Introduction
Overview
Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase (SCD) is an integral membrane protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum and is conserved across all eukaryotes [1]. SCD-1 is expressed in Mus musculus. The human homolog, SCD1, shares 85% sequence identity with all four SCD’s found in M. musculus (Scd1-Scd4). The expression of SCD is seen mainly in the liver and brain [2].
SCD is an enzyme which catalyzes desaturation of a double bond within a fatty acid hydrocarbon chain. The addition of a double bond is necessary for the biosynthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids such as: cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides. The enzyme’s main function is lipid biosynthesis as well as regulating gene expression for lipogenesis [1]. SCD is regulated by transcription and its promoter has multiple binding sites for transcription factors that assist in regulation of lipogenesis [2]. It was discovered that when M. musculus were SCD-deficient, there was no obesity seen in the mice [1] This is why SCD is a popular target in treating metabolic diseases. Functioning SCD creates the balance between the accumulation and use of fats in the body.
SCD-1 is interacts with either of the two different substrates: stearoyl-CoA or palmitoyl-CoA. When SCD interacts with stearoyl-CoA and performs desaturation, the product is oleoyl-CoAand has the first cis-double bond introduced into the fatty acid chain. The introduction of the cis-double bond into the hydrocarbon chain will increase fluidity of the lipid bilayer. The process of desaturation is tightly regulated by multiple transcription factors.
The desaturase enzyme also works in combat with inhibitors. SCD is affected by hormones, growth factors, and nutritional status [2]. Leptin is a hormone that plays a role in regulation of energy homeostasis and is also able to stop SCD-1 expression by activating specific transcription factors to bind to SCD promoter and overpower the insulin signals [2]. Other negative regulators of SCD include estrogen and glucagon. Interestingly enough, SCD can also be inhibited by one’s nutritional status because of the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs).
Structure
SCD1 has arranged in a “mushroom"-like shape [3]. The cytosolic domain makes up the crown of the enzyme and the TM domains make up the stem. There is a conserved and catalytic histidine box (pic). Coordinated by the . Two metal molecules (iron or zinc) separated by 6.4 Angstroms, make up the dimetal center within the binding pocket.
Binding Pocket
SCD-1 consists of a hydrophobic V-shaped tunnel deep within the protein that the substrates will enter [4]. The tunnel is regioselective and stereospecific such that the substrate’s binding site lines up C9 and C10 at the kink of the V-shaped tunnel with the di-iron center that consists of an oxygen molecule bound to one of the metals. The kink is formed by two conserved Trp149 and Thr257 residues [1]. It is at this kink of the tunnel where desaturation occurs. Precise placement of the C9-C10 atoms near the two iron metals provides the tunnel with regioselectivity and stereospecificity, stabilizing the substrate for oxygen to extract the hydrogens in order to form the double bond.
Metal Cations
Typically, SCD contains a in the core of the protein that contributes to its desaturation function. Crystallized structures of SCD indicated a substitution of Zinc as the di-metal center instead of [1]. It is proposed that the difference in size of Zinc and Iron (8.8 Å and 9.2 Å respectively) would not affect the structure of SCD (Figure containing all 3 of Treys photos?). However, the substitution of Zinc as the di-iron center is found to inhibit the function of SCD due to a farther distance between the two metals compared to iron (Figure containing all 3 of Treys photos) [1].
In other di-metal centered enzymes such as ACP desaturase and ribonucleotide reductase, the enzymatic mechanism involves an oxo-bridge: a water molecule that is recruited by the di-iron center to be directly involved in the desaturase mechanism. This water gets deprotonated by the two metal ions and it becomes nucleophilic enough to attack the substrate (Mechanism figure). Based on electron density mapping, this oxo-bridge formation is suggested to be short-lived [3].
Mutations and Substrate Specificity
Different desaturases have varying catalytic rates depending on the carbon chain length of the substrate. For example, desaturase ChDes1 found in arctic copepod Calanus hyperboreus contains a threonine instead of a highly conserved tyrosine at position 104 in SCD1 and other desaturases which caused the loss of desaturase function in 26C substrates while retaining activity with 18C substrates. In SCD3, stacked mutations I112A and Q113L changed the enzyme’s specificity from a 16C to a 18C desaturase (Bai et al.). It is hypothesized that mutations that occur on TM2 near the substrate binding tunnel change the substrate specificity of SCD. (Tell Trey to make this as a green link)
Function
Palmitoyl and Stearoyl CoA are substrates of SCD1. These substrates enter the hydrophobic V-shaped tunnel inside SCD1. The tunnel is regioselective and stereospecific such that the substrate’s binding site lines up C9 and C10 at the kink of the V-shaped tunnel with the di-iron center that consists of an oxygen molecule bound to one of the metals. The kink is formed by two conserved . It is at this kink of the tunnel that desaturation occurs. Hydrogens are removed at the C9, then C10 to introduce the double bond through mechanism (link to mechanism section?). Precise placement of the atoms near the two iron metals provides the tunnel with regioselectivity and stereospecificity, stabilizing the substrate for oxygen to extract the hydrogens in order to form the double bond.
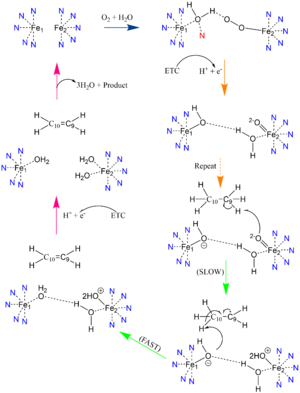
Desaturation Mechanism
Due to the novel coordination of histidine residues and lack of presence of an oxo-bridge, the mechanism of desaturase activity for SCD is unknown. For typical desaturases, the elements involved in catalysis include the di-metal center, metal-bound water and oxygen, electrons from an Electron Transport Chain, and the acyl-CoA substrate. For the proposed mechanism
, catalysis occurs in four phases: the binding of water and oxygen to the di-metal complex using Asn261, the nucleophilic activation of the water/oxygen using the ETC, the interaction of the complex with the substrate, and the recovery of the enzyme. The rate-limiting step of the mechanism is the primary elimination reaction on the substrate due to the nucleophilic attack occurring on an already stable C9-C10 sigma bond.
Product Conversion and Release
The acyl-CoA substrate, due to it containing all sigma bonds, is able to freely rotate around its carbon axes to fit into the deep, kinked binding pocket. Upon double bond formation between C9 and C10, the acyl-CoA rotates from Gauche conformation to eclipsed conformation across C9 and C10 (Figure). The double bond also restricts rotation along carbons 9 and 10 which likely prevents the substrate from exiting through the site that it entered. To allow for product exit, it is hypothesized that a hydrogen bond between Gln143 and Thr257 is broken which creates a hole below the kink into the hydrophobic core of the enzyme (Green link). This would allow for the lateral transfer of the product out of the binding pocket without removing the double bond.
Related Disease
Diabetes and Obesity
The deficiency and/or inhibition of SCD1 results in increased insulin sensitivity, reduced body obesity and resistance to diet-induced obesity. SCD1 is a target for treatment of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic diseases [1].
Cancer
Increased expression levels of SCD1 has shown to enhance cancer cell proliferation. The concentration of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) is much higher in a cancer cell versus a healthy cell. When expression of SCD1 in breast cancer patients was examined, results proved that increased expression of SCD1 was associated with shorter survival [5].
Inhibition of SCD1 can stop cancer cell propagation both directly and indirectly [2]. The enzyme directly regulates signaling pathways, and indirectly interrupts the ratio of monounsaturated to saturated fatty acids. SCD1 is proving as a positive anticancer therapy, considering the difficulty many patients face when going through multiple rounds of chemotherapy. The reason cancer cells often are able to become resistant to chemotherapeutic drugs is because they possess stem cell-like phenotypes [2]. SCD1 inhibition has shown to repress tumor growth from cancer stem cells (CSC) and prevent any new proliferation of the CSC [6].