DNA Polymerase Theta
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
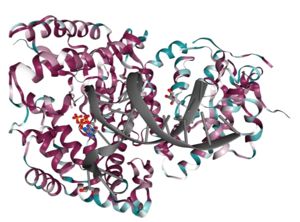
| - | <StructureSection load='4X0P' size='350' side='right' caption='DNA polymerase theta polymerase domain in complex with double-stranded DNA substrate and incoming ddATP ( | + | <StructureSection load='4X0P' size='350' side='right' caption='DNA polymerase theta polymerase domain in complex with double-stranded DNA substrate and incoming ddATP (4x0p)' scene=''> |
==Structural Description== | ==Structural Description== | ||
| - | The polymerase domain of DNA polymerase theta (<scene name='84/842971/Qm1/1'>QM1</scene>) is a member of the A-family of polymerases which includes Pol I <ref>PMID: 8469987</ref> and T7 DNA polymerase <ref>PMID: 9440688</ref>. A-family polymerases contain <scene name='84/842971/A-family_motifs/1'>6 conserved motifs</scene>. These motifs allow for identification of A-family polymerases based on their amino acid sequence. In addition to the A-family motifs, the <scene name='84/842971/Finger-thumb-palm/1'>finger-palm-thumb</scene> subdomains that are typical of many polymerases are also conserved in QM1. The <scene name='84/842971/Fingers/1'>fingers subdomain</scene> coordinate the <scene name='84/842971/Dna/1'>DNA</scene> template and the <scene name='84/842971/Dds/1'>incoming nucleotide</scene> while the <scene name='84/842971/Palm/1'>palm subdomain</scene> performs catalysis and the <scene name='84/842971/Thumb/1'>thumb subdomain</scene> contacts the double stranded DNA. Within these subdomains exist disordered structural inserts that are not present in bacterial homologs. These inserts impart unique properties to QM1;<scene name='84/842971/Insert1/1'> insert 1</scene> in the thumb increases processivity while inserts <scene name='84/842971/Insert2/1'>2</scene> and <scene name='84/842971/Insert3/1'>3</scene> facilitate the ability of QM1 to bypass <scene name='84/842971/Thf/1'>DNA lesions</scene> that typically block synthesis by other A-family polymerases. This error prone synthesis makes QM1 more functionally similar to Y-family translesion polymerases. | + | The polymerase domain of '''DNA polymerase theta''' (<scene name='84/842971/Qm1/1'>QM1</scene>) is a member of the A-family of polymerases which includes Pol I <ref>PMID: 8469987</ref> and T7 DNA polymerase <ref>PMID: 9440688</ref>. A-family polymerases contain <scene name='84/842971/A-family_motifs/1'>6 conserved motifs</scene>. These motifs allow for identification of A-family polymerases based on their amino acid sequence. In addition to the A-family motifs, the <scene name='84/842971/Finger-thumb-palm/1'>finger-palm-thumb</scene> subdomains that are typical of many polymerases are also conserved in QM1. The <scene name='84/842971/Fingers/1'>fingers subdomain</scene> coordinate the <scene name='84/842971/Dna/1'>DNA</scene> template and the <scene name='84/842971/Dds/1'>incoming nucleotide</scene> while the <scene name='84/842971/Palm/1'>palm subdomain</scene> performs catalysis and the <scene name='84/842971/Thumb/1'>thumb subdomain</scene> contacts the double stranded DNA. Within these subdomains exist disordered structural inserts that are not present in bacterial homologs. These inserts impart unique properties to QM1;<scene name='84/842971/Insert1/1'> insert 1</scene> in the thumb increases processivity while inserts <scene name='84/842971/Insert2/1'>2</scene> and <scene name='84/842971/Insert3/1'>3</scene> facilitate the ability of QM1 to bypass <scene name='84/842971/Thf/1'>DNA lesions</scene> that typically block synthesis by other A-family polymerases. This error prone synthesis makes QM1 more functionally similar to Y-family translesion polymerases. |
Beyond the canonical polymerase folds, QM1 also possesses a vestigial <scene name='84/842971/Exonuclease/1'>exonuclease</scene> domain that no longer performs proof-reading activities. This domain also contains <scene name='84/842971/Exo_1_2/1'>two structural inserts</scene> that are thought to contact the more distant helicase-like and central domains of full-length polymerase theta (see Function). | Beyond the canonical polymerase folds, QM1 also possesses a vestigial <scene name='84/842971/Exonuclease/1'>exonuclease</scene> domain that no longer performs proof-reading activities. This domain also contains <scene name='84/842971/Exo_1_2/1'>two structural inserts</scene> that are thought to contact the more distant helicase-like and central domains of full-length polymerase theta (see Function). | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||