We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Megan Fleshman/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
The <scene name='87/877605/C_tunnel/1'>C tunnel</scene> is open to the cytosolic side of the protein in which the Acyl CoA enters into the catalytic domain. | The <scene name='87/877605/C_tunnel/1'>C tunnel</scene> is open to the cytosolic side of the protein in which the Acyl CoA enters into the catalytic domain. | ||
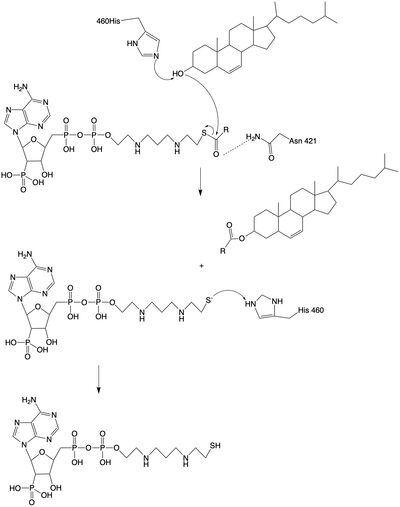
| - | The catalytic site contains conserved <scene name='87/877605/Catalytic_residues/1'>residues</scene> that are essential to the mechanism of the ACAT1 mechanism. These residues include His460 to function as a base catalyst and Asn421 which functions as transition state stabilization with hydrogen bonding. | + | The catalytic site contains conserved <scene name='87/877605/Catalytic_residues/1'>residues</scene> that are essential to the mechanism of the ACAT1 mechanism. These residues include His460 to function as a base catalyst and Asn421 which functions as transition state stabilization with hydrogen bonding. Also important for orientation of the Acyl CoA ligand is the presence of hydrophobic residues to stabilize the fatty acid tail. |
The <scene name='87/877605/T_tunnel/1'>T tunnel</scene> is the transmembrane tunnel in which the cholesterol enters into the catalytic domain space. Important <scene name='87/877605/T_tunnel_residues/1'>residues</scene> of the T tunnel include Arginine262, Phenylalanine 263, and Leucine 306. These residues are important for the proper entrance and orientation of the cholesterol to allow for its deprotonation in the mechanism. | The <scene name='87/877605/T_tunnel/1'>T tunnel</scene> is the transmembrane tunnel in which the cholesterol enters into the catalytic domain space. Important <scene name='87/877605/T_tunnel_residues/1'>residues</scene> of the T tunnel include Arginine262, Phenylalanine 263, and Leucine 306. These residues are important for the proper entrance and orientation of the cholesterol to allow for its deprotonation in the mechanism. | ||
Revision as of 21:46, 5 April 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
- ↑ Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
Student Contributors
- Megan Fleshman