User:Betsy Johns/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | [[Image:Screen_Shot_2021-04-05_at_7.21.43_PM.png| | + | [[Image:Screen_Shot_2021-04-05_at_7.21.43_PM.png|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 1: DGAT Structure Overview''' Shown is one transmembrane subunit of DGAT with its N-terminus on the cytosolic side and its C-terminus on the luminal side. Labeled are the transmembrane domains (TM 1-7), the intracellular loops (IL1 and IL2), and the ER lumenal loop (EL1). The catalytic Histidine (His415) is labeled with a star on TM7.]] |
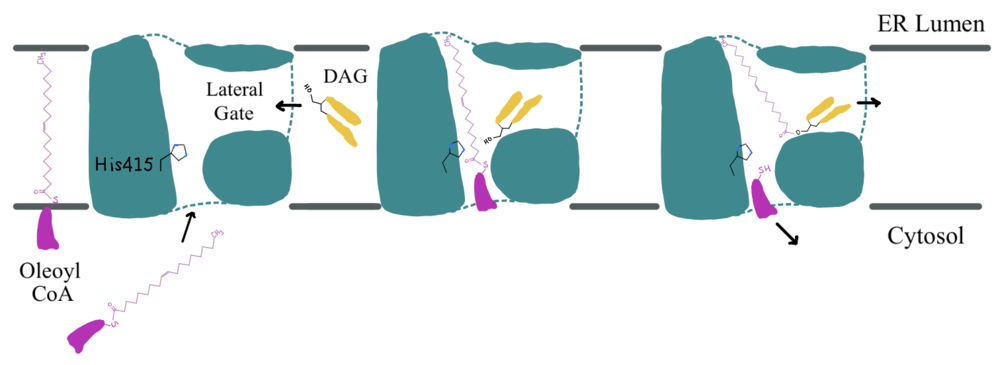
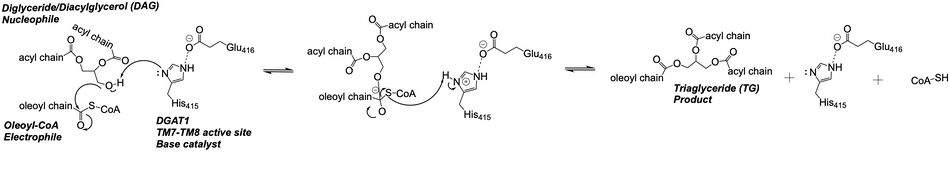
DGAT is a dimer that has two identical <scene name='87/877512/Labeled_subunits/1'>subunits</scene>. Each of the individual subunits contains an MBOAT core that acts as its active site. Each subunit also contains <scene name='87/877515/Labeled_helices/3'>nine transmembrane helices</scene> (TM), 2 intracellular loops (IL), and one ER lumenal loop (EL). TM2-9, IL1, and IL2 form the structure of the MBOAT core active site. A schematic of DGAT’s structure is shown in Figure 1. | DGAT is a dimer that has two identical <scene name='87/877512/Labeled_subunits/1'>subunits</scene>. Each of the individual subunits contains an MBOAT core that acts as its active site. Each subunit also contains <scene name='87/877515/Labeled_helices/3'>nine transmembrane helices</scene> (TM), 2 intracellular loops (IL), and one ER lumenal loop (EL). TM2-9, IL1, and IL2 form the structure of the MBOAT core active site. A schematic of DGAT’s structure is shown in Figure 1. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
=== Dimer Interface === | === Dimer Interface === | ||
| - | |||
| - | The DGAT dimer is held together at the dimer interface by both hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions between the residues of the TM1 and EL1 regions | ||
| - | |||
DGAT is a dimer that has two identical subunits with 9 transmembrane alpha helices (TM), 2 intracellular loops (IL), and one ER luminal loop (EL). The dimer is held together at the <scene name='87/877515/Dimer-interface/3'>dimer interface</scene>. Both <scene name='87/877515/Dimer_interface/5'>hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions</scene> between the residues of the TM1 and EL1 regions of both subunits act to hold the subunits of the dimer together. | DGAT is a dimer that has two identical subunits with 9 transmembrane alpha helices (TM), 2 intracellular loops (IL), and one ER luminal loop (EL). The dimer is held together at the <scene name='87/877515/Dimer-interface/3'>dimer interface</scene>. Both <scene name='87/877515/Dimer_interface/5'>hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions</scene> between the residues of the TM1 and EL1 regions of both subunits act to hold the subunits of the dimer together. | ||
Revision as of 01:42, 23 April 2021
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase, DGAT, synthesizes triacylglycerides
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Wang L, Qian H, Nian Y, Han Y, Ren Z, Zhang H, Hu L, Prasad BVV, Laganowsky A, Yan N, Zhou M. Structure and mechanism of human diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):329-332. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433610 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sui X, Wang K, Gluchowski NL, Elliott SD, Liao M, Walther TC, Farese RV Jr. Structure and catalytic mechanism of a human triacylglycerol-synthesis enzyme. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):323-328. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433611 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Ma D, Wang Z, Merrikh CN, Lang KS, Lu P, Li X, Merrikh H, Rao Z, Xu W. Crystal structure of a membrane-bound O-acyltransferase. Nature. 2018 Oct;562(7726):286-290. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0568-2. Epub 2018 Oct, 3. PMID:30283133 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0568-2
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Denison H, Nilsson C, Lofgren L, Himmelmann A, Martensson G, Knutsson M, Al-Shurbaji A, Tornqvist H, Eriksson JW. Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 inhibition with AZD7687 alters lipid handling and hormone secretion in the gut with intolerable side effects: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Apr;16(4):334-43. doi: 10.1111/dom.12221. Epub 2013 Oct, 31. PMID:24118885 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dom.12221
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Stephen J, Vilboux T, Haberman Y, Pri-Chen H, Pode-Shakked B, Mazaheri S, Marek-Yagel D, Barel O, Di Segni A, Eyal E, Hout-Siloni G, Lahad A, Shalem T, Rechavi G, Malicdan MC, Weiss B, Gahl WA, Anikster Y. Congenital protein losing enteropathy: an inborn error of lipid metabolism due to DGAT1 mutations. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016 Aug;24(9):1268-73. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2016.5. Epub 2016 Feb , 17. PMID:26883093 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.5
- ↑ Rebello CJ, Greenway FL. Obesity medications in development. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020 Jan;29(1):63-71. doi:, 10.1080/13543784.2020.1705277. Epub 2019 Dec 19. PMID:31847611 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2020.1705277
- ↑ Scott SA, Mathews TP, Ivanova PT, Lindsley CW, Brown HA. Chemical modulation of glycerolipid signaling and metabolic pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Aug;1841(8):1060-84. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 15. PMID:24440821 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.01.009
Student Contributors
- Betsy Johns
- Elise Wang
- Tyler Bihasa