User:Madison Unger/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=ACAT/SOAT= | =ACAT/SOAT= | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='6l47' size='340' frame='true' side='right' caption='ACAT/SOAT 6l47' scene='87/ | + | <StructureSection load='6l47' size='340' frame='true' side='right' caption='ACAT/SOAT 6l47' scene='87/877508/Overall_structure/1'> |
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
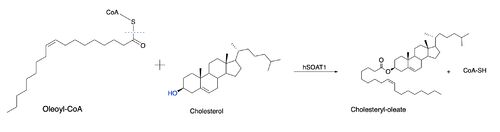
[[Image:overallstructureacat.png|400px|left|thumb|Figure 1.Tetrameric dimer of dimer for ACAT]] Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT), also known as Human Sterol O-acyltransferase (hSOAT) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between long chain [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Long-chain-fatty-acid%E2%80%94CoA_ligase fatty acyl CoA] and intracellular [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesterol cholesterol] to form the more hydrophobic cholesteryl ester for cholesterol storage. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesteryl_ester Cholesteryl ester] is the primary form of how cholesterol is stored in multiple types of cells and transported through the circulatory system. ACAT is an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein, and ACAT is a part of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MBOAT MBOAT] (membrane-bound O-acyltransferase) family, which also includes acyl-coenzyme A: diacylglycerol acyltransferase ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diglyceride_acyltransferase DGAT]) and ghrelin O-acyltransferase ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ghrelin_O-acyltransferase GOAT]). | [[Image:overallstructureacat.png|400px|left|thumb|Figure 1.Tetrameric dimer of dimer for ACAT]] Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT), also known as Human Sterol O-acyltransferase (hSOAT) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between long chain [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Long-chain-fatty-acid%E2%80%94CoA_ligase fatty acyl CoA] and intracellular [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesterol cholesterol] to form the more hydrophobic cholesteryl ester for cholesterol storage. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesteryl_ester Cholesteryl ester] is the primary form of how cholesterol is stored in multiple types of cells and transported through the circulatory system. ACAT is an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein, and ACAT is a part of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MBOAT MBOAT] (membrane-bound O-acyltransferase) family, which also includes acyl-coenzyme A: diacylglycerol acyltransferase ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diglyceride_acyltransferase DGAT]) and ghrelin O-acyltransferase ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ghrelin_O-acyltransferase GOAT]). | ||
Revision as of 20:14, 29 March 2021
ACAT/SOAT
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
- ↑ Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ Rogers MA, Liu J, Song BL, Li BL, Chang CC, Chang TY. Acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferases (ACATs/SOATs): Enzymes with multiple sterols as substrates and as activators. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;151:102-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.09.008., Epub 2014 Sep 12. PMID:25218443 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2014.09.008
Student Contributors
- Leah Goehring
- Gabby Smith
- Anna Campbell