Introduction
Sterol O-acyltransferase(SOAT), otherwise known as Acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase(ACAT), is the founding member of the membrane-bound O-acyl transferase(MBOAT) enzyme family. MBOAT enzymes transfer acyl chains onto various substrates, including lipids, peptides, and small proteins. There are 11 MBOAT family members in humans, which participate in a variety of physiological processes.[1]
SOAT specifically catalyzes the esterification of cholesterol for efficient storage within the cell. Cholesterol is a membrane lipid that plays an essential role in maintaining the fluidity and integrity of the membrane, and cholesteryl esters are formed when an excess of cholesterol is present.
Structure
Tertiary Structure
The overall structure of the enzyme is a structure or a dimer of dimers. The functional building block of SOAT is a which is made up of two identical structures. The residues that form the dimer interface are mostly hydrophobic and interact with each other in a shape-complementary manner. Mutating residues within the dimer interface reduced the dimers to monomer fractions, indicating that the dimeric architecture is important for the activity of the enzyme. The dimerization of SOAT is mainly mediated by extensive van der Waals interactions between TM1 in one protomer and the lumenal segment of TM6 and the cytosolic segment of TM9 in the other. TM1, TM5, TM6 and TM9 from the two protomers enclose a deep hydrophobic pocket that is open to the lumenal side. Numerous hydrophobic residues on TM6 and TM9 from one protomer contact those on TM1 from the other protomer. On the intracellular side, hydrophobic residues on IH1 of each protomer interact with each other to stabilize the dimer.[2]
Tunnel System
A main structural element of this enzyme is the tunnel systems. There are 3 main tunnels in each monomer: the cytosolic (C) tunnel opening to the cytosol, the transmembrane(T) tunnel opening to the membrane, and the lumenal(L) tunnel opens to the lumen. The C tunnel opens to the cytosol of the cell and is the entrance site for the Acyl CoA into the active site. Surface representations of SOAT indicate that there are 2 alpha helices that block the entrance to the C tunnel, therefore a conformational change needs to occur to move the 2 helices so the substrate can enter the tunnel. The T tunnel opens into the membrane and is where cholesterol enters to have access to the active site. The two substrates are catalyzed by the H460 in the active site to form the cholesteryl ester. The products then leave via different pathways. The CoA-SH in the C tunnel leaves via that tunnel and is released back into the cytosol. The cholesteryl ester then leaves via either the T tunnel into the membrane or through the L tunnel into the lumen of the cell.
Active Site
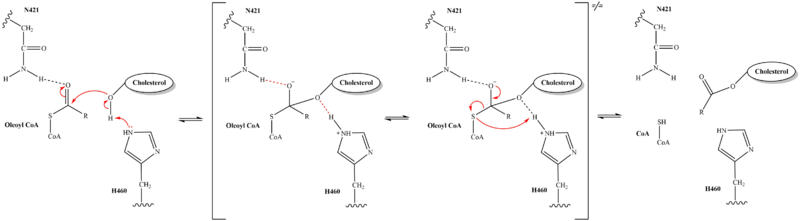
The of this enzyme has 3 main residues that are essential for the catalytic activity of SOAT. work to stabilize the substrates as well as serve other roles in the mechanism of action. Many acyl transferases utilize histidine as the catalytic base. The conserved H460 is crucial for SOAT activity and is the putative catalytic residue. A single point mutation of the histidine at position 460 to alanine resulted in the complete abolition of enzymatic activity indicating its essential role in the mechanism. Along with H460, there are several other residues in the central cavity that are important for SOAT function. Most residues aligning the interior of the reaction chamber are highly conserved indicating that the local environment in the central cavity is important for the catalytic reaction.
Catalytic Mechanism
The distal-most nitrogen on H460 acts as a base catalyst to deprotonate the hydroxyl group of a cholesterol molecule. This leaves the cholesterol oxygen with a negative charge, making it a good nucleophile. The nucleophilic oxygen attacks the Acyl CoA substrate at the carbonyl carbon, kicking electron density up to the carbonyl oxygen. Shown in brackets, the transition state is stabilized by N421 and newly protonated H460.
From the transition state, excess electron density on the carbonyl oxygen is collapsed back into a double bond. This causes the bond between the carbonyl carbon and sulfur to break, shifting electron density to the sulfur atom. To complete the mechanism, the negatively charged sulfur would reclaim the hydrogen from protonated H460. Acyl CoA would exit the active site as a leaving group, leaving its R group attached to cholesterol in the form of a cholesterol ester.
It should be noted that this mechanism is largely hypothesized. Further analysis is needed to confirm the proposed steps. Additionally, the role of W420 is unclear. Mutations of W420A rendered the SOAT enzyme nonfunctional, indicating that it must be essential for catalytic activity. However, its role in the mechanism, direct or indirect, is unknown at this time.
Inhibitors
CI-976 inhibits SOAT activity in a dose-dependent manner. The location of CI-976 is found right in the with its large trimethoxyphenyl head sandwiched right between the catalytic residues . This suggests that CI-976 inhibits the enzyme by preventing the loading of the substrate into the catalytic center, which makes sense given the competitive behavior of CI-976. Mutations of CI-976 interaction residues, N421A, H460A, and H460N greatly diminish the enhancement effect of CI976 on the thermostability of the SOAT dimer.
Biological Relevance
SOAT can actually use multiple sterols as substrates and activators. Because of its functional importance, SOAT is a potential drug target for Alzheimer’s disease, atherosclerosis, and several types of cancers.