation of inclusion bodies. Mutant huntingtin (mHTT) is prone to conformational changing that can lead to the formation of very stable anti-parallel β-sheets; more specifically, amyloid structures [2]. Despite its ubiquitous expression, mHTT affects primarily the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of striatum and to a lesser extent the neurons of cerebral cortex [3].
Function
Since the discovery of HTT and its relevance to HD, efforts have been made to understand the physiological functions of wild-type huntingtin. However, an integrative understanding of its biological functions is still lacking. Many studies suggest that HTT is essential for cell survival and thereby its loss of function caused by the mutation is source for the neurodegeneration. Although it does, up to a certain degree, add to the disease phenotype, it is now generally believed that the main source of the disease is not the loss of its physiological functions, but the gain of function associated with the polyQ expansion.
Huntingtin and Embryonic Development
The crucial role of HTT for embryonic development has been shown using mouse knock-out (KO) models, in which homozygous KO mice die at day 8.5 and don't emerge the nervous system. [4] Furthermore, HTT was shown to play a key role in neurulation homotypic interactions of neuroepithelial cells, thereby providing more evidence on its importace for development of the nervous system.
Huntingtin and Transcription Regulation
HTT is mostly cytoplasmic. However, it can be aslo observed in the nucleus, as HTT comprises nuclear localization sequence in its NH2 terminus [5]. Its nuclear localization implies for its role in transcription regulation. An example of a well described target gene of HTT-mediated transcription regulation is the brain derived nerve growth factor (BDNF) [6]. However, there are more transcription factors described to interact with mHTT, as their interaction may lead to transcription dysregulation. Thanks to its abnormal structure, mHTT supresses the expression of PGC1-α — a transcription factor responsible for the regulation of many mitochondrial genes [7].
Huntingtin as a Scaffold Protein
Wild-type HTT is well known for its scaffolding function. It interacts with β-tubulin and binds to microtubules. Besides, it interacts with the dynein/dynactin complex, thereby regulating vesicular transport [8]. Furthermore, HTT has been shown to localize to spindle poles during mitosis, regulating spindle orientation in mouse neuronal cells[9]. On the other hand, the abnormal scaffolding function for molecular motors operated via mHTT results in abrupted axonal transport. That leads to inefficient distribution of mitochondria within nerve cells, causing low transfer of energy to places like synapses [10]
Huntingtin Protein and Autophagy
Structure
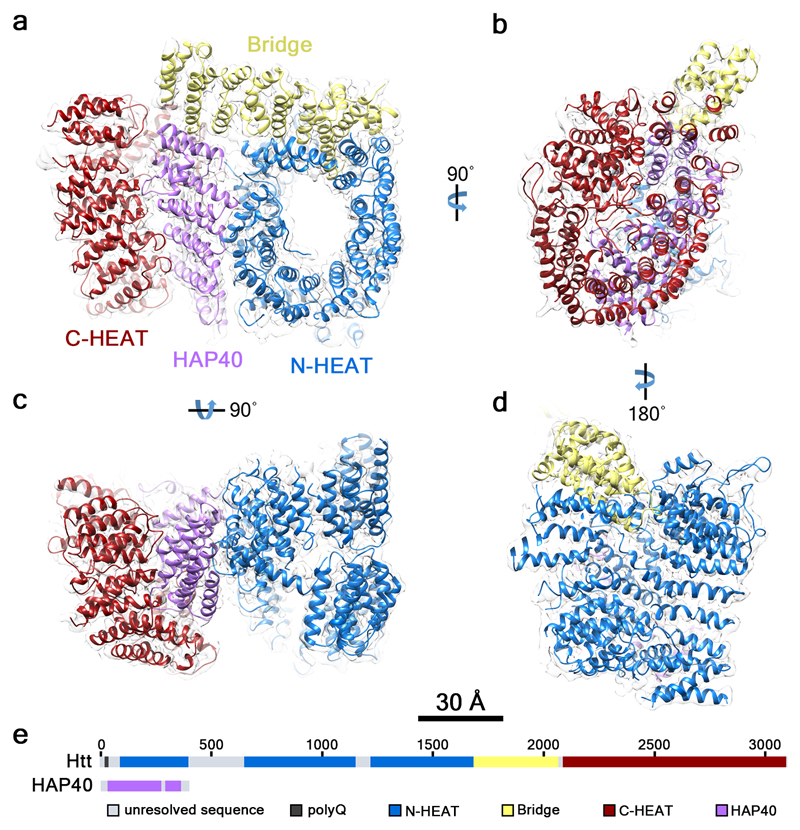
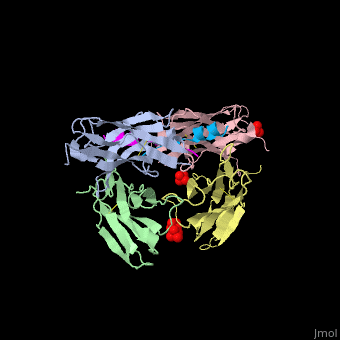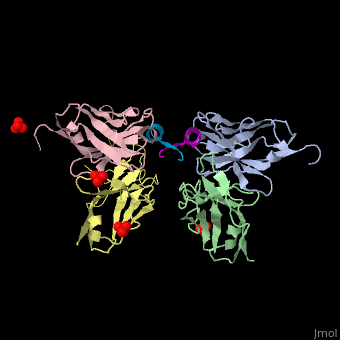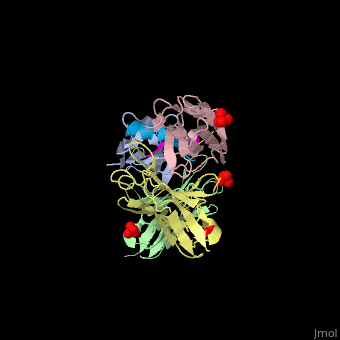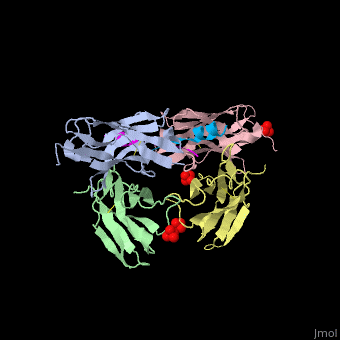
This ribbon representation shows the HTT-HAP40 complex. Domains are color-coded as followed: blue - Htt N-HEAT domain; yellow - Htt bridge domain; maroon - Htt C-HEAT domain; purple - HAP40. a, b, c, d show different views of the complex. e - Schematic diagram of domain organization of Htt and HAP40 [11].
HTT is a 3144 amino acids comprising protein, which possesses the polyglutamine chain at the amino-terminal region. It also contains multiple consesnsus sequences called HEAT (huntingtin, elongation factor 3, protein phosphatase 2A, and TOR1 (target of rapamycin)) repeats. These HEAT repeats are very important for protein-protein interactions — HTT interacts with more over 200 other proteins. Each HEAT unit consists of a pair of antiparallel alpha-helices. These antiparallel helices assemble in a L-shaped fashion resulting in an overall shape of a double layer of alpha helices. These HEAT units are responsible for a majority of the overall protein packing and structure by interactions of the ridges of each HEAT unit [12]. The presence of HEAT repeats enables HTT to participate in endocytosis-related trafficking, as clathrin and COPI (coat protein complex I) coatomer contain HEAT repeats as well [13].
Pathology
The general consensus is that the toxicity originates from the gain of function of mHTT, as the polyQ solely could still stretch and let to the development of neurological symptoms in mouse models [14][15][16]. However, the contribution of loss of function of the wild-type HTT cannot be abandoned, as wild-type HTT inactivation or deletion also leads to neurodegeneration [17][18].
As mentioned above, patients with mHTT develop HD. HD is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder characterized by behavioral, cognitive and motor dysfunctions. Although HD mostly affects middle-aged people, the age of onset is inversely correlated with the length of the polyQ tract. Very large expansion can even lead to juvenile and in rare cases infantile forms of the disease [19].
Mutant Huntingtin Impairs Autophagy
There are two major pathways that secure the degradation of intracellular proteins. The ubiquitin-proteasome system, which serve to degrade wild-type HTT, and autophagy, which seems to be more important for the degradation of the expanded mutant forms as well as dysfunctional organelles [20]. Wild-type HTT seems to act as a scaffold for many parts of the autophagic machinery. The C-terminal part of HTT was found to have similar structure to Atg11, a yeast scaffolding protein associated with autophagy. Moreover, HTT was shown to interact with human homolog proteins, such as ULK1 (Unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase; homolog of yeast Atg1) and SQSTM1/p62 (homolog of yeast Atg19), which interact with Atg11 [21]. In mammals, the induction of autophagy depends on the ULK1-Atg13-FIP2000 complex. This complex is for most of the time inhibited by mTORC1-mediated phosphorylation. Furthermore, an exclusive complex with HTT can be formed. This complex does not lead to the inhibition of ULK1 and promotes the initiation of autophagy [22]. However, ULK1 has reduced affinity to mHTT and thereby reamins more inactive and bound to mTOR [23].
SQSTM1/p62 is an autophagy adaptor protein that binds cargo tagged with polyubiquitin chains to autophagosomes via the interaction with LC3-II. Although autophagosomes seem to be formed at a higher rate in HD models, HD autophagosomes cannot sequester the cargo properly and leads to the accumulation of dysfuncitonal proteins and organelles [24].
Structural highlights
The huntingtin N-terminal assumes a helical conformation (residues 3-11) followed by an extended conformation (residues 12-17). It forms [25].
3D Structures of huntingtin
Updated on 11-February-2021
4rav – hHTT N-terminal + antibody - human
2ld0, 2ld2, 6n8c – hHTT N-terminal - NMR
3io4, 3io6, 3ior, 3iot, 3iou, 3iov, 3iow – hHTT N-terminal/MBP
4fe8, 4feb, 4fec, 4fed – hHTT residues 1-164 (mutant)/MBP
6rmh – hHTT – Cryo EM
6ez8, 6x9o – hHTT + CPG island protein – Cryo EM
References
- ↑ Vonsattel JP, DiFiglia M. Huntington disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1998 May;57(5):369-84. doi:, 10.1097/00005072-199805000-00001. PMID:9596408 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00005072-199805000-00001
- ↑ McGowan DP, van Roon-Mom W, Holloway H, Bates GP, Mangiarini L, Cooper GJ, Faull RL, Snell RG. Amyloid-like inclusions in Huntington's disease. Neuroscience. 2000;100(4):677-80. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00391-2. PMID:11036200 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(00)00391-2
- ↑ Guedes-Dias P, Pinho BR, Soares TR, de Proenca J, Duchen MR, Oliveira JM. Mitochondrial dynamics and quality control in Huntington's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Jun;90:51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.09.008. Epub 2015 Sep, 24. PMID:26388396 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.09.008
- ↑ Zeitlin S, Liu JP, Chapman DL, Papaioannou VE, Efstratiadis A. Increased apoptosis and early embryonic lethality in mice nullizygous for the Huntington's disease gene homologue. Nat Genet. 1995 Oct;11(2):155-63. doi: 10.1038/ng1095-155. PMID:7550343 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng1095-155
- ↑ Desmond CR, Atwal RS, Xia J, Truant R. Identification of a karyopherin beta1/beta2 proline-tyrosine nuclear localization signal in huntingtin protein. J Biol Chem. 2012 Nov 16;287(47):39626-33. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.412379. Epub, 2012 Sep 25. PMID:23012356 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.412379
- ↑ Zuccato C, Tartari M, Crotti A, Goffredo D, Valenza M, Conti L, Cataudella T, Leavitt BR, Hayden MR, Timmusk T, Rigamonti D, Cattaneo E. Huntingtin interacts with REST/NRSF to modulate the transcription of NRSE-controlled neuronal genes. Nat Genet. 2003 Sep;35(1):76-83. doi: 10.1038/ng1219. Epub 2003 Jul 27. PMID:12881722 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng1219
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11062-013-9341-1
- ↑ Caviston JP, Ross JL, Antony SM, Tokito M, Holzbaur EL. Huntingtin facilitates dynein/dynactin-mediated vesicle transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jun 12;104(24):10045-50. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0610628104. Epub 2007 Jun 4. PMID:17548833 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610628104
- ↑ Godin JD, Colombo K, Molina-Calavita M, Keryer G, Zala D, Charrin BC, Dietrich P, Volvert ML, Guillemot F, Dragatsis I, Bellaiche Y, Saudou F, Nguyen L, Humbert S. Huntingtin is required for mitotic spindle orientation and mammalian neurogenesis. Neuron. 2010 Aug 12;67(3):392-406. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.027. PMID:20696378 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.06.027
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11062-013-9341-1
- ↑ Unknown PubmedID 10.1038
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80963-0
- ↑ Neuwald AF, Hirano T. HEAT repeats associated with condensins, cohesins, and other complexes involved in chromosome-related functions. Genome Res. 2000 Oct;10(10):1445-52. doi: 10.1101/gr.147400. PMID:11042144 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gr.147400
- ↑ Ikeda H, Yamaguchi M, Sugai S, Aze Y, Narumiya S, Kakizuka A. Expanded polyglutamine in the Machado-Joseph disease protein induces cell death in vitro and in vivo. Nat Genet. 1996 Jun;13(2):196-202. doi: 10.1038/ng0696-196. PMID:8640226 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng0696-196
- ↑ Mangiarini L, Sathasivam K, Seller M, Cozens B, Harper A, Hetherington C, Lawton M, Trottier Y, Lehrach H, Davies SW, Bates GP. Exon 1 of the HD gene with an expanded CAG repeat is sufficient to cause a progressive neurological phenotype in transgenic mice. Cell. 1996 Nov 1;87(3):493-506. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81369-0. PMID:8898202 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81369-0
- ↑ 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80464-x
- ↑ O'Kusky JR, Nasir J, Cicchetti F, Parent A, Hayden MR. Neuronal degeneration in the basal ganglia and loss of pallido-subthalamic synapses in mice with targeted disruption of the Huntington's disease gene. Brain Res. 1999 Feb 13;818(2):468-79. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(98)01312-2. PMID:10082833 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(98)01312-2
- ↑ Dragatsis I, Levine MS, Zeitlin S. Inactivation of Hdh in the brain and testis results in progressive neurodegeneration and sterility in mice. Nat Genet. 2000 Nov;26(3):300-6. doi: 10.1038/81593. PMID:11062468 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/81593
- ↑ Guedes-Dias P, Pinho BR, Soares TR, de Proenca J, Duchen MR, Oliveira JM. Mitochondrial dynamics and quality control in Huntington's disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Jun;90:51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.09.008. Epub 2015 Sep, 24. PMID:26388396 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.09.008
- ↑ Jimenez-Sanchez M, Licitra F, Underwood BR, Rubinsztein DC. Huntington's Disease: Mechanisms of Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2017 Jul 5;7(7). pii: cshperspect.a024240. doi:, 10.1101/cshperspect.a024240. PMID:27940602 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a024240
- ↑ Ochaba J, Lukacsovich T, Csikos G, Zheng S, Margulis J, Salazar L, Mao K, Lau AL, Yeung SY, Humbert S, Saudou F, Klionsky DJ, Finkbeiner S, Zeitlin SO, Marsh JL, Housman DE, Thompson LM, Steffan JS. Potential function for the Huntingtin protein as a scaffold for selective autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Nov 25;111(47):16889-94. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1420103111. Epub 2014 Nov 10. PMID:25385587 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1420103111
- ↑ Rui YN, Xu Z, Patel B, Cuervo AM, Zhang S. HTT/Huntingtin in selective autophagy and Huntington disease: A foe or a friend within? Autophagy. 2015;11(5):858-60. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1039219. PMID:25985010 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1039219
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1101/330001
- ↑ Martinez-Vicente M, Talloczy Z, Wong E, Tang G, Koga H, Kaushik S, de Vries R, Arias E, Harris S, Sulzer D, Cuervo AM. Cargo recognition failure is responsible for inefficient autophagy in Huntington's disease. Nat Neurosci. 2010 May;13(5):567-76. doi: 10.1038/nn.2528. Epub 2010 Apr 11. PMID:20383138 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nn.2528
- ↑ De Genst E, Chirgadze DY, Klein FA, Butler DC, Matak-Vinkovic D, Trottier Y, Huston JS, Messer A, Dobson CM. Structure of a single-chain Fv bound to the 17 N-terminal residues of huntingtin provides insights into pathogenic amyloid formation and suppression. J Mol Biol. 2015 Jun 19;427(12):2166-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.03.021. Epub, 2015 Apr 8. PMID:25861763 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2015.03.021
|