User:Megan Fleshman/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
| - | ===Disease | + | ===Disease=== |
==Alzheimer's Disease== | ==Alzheimer's Disease== | ||
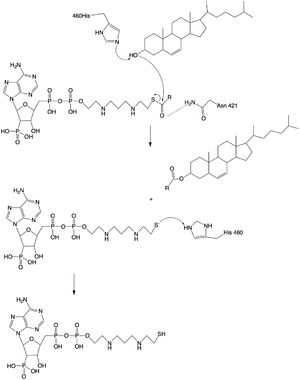
| - | Alzheimer's Disease is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by accumulation of extracellular plaques that cause interferences with memory retrieval. These plaques are made up of amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides which are products of the cleavage of human Amyloid Precursor Protein (hAPP) <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name "Shibuya">PMID:26669800</ref>. Within the cells, there is an accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name "Shibuya">PMID:26669800</ref>. Research has shown that the concentration of cholesterol within cells can affect the production of Aβ <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name "Shibuya">PMID:26669800</ref>. As the concentration of cholesterol in the endoplasmic reticulum of neurons increases, hAPP is | + | Alzheimer's Disease is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by accumulation of extracellular plaques that cause interferences with memory retrieval. These plaques are made up of amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides which are products of the cleavage of human Amyloid Precursor Protein (hAPP) <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name="Shibuya"> PMID:26669800</ref>. Within the cells, there is an accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name="Shibuya"> PMID:26669800</ref>. Research has shown that the concentration of cholesterol within cells can affect the production of Aβ <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name="Shibuya"> PMID:26669800</ref>. As the concentration of cholesterol in the endoplasmic reticulum of neurons increases, hAPP is down regulated <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref><ref name="Shibuya"> PMID:26669800</ref>. Inhibition of ACAT1 would lead to higher concentrations of cholesterol in the cells, signaling down regulation of hAPP. Less hAPP available decreases the amount of Aβ peptides being produced and decreases the available Aβ peptides that could form the extracellular plaques associated with Alzheimer's Disease <ref name "Chang">doi:10.1002/iub.305</ref> <ref name="Shibuya"> PMID:26669800</ref>. |
==Other Diseases== | ==Other Diseases== | ||
| - | ACAT is also involved in diseases such as Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases, as well as artherosclerosis. After research on glioma, prostate, pancreatic, leukemia, and breast cancers, it has been noted that ACAT plays a role in the progression of cancer over time. Recently, | + | ACAT is also involved in diseases such as Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases, as well as artherosclerosis. After research on glioma, prostate, pancreatic, leukemia, and breast cancers, it has been noted that ACAT plays a role in the progression of cancer over time. Recently, Ayyagari et al. found that there was a significant increase in ACAT-1 expression in ovarian cancer cell lines <ref name="Ayyagari"> doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228024</ref>. |
Revision as of 18:49, 6 April 2021
| |||||||||||
References
ACAT article [5] SOAT Article [6]
- ↑ Farese RV Jr. The nine lives of ACAT inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006 Aug;26(8):1684-6. doi:, 10.1161/01.ATV.0000227511.35456.90. PMID:16857957 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000227511.35456.90
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Chang TY, Chang CC, Bryleva E, Rogers MA, Murphy SR. Neuronal cholesterol esterification by ACAT1 in Alzheimer's disease. IUBMB Life. 2010 Apr;62(4):261-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.305. PMID:20101629 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/iub.305
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Shibuya Y, Chang CC, Chang TY. ACAT1/SOAT1 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Future Med Chem. 2015;7(18):2451-67. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.161. Epub 2015 Dec 15. PMID:26669800 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.161
- ↑ Ayyagari VN, Wang X, Diaz-Sylvester PL, Groesch K, Brard L. Assessment of acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT-1) role in ovarian cancer progression-An in vitro study. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0228024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228024., eCollection 2020. PMID:31978092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228024
- ↑ Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
Student Contributors
- Megan Fleshman, Tori Templin, Haylie Moehlenkamp