This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
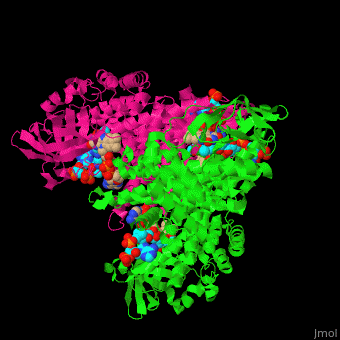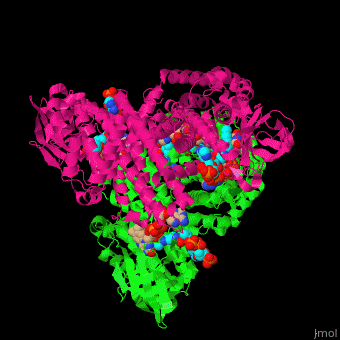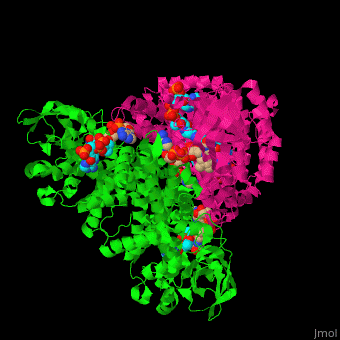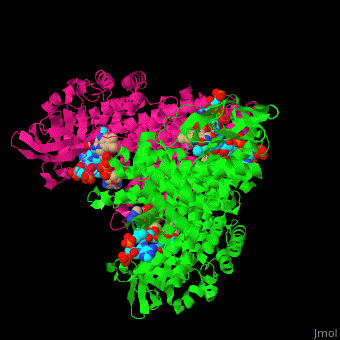
| - | '''Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase''' (ACDH) catalyzes the introduction of a double bond between C2 and C3 of the thio-ester CoA substrate. This is the first reaction in fatty acid metabolism which produces acetyl-CoA. FAD is the cofactor of ACDH activity. ACDH is classified according to the length of its substrates as short- (SCAD), medium- (MCAD), very- and very long-chain (VLCAD) ACDH. MCAD can bind a broad range of chain length acyl-CoA substrates.<ref>PMID:7601336</ref> | + | '''Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase''' (ACDH) catalyzes the introduction of a double bond between C2 and C3 of the thio-ester CoA substrate. This is the first reaction in fatty acid metabolism which produces acetyl-CoA. FAD is the cofactor of ACDH activity. ACDH is classified according to the length of its substrates as short- (SCAD), medium- (MCAD), very- and very long-chain (VLCAD) ACDH. MCAD can bind a broad range of chain length acyl-CoA substrates.<ref>PMID:7601336</ref> See also [[Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase]]. |
| + | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 12:39, 7 March 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Thorpe C, Kim JJ. Structure and mechanism of action of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. FASEB J. 1995 Jun;9(9):718-25. PMID:7601336
- ↑ Battaile KP, Molin-Case J, Paschke R, Wang M, Bennett D, Vockley J, Kim JJ. Crystal structure of rat short chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase complexed with acetoacetyl-CoA: comparison with other acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 5;277(14):12200-7. Epub 2002 Jan 25. PMID:11812788 doi:10.1074/jbc.M111296200