User:Megan Fleshman/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Cholesterol esters were found in arterial lesions in 1910, but the first ACAT activity was discovered in the mid 1900's. This led to the inhibition of ACAT as being looked at as a possible strategy of preventing or treating atherosclerosis. Between 1980-1995, the interest in ACAT inhibitors grew, but some of the compounds looked at exhibited toxicity. As they were looking into the function of the ACAT1 gene, ACAT2 was discovered. In 1993, an ACAT gene was successfully cloned. This discovery led to more studies with ACAT and atherosclerosis. Some of these studies used mice and showed cellular toxicity. ACAT inhibition is still being looked into as a strategy for treatment or prevention of atherosclerosis and related diseases. | Cholesterol esters were found in arterial lesions in 1910, but the first ACAT activity was discovered in the mid 1900's. This led to the inhibition of ACAT as being looked at as a possible strategy of preventing or treating atherosclerosis. Between 1980-1995, the interest in ACAT inhibitors grew, but some of the compounds looked at exhibited toxicity. As they were looking into the function of the ACAT1 gene, ACAT2 was discovered. In 1993, an ACAT gene was successfully cloned. This discovery led to more studies with ACAT and atherosclerosis. Some of these studies used mice and showed cellular toxicity. ACAT inhibition is still being looked into as a strategy for treatment or prevention of atherosclerosis and related diseases. | ||
<ref name=”Farese Jr.”>PMID: 16857957</ref> | <ref name=”Farese Jr.”>PMID: 16857957</ref> | ||
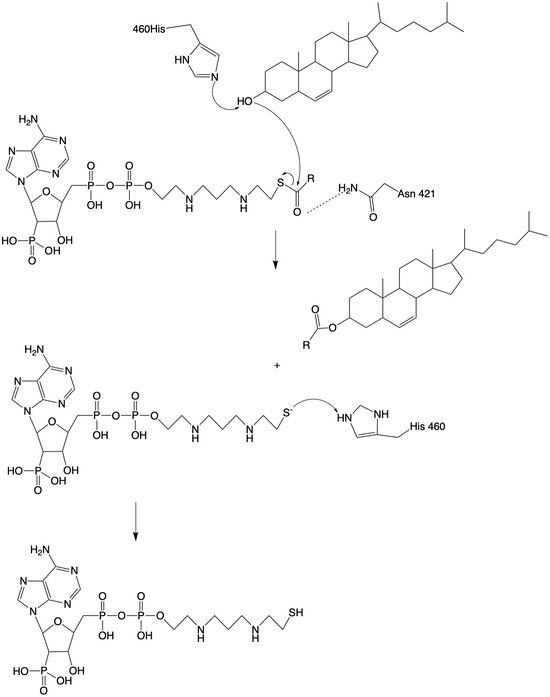
| - | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thiolase ACAT] is an important enzyme that catalyzes the esterification of cholesterol to form cholesterol esters, and it belongs to the class of enzymes called acyltransferases. It is also a member of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MBOAT MBOAT] family because it is key in lipid metabolism. This enzyme is biologically important because it affects the solubility of cholesterol in the cell membrane and promotes accumulation of cholesterol ester in the cytoplasm as fat droplets. Accumulation of cholesterol ester as these lipid droplets is a main characteristic of macrophage foaming, which can lead to atherosclerotic diseases <ref name=”Qian”>PMID:32433614</ref>. |
[[Image:Screen Shot 2021-03-16 at 3.11.39 PM.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. ACAT as a Dimer of Dimers - One Monomer is Highlighted]] | [[Image:Screen Shot 2021-03-16 at 3.11.39 PM.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. ACAT as a Dimer of Dimers - One Monomer is Highlighted]] | ||
Revision as of 18:57, 13 April 2021
Acyl-Coenzyme Cholesterol Acetyltransferase (ACAT)
| |||||||||||
References
ACAT article [8] SOAT Article [9]
- ↑ Farese RV Jr. The nine lives of ACAT inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006 Aug;26(8):1684-6. doi:, 10.1161/01.ATV.0000227511.35456.90. PMID:16857957 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000227511.35456.90
- ↑ Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Chang TY, Chang CC, Bryleva E, Rogers MA, Murphy SR. Neuronal cholesterol esterification by ACAT1 in Alzheimer's disease. IUBMB Life. 2010 Apr;62(4):261-7. doi: 10.1002/iub.305. PMID:20101629 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/iub.305
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Shibuya Y, Chang CC, Chang TY. ACAT1/SOAT1 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Future Med Chem. 2015;7(18):2451-67. doi: 10.4155/fmc.15.161. Epub 2015 Dec 15. PMID:26669800 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4155/fmc.15.161
- ↑ Ayyagari VN, Wang X, Diaz-Sylvester PL, Groesch K, Brard L. Assessment of acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT-1) role in ovarian cancer progression-An in vitro study. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0228024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228024., eCollection 2020. PMID:31978092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228024
- ↑ Vaziri ND, Liang KH. Acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibition ameliorates proteinuria, hyperlipidemia, lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase, SRB-1, and low-denisty lipoprotein receptor deficiencies in nephrotic syndrome. Circulation. 2004 Jul 27;110(4):419-25. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000136023.70841.0F. , Epub 2004 Jul 19. PMID:15262831 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000136023.70841.0F
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Willner EL, Tow B, Buhman KK, Wilson M, Sanan DA, Rudel LL, Farese RV Jr. Deficiency of acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase 2 prevents atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Feb 4;100(3):1262-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0336398100., Epub 2003 Jan 21. PMID:12538880 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0336398100
- ↑ Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
Student Contributors
- Megan Fleshman, Tori Templin, Haylie Moehlenkamp