User:Jacob Holt/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Introduction== | == Introduction== | ||
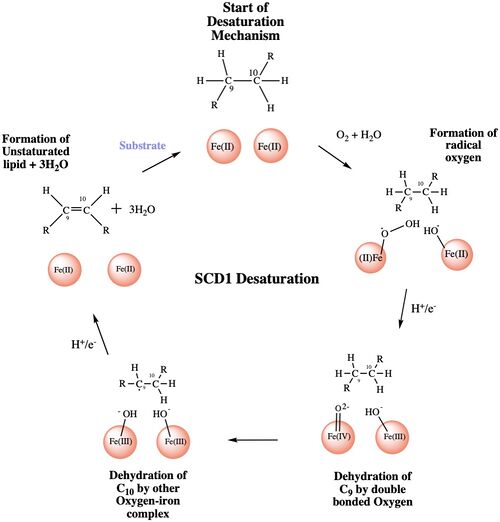
| - | Stearyol CoA Desaturase (SCD1) functions as a lipogenic enzyme which is essential for fatty acid metabolism<ref name= | + | Stearyol CoA Desaturase (SCD1) functions as a lipogenic enzyme which is essential for fatty acid metabolism<ref name="Bai">PMID: 26098370 </ref>. SCD1 desaturates the sigma bond, within the 18-carbon acyl-CoA ligand, that attaches carbons 9 and 10 <ref name="Bai" />. The desaturated ligand is used in the synthesis of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesteryl_ester cholesteryl esters] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides]<ref name="Paton">PMID: 19066317 </ref>. The exact origin of SCD1 is unknown. Current studies have used mouse SCD to determine the structure and function of the enzyme<ref name="Shen">PMID: 32470559 </ref>. The metal ions within the structure of SCD1 were determined by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_fluorescence X-Ray Flourescense]. The structure of the ligand before the reaction takes place and how it interacts with the enzyme was determined by using [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zinc zinc] as the metal ions which inhibits the enzymes activity<ref name="Bai" />. The structure of the ligand post reaction was determined by using [hhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron iron] as the metal ions which allowed the enzyme to be active and complete the reaction<ref name="Shen" />. SCD1 is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmembrane_protein transmembrane protein title] with 4 helices within the membrane, and 8 helices in cytoplasm. This protein acquires electrons via an electron transport chain which includes [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytochrome_b5_reductase cytochrome B5 reductase] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytochrome_b5 cytochrome B5]<ref name="Shen" />. The electrons are transferred via a ternary complex and accepted by SCD1 by the iron metal ions<ref name="Shen" />. SCD1 has 8 helices that are hydrophobic, 4 helices that are hydrophilic, and 3 helices that are amphipathic<ref name="Bai" /><ref name="Shen" />. |
== Biological Relevance == | == Biological Relevance == | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | The primary job of SCD1 in the body is to catalyze the biosynthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) via saturated [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyl-CoA Acyl-CoAs] with an acyl chain length of 14-19 carbons<ref name="Paton" /><ref name="Shen" />. Variations of the monounsaturated fatty acids function as precursors for the biosynthesis of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipid phospholipids], cholesterol esters, and triglycerides; therefore, SCD1 is a promising candidate for drug targeting1. Absence or a deficit of SCD1 in the body is associated with obesity and insulin resistance which is a main cause of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes type II diabetes]<ref name="Shen" />. Cancer sites in the body tend to show a much higher expression rate of SCD13. Focusing on SCD1 as a drug target could lead to advancements in treatment of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic diseases<ref name="Bai" />. | ||
| + | |||
<scene name='87/877556/Diiron_center/1'>Dizinc Center</scene> | <scene name='87/877556/Diiron_center/1'>Dizinc Center</scene> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
[http://https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fatty_acid_desaturase Desaturase Enzyme] | [http://https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fatty_acid_desaturase Desaturase Enzyme] | ||
<scene name='87/877552/140-160_amino_highlight/1'>SCD thing</scene> | <scene name='87/877552/140-160_amino_highlight/1'>SCD thing</scene> | ||
| - | + | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | [[Image:SCD1_New.jpeg| | + | [[Image:SCD1_New.jpeg|500px|Right|]] |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 14:27, 30 March 2021
Mouse Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 Structure
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Bai Y, McCoy JG, Levin EJ, Sobrado P, Rajashankar KR, Fox BG, Zhou M. X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Nature. 2015 Jun 22. doi: 10.1038/nature14549. PMID:26098370 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14549
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Paton CM, Ntambi JM. Biochemical and physiological function of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jul;297(1):E28-37. doi:, 10.1152/ajpendo.90897.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 9. PMID:19066317 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.90897.2008
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Shen J, Wu G, Tsai AL, Zhou M. Structure and Mechanism of a Unique Diiron Center in Mammalian Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. J Mol Biol. 2020 May 27. pii: S0022-2836(20)30367-3. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017. PMID:32470559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017
Student Contributions
Delete Later: