User:Megan Fleshman/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
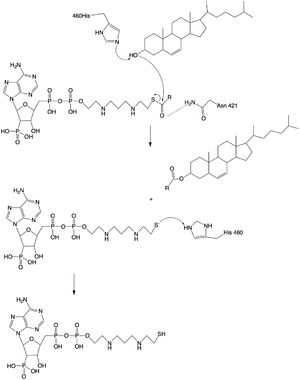
The mechanism of the [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyltransferase#:~:text=Acyltransferase%20is%20a%20type%20of,%2Dalcohol%20O%2Dfatty%2Dacyltransferase acyltransferace]]reaction occurs in the catalytic site one of the monomers in the dimer of ACAT1. The T tunnel and and C tunnel converge to the same space to allow the proper orientation of the Acyl CoA and the incoming cholesterol from the transmembrane. The Acyl CoA is oriented in a way to allow the His460 to act as a base catalyst to begin the reaction by deprotonation of the cholesterol which allows it to attack the carbonyl carbon which breaks the sulfur carbonyl bond (figure 2). This mechanism produced Acyl-CoASH and cholesteryl ester. The Acyl-CcASH leaves through the C tunnel to the cytosol. | The mechanism of the [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyltransferase#:~:text=Acyltransferase%20is%20a%20type%20of,%2Dalcohol%20O%2Dfatty%2Dacyltransferase acyltransferace]]reaction occurs in the catalytic site one of the monomers in the dimer of ACAT1. The T tunnel and and C tunnel converge to the same space to allow the proper orientation of the Acyl CoA and the incoming cholesterol from the transmembrane. The Acyl CoA is oriented in a way to allow the His460 to act as a base catalyst to begin the reaction by deprotonation of the cholesterol which allows it to attack the carbonyl carbon which breaks the sulfur carbonyl bond (figure 2). This mechanism produced Acyl-CoASH and cholesteryl ester. The Acyl-CcASH leaves through the C tunnel to the cytosol. | ||
| - | [[Image:acatmechanism.jpg| | + | [[Image:acatmechanism.jpg|300px|left|thumb|Figure 2: Acyltransferase mechanism of ACAT1 with conserved MBOAT family catalytic residues.]] |
==Inhibitor== | ==Inhibitor== | ||
Revision as of 18:36, 6 April 2021
| |||||||||||
References
ACAT article [3] SOAT Article [4]
- ↑ Farese RV Jr. The nine lives of ACAT inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006 Aug;26(8):1684-6. doi:, 10.1161/01.ATV.0000227511.35456.90. PMID:16857957 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000227511.35456.90
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 Chang TY, Chang CC, Bryleva E, Rogers MA, Murphy SR. Neuronal cholesterol esterification by ACAT1 in Alzheimer's disease. IUBMB Life. 2010 Apr;62(4):261-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.305. PMID:20101629 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/iub.305
- ↑ Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
Student Contributors
- Megan Fleshman, Tori Templin, Haylie Moehlenkamp