This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Maggie Stopa/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
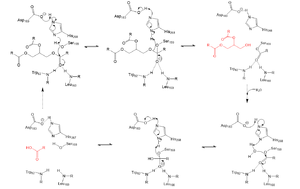
| - | A [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipase lipase] is an enzyme that is capable of catalyzing the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysis] of fats/lipids which are consumed through oils. It is encoded by the [https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LPL p22 region in chromosome 8]. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the interstitial space in several tissues. The main site of action for LPL is in the [https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/116/5/1480/F1.large.jpg capillary lumen] within muscle and adipose tissue. The function of this lipase is to hydrolyze [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides] of very low density lipoproteins ([https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-8e874e647baeb69b00203c47165247e2 VLDL]) and to aid in the delivery of lipid nutrients to vital tissues. The enzyme is commonly found on the surface of cells that line blood capillaries. Two different lipoproteins are essential to break down triglycerides. One of the lipoproteins is utilized to transport fat into the bloodstream from different organs. The lipoproteins essential, in the transport of fat from the intestine are referred to as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chylomicron chylomicrons]. VLDL are utilized in carrying triglycerides from the liver into the bloodstream. The hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase results in fat molecules to be used by the body as energy or stored in fatty tissue. | + | A [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipase lipase] is an enzyme that is capable of catalyzing the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysis] of fats/lipids which are consumed through oils. It is encoded by the [https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LPL p22 region in chromosome 8]. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the interstitial space in several tissues. The main site of action for<scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is in the [https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/116/5/1480/F1.large.jpg capillary lumen] within muscle and adipose tissue. The function of this lipase is to hydrolyze [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides] of very low density lipoproteins ([https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-8e874e647baeb69b00203c47165247e2 VLDL]) and to aid in the delivery of lipid nutrients to vital tissues. The enzyme is commonly found on the surface of cells that line blood capillaries. Two different lipoproteins are essential to break down triglycerides. One of the lipoproteins is utilized to transport fat into the bloodstream from different organs. The lipoproteins essential, in the transport of fat from the intestine are referred to as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chylomicron chylomicrons]. VLDL are utilized in carrying triglycerides from the liver into the bloodstream. The hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase results in fat molecules to be used by the body as energy or stored in fatty tissue. |
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
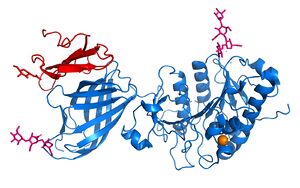
==Structural Overview== | ==Structural Overview== | ||
| - | + | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is assumed to only be active as a <scene name='87/877513/Lpl_dimer/1'>homodimer</scene>, however, previous studies have argued that the lipase can be active in its monomeric form. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6442593/) The N-terminal domain of lipoprotein lipase is known to consist of an alpha/beta hydrolase domain, which is composed of six alpha helices and ten beta-strands. This domain creates an <scene name='87/877513/Secondary_structure/1'>alpha/beta hydrolase fold</scene>. The C-terminal domain of lipoprotein lipase is composed of twelve beta strands which form a “<scene name='87/877513/Secondary_structure/1'>barrel domain | |
</scene>”. | </scene>”. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPIHBP1 GPIHBP1]) is necessary for LPL function and stability. (LIVE REFERENCED NEEDED) | + | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPIHBP1 GPIHBP1]) is necessary for <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> function and stability. (LIVE REFERENCED NEEDED) |
[[Image:LLP11.jpg|300 px|left|thumb|LPL Image]] | [[Image:LLP11.jpg|300 px|left|thumb|LPL Image]] | ||
| + | Original look: <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> | ||
GPI/LPL interface: <scene name='87/877513/Hydrophobic_interface/1'>hydrophobic interface</scene> | GPI/LPL interface: <scene name='87/877513/Hydrophobic_interface/1'>hydrophobic interface</scene> | ||
Calcium ion stabilization:<scene name='87/877513/Calcium_stabilization/5'>calcium ion</scene> | Calcium ion stabilization:<scene name='87/877513/Calcium_stabilization/5'>calcium ion</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='87/877514/Lipid_binding_and_lid/1'>lipid binding region</scene> | ||
Lid: <scene name='87/877514/Lid_region_final/1'>Lid Region</scene> | Lid: <scene name='87/877514/Lid_region_final/1'>Lid Region</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | == References == | ||
| - | <references/> | ||
| - | <ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> | ||
| - | <ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> | ||
| - | <ref name=”Davies”>PMID:20620994</ref> | ||
| - | <ref name=”Beigneux”>PMID:30850549</ref> | ||
| - | <ref name=”Mead”>PMID:12483461</ref> (LPL GENERAL REFERENCE) | ||
| - | <ref name=”Eckel”>PMID:2648155</ref> (LPL GENERAL REFERENCE BOOK IF NEEDED) | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | ==Student Contributors== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Giselle Flores | ||
| - | |||
| - | Dustin Soe | ||
| - | |||
| - | Maggie Stopa | ||
Revision as of 20:16, 19 April 2021
Lipoprotein Lipase LPL
| |||||||||||