This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Megan Fleshman/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
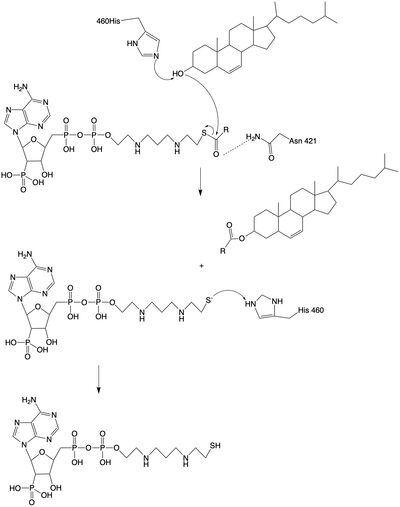
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
Tunnels | Tunnels | ||
| - | The catalytic site is accessed through three different tunnels that lead from the center catalytic domain of the monomer, to the [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lumen_(anatomy)lumen]], cytosol, and transmembrane space. The tunnels allow the entrance of reactants into the acyl transferase mechanism and the exit of the products to the correct location depending on their function. | + | The catalytic site is accessed through three different tunnels that lead from the center catalytic domain of the monomer, to the [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lumen_(anatomy) lumen]], cytosol, and transmembrane space. The tunnels allow the entrance of reactants into the acyl transferase mechanism and the exit of the products to the correct location depending on their function. |
The <scene name='87/877605/C_tunnel/1'>C tunnel</scene> is open to the cytosolic side of the protein in which the Acyl CoA enters into the catalytic domain. | The <scene name='87/877605/C_tunnel/1'>C tunnel</scene> is open to the cytosolic side of the protein in which the Acyl CoA enters into the catalytic domain. | ||
The <scene name='87/877605/T_tunnel/1'>T tunnel</scene> is the transmembrane tunnel in which the cholesterol enters into the catalytic domain space. Important <scene name='87/877605/T_tunnel_residues/1'>residues</scene> of the T tunnel include Arginine262, Phenylalanine 263, and Leucine 306. These residues are important for the proper entrance and orientation of the cholesterol to allow for its deprotonation in the mechanism. | The <scene name='87/877605/T_tunnel/1'>T tunnel</scene> is the transmembrane tunnel in which the cholesterol enters into the catalytic domain space. Important <scene name='87/877605/T_tunnel_residues/1'>residues</scene> of the T tunnel include Arginine262, Phenylalanine 263, and Leucine 306. These residues are important for the proper entrance and orientation of the cholesterol to allow for its deprotonation in the mechanism. | ||
Revision as of 21:38, 5 April 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
Student Contributors
- Megan Fleshman