User:Brianna Avery/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA_desaturase-1 Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase] (SCD) is an integral membrane protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum and is conserved across all eukaryotes <ref name="Bai">DOI: 10.1038/nature14549</ref>. SCD-1 is expressed in Mus musculus. The human homolog, SCD1, shares 85% sequence identity with all four SCD’s found in M. musculus (Scd1-Scd4). The expression of SCD is seen mainly in the liver and brain <ref name="Dobrzyn">PMID: 31284458</ref>. | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA_desaturase-1 Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase] (SCD) is an integral membrane protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum and is conserved across all eukaryotes <ref name="Bai">DOI: 10.1038/nature14549</ref>. SCD-1 is expressed in Mus musculus. The human homolog, SCD1, shares 85% sequence identity with all four SCD’s found in M. musculus (Scd1-Scd4). The expression of SCD is seen mainly in the liver and brain <ref name="Dobrzyn">PMID: 31284458</ref>. | ||
| - | SCD is an enzyme which catalyzes desaturation of a double bond within a fatty acid hydrocarbon chain. The addition of a double bond is necessary for the biosynthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids such as: cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides. The enzyme’s main function is [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipid_metabolism#:~:text=%2B-,Lipid%20biosynthesis,the%20organisms%20through%20various%20pathways. lipid biosynthesis] as well as regulating gene expression for | + | SCD is an enzyme which catalyzes desaturation of a double bond within a fatty acid hydrocarbon chain. The addition of a double bond is necessary for the biosynthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids such as: cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides. The enzyme’s main function is [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipid_metabolism#:~:text=%2B-,Lipid%20biosynthesis,the%20organisms%20through%20various%20pathways. lipid biosynthesis] as well as regulating gene expression for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipogenesis#:~:text=Lipogenesis%20is%20the%20metabolic%20process,packaged%20within%20cytoplasmic%20lipid%20droplets. lipogensis] <ref name="Bai" />. SCD is regulated by transcription and its promoter has multiple binding sites for transcription factors that assist in regulation of lipogenesis <ref name="Dobrzyn" />. It was discovered that when M. musculus were SCD-deficient, there was no obesity seen in the mice <ref name="Bai" /> This is why SCD is a popular target in treating metabolic diseases. Functioning SCD creates the balance between the accumulation and use of fats in the body. |
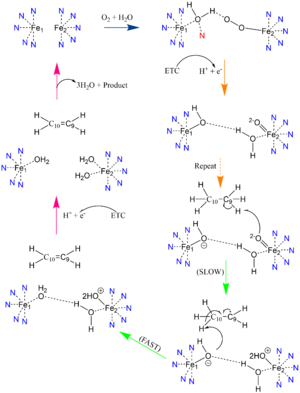
SCD-1 is interacts with either of the two different substrates: [https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/94140 stearoyl-CoA] or [https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/644109 palmitoyl-CoA]. When SCD interacts with stearoyl-CoA and performs desaturation, the product is [https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Oleoyl-CoA oleoyl-CoA]and has the first cis-double bond introduced into the fatty acid chain. The introduction of the cis-double bond into the hydrocarbon chain will increase fluidity of the lipid bilayer. The process of desaturation is tightly regulated by multiple transcription factors. | SCD-1 is interacts with either of the two different substrates: [https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/94140 stearoyl-CoA] or [https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/644109 palmitoyl-CoA]. When SCD interacts with stearoyl-CoA and performs desaturation, the product is [https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Oleoyl-CoA oleoyl-CoA]and has the first cis-double bond introduced into the fatty acid chain. The introduction of the cis-double bond into the hydrocarbon chain will increase fluidity of the lipid bilayer. The process of desaturation is tightly regulated by multiple transcription factors. | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 21 April 2021
Desaturation of Fatty Stearoyl-CoA by SCD
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Bai Y, McCoy JG, Levin EJ, Sobrado P, Rajashankar KR, Fox BG, Zhou M. X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Nature. 2015 Jun 22. doi: 10.1038/nature14549. PMID:26098370 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14549
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Tracz-Gaszewska Z, Dobrzyn P. Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 as a Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 5;11(7). pii: cancers11070948. doi:, 10.3390/cancers11070948. PMID:31284458 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070948
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Shen J, Wu G, Tsai AL, Zhou M. Structure and Mechanism of a Unique Diiron Center in Mammalian Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. J Mol Biol. 2020 May 27. pii: S0022-2836(20)30367-3. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017. PMID:32470559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017
- ↑ Wang H, Klein MG, Zou H, Lane W, Snell G, Levin I, Li K, Sang BC. Crystal structure of human stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase in complex with substrate. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Jul;22(7):581-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3049. Epub 2015 Jun , 22. PMID:26098317 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.3049
- ↑ Holder AM, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Chen H, Akcakanat A, Do KA, Fraser Symmans W, Pusztai L, Hortobagyi GN, Mills GB, Meric-Bernstam F. High stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 expression is associated with shorter survival in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jan;137(1):319-27. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2354-4. , Epub 2012 Dec 4. PMID:23208590 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2354-4
- ↑ Li J, Condello S, Thomes-Pepin J, Ma X, Xia Y, Hurley TD, Matei D, Cheng JX. Lipid Desaturation Is a Metabolic Marker and Therapeutic Target of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Mar 2;20(3):303-314.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.004., Epub 2016 Dec 29. PMID:28041894 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.004
Student Contributors
- Brianna M. Avery
- William J. Harris III
- Emily M. Royston