We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Leanne Price/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=DGAT Human= | =DGAT Human= | ||
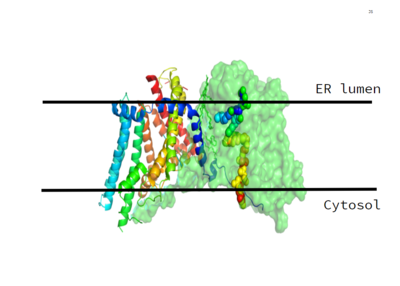
| - | <StructureSection load='6vp0' size='340' side='right' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='6vp0' size='340' side='right' caption='General structure of DGAT with one protein chain in pink, and the other in magenta. The grey chains represent diglycerides and enzymes located within the active site. ' scene=''> |
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
DGAT consists of two domains, one cytoplasmic and one luminal. The cytoplasmic domain interacts with the interior of the cell and relays signals. The luminal domain senses misfolded proteins. The structure of DGAT consists of two protein chains, one ligand, two polymers, eighteen alpha helices and zero beta sheets. The majority of the transmembrane helices present within the structure form a concave-shaped ridge on either side of the membrane. | DGAT consists of two domains, one cytoplasmic and one luminal. The cytoplasmic domain interacts with the interior of the cell and relays signals. The luminal domain senses misfolded proteins. The structure of DGAT consists of two protein chains, one ligand, two polymers, eighteen alpha helices and zero beta sheets. The majority of the transmembrane helices present within the structure form a concave-shaped ridge on either side of the membrane. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The DGAT dimer structure is formed primarily through many [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_bond hydrogen-bonding] interactions between the first 20 resolved residues (His69-Gly87). Hydrophobic interactions of the transmembrane helix region (Phe82-Ile98) with the other monomer also support the dimer structure formation. Additionally, there are four phospholipids present at the dimer interface that have been thought to contribute to the interactions between DGAT monomers. | ||
===Tunnels=== | ===Tunnels=== | ||
Revision as of 22:33, 17 March 2021
DGAT Human
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Wang L, Qian H, Nian Y, Han Y, Ren Z, Zhang H, Hu L, Prasad BVV, Laganowsky A, Yan N, Zhou M. Structure and mechanism of human diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):329-332. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433610 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2
- ↑ Sui X, Wang K, Gluchowski NL, Elliott SD, Liao M, Walther TC, Farese RV Jr. Structure and catalytic mechanism of a human triacylglycerol-synthesis enzyme. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):323-328. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433611 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6
Student Contributors
- Justin Smith
- Eloi Bigirimana
- Leanne Price