We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
DNA Polymerase Theta
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
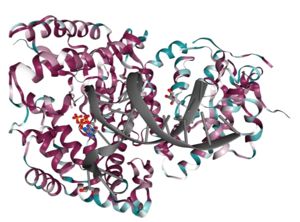
| - | Full length polymerase theta consists of an N-terminal helicase-like domain that is connected to the C-terminal polymerase domain by a central linker region<ref> | + | Full length polymerase theta consists of an N-terminal helicase-like domain that is connected to the C-terminal polymerase domain by a central linker region <ref>pmid 14576298</ref>. |
[[Image:Full-lengthpoltheta.jpg | thumb | center | 700px | Full-length DNA polymerase theta]] | [[Image:Full-lengthpoltheta.jpg | thumb | center | 700px | Full-length DNA polymerase theta]] | ||
Polymerase theta is a DNA double strand break repair protein. Double strand breaks can occur as a result of both exogenous (ionizing radiation) and endogenous (reactive oxygen species, replication fork collapse) damage. To repair breaks, polymerase theta employs theta-mediated end-joining (TMEJ), which is a form of alternative end-joining (altEJ). TMEJ begins with pairing of microhomologies in 3' single stranded overhangs that have been exposed through 5' end resectioning at the site of the break. If the microhomologies are internal to the 3' end of the overhanging DNA, the resulting flaps will be removed and a deletion will be introduced. If microhomologies arise from brief templated synthesis with a more distant strand, insertions will occur. Once microhomologies are aligned, pol theta synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps on either side of the microhomologies.<ref>PMID: 28668117</ref> | Polymerase theta is a DNA double strand break repair protein. Double strand breaks can occur as a result of both exogenous (ionizing radiation) and endogenous (reactive oxygen species, replication fork collapse) damage. To repair breaks, polymerase theta employs theta-mediated end-joining (TMEJ), which is a form of alternative end-joining (altEJ). TMEJ begins with pairing of microhomologies in 3' single stranded overhangs that have been exposed through 5' end resectioning at the site of the break. If the microhomologies are internal to the 3' end of the overhanging DNA, the resulting flaps will be removed and a deletion will be introduced. If microhomologies arise from brief templated synthesis with a more distant strand, insertions will occur. Once microhomologies are aligned, pol theta synthesizes DNA to fill the gaps on either side of the microhomologies.<ref>PMID: 28668117</ref> | ||
Revision as of 11:05, 18 February 2021
| |||||||||||