We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
1qki
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<StructureSection load='1qki' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1qki]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.00Å' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='1qki' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1qki]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 3.00Å' scene=''> | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
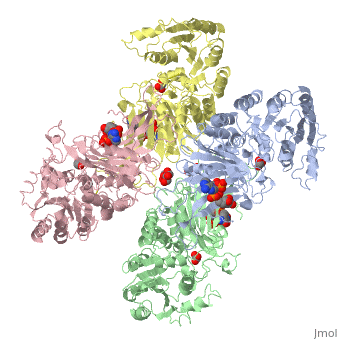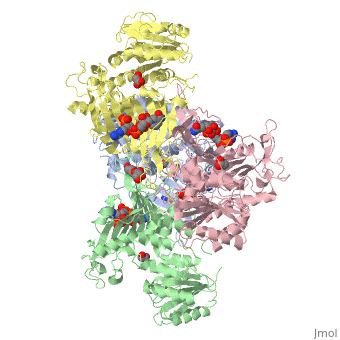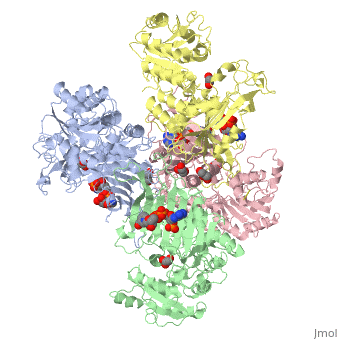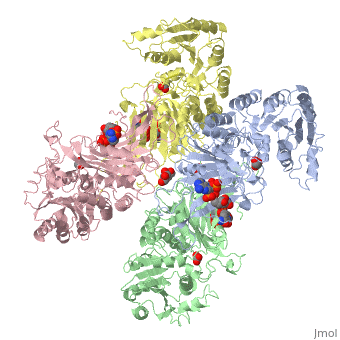
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1qki]] is a 8 chain structure with sequence from [ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1qki]] is a 8 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human Human]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1QKI OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1QKI FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><scene name='pdbligand=GOA:GLYCOLIC+ACID'>GOA</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GOL:GLYCEROL'>GOL</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NAP:NADP+NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE+PHOSPHATE'>NAP</scene></td></tr> | + | </td></tr><tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=GOA:GLYCOLIC+ACID'>GOA</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=GOL:GLYCEROL'>GOL</scene>, <scene name='pdbligand=NAP:NADP+NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE+PHOSPHATE'>NAP</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1dpg|1dpg]], [[2dpg|2dpg]]</td></tr> | + | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><div style='overflow: auto; max-height: 3em;'>[[1dpg|1dpg]], [[2dpg|2dpg]]</div></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">G6PD ([ | + | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">G6PD ([https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=9606 HUMAN])</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | <tr id='activity'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Activity:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucose-6-phosphate_dehydrogenase Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase], with EC number [https://www.brenda-enzymes.info/php/result_flat.php4?ecno=1.1.1.49 1.1.1.49] </span></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1qki FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1qki OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1qki PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1qki RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1qki PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1qki ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
</table> | </table> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | [[ | + | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/G6PD_HUMAN G6PD_HUMAN]] Defects in G6PD are the cause of chronic non-spherocytic hemolytic anemia (CNSHA) [MIM:[https://omim.org/entry/305900 305900]]. Deficiency of G6PD is associated with hemolytic anemia in two different situations. First, in areas in which malaria has been endemic, G6PD-deficiency alleles have reached high frequencies (1% to 50%) and deficient individuals, though essentially asymptomatic in the steady state, have a high risk of acute hemolytic attacks. Secondly, sporadic cases of G6PD deficiency occur at a very low frequencies, and they usually present a more severe phenotype. Several types of CNSHA are recognized. Class-I variants are associated with severe NSHA; class-II have an activity <10% of normal; class-III have an activity of 10% to 60% of normal; class-IV have near normal activity.<ref>PMID:1611091</ref> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [[ | + | [[https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/G6PD_HUMAN G6PD_HUMAN]] Produces pentose sugars for nucleic acid synthesis and main producer of NADPH reducing power. |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| - | *[[G6PD (Hebrew)|G6PD (Hebrew)]] | ||
*[[Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase|Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase]] | *[[Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase|Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase]] | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 07:07, 24 February 2021
X-RAY STRUCTURE OF HUMAN GLUCOSE 6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE (VARIANT CANTON R459L) COMPLEXED WITH STRUCTURAL NADP+
| |||||||||||