We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Kaitlyn Roberts/Sandbox 2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
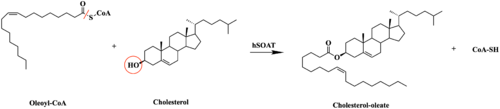
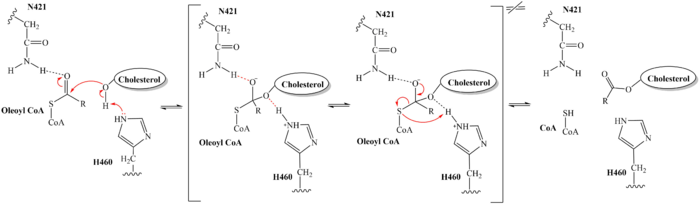
[[Image:SOATfirstreaction.png|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Esterification Reaction of Oleoyl-CoA and Cholesterol catalyzed by SOAT]] Sterol O-acyltransferase(SOAT), otherwise known as Acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase(ACAT), is the first discovered member of the membrane-bound O-acyl [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transferase transferase] or MBOAT enzyme group. MBOAT enzymes are responsible for the transfer of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyl_group acyl chains] onto multiple types of substrates within the cell. There are 11 MBOAT enzyme types that can be found in humans, all of which serve a different function in the overall makeup of human biology.<ref name="Guan">PMID:32424158</ref> | [[Image:SOATfirstreaction.png|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Esterification Reaction of Oleoyl-CoA and Cholesterol catalyzed by SOAT]] Sterol O-acyltransferase(SOAT), otherwise known as Acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase(ACAT), is the first discovered member of the membrane-bound O-acyl [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transferase transferase] or MBOAT enzyme group. MBOAT enzymes are responsible for the transfer of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyl_group acyl chains] onto multiple types of substrates within the cell. There are 11 MBOAT enzyme types that can be found in humans, all of which serve a different function in the overall makeup of human biology.<ref name="Guan">PMID:32424158</ref> | ||
| - | SOAT specifically catalyzes the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fischer–Speier_esterification esterification] of cholesterol for efficient storage within the cell. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesterol Cholesterol] is a type of membrane lipid that is responsible for controlling the fluidity and integrity of the membrane, | + | SOAT specifically catalyzes the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fischer–Speier_esterification esterification] of cholesterol for efficient storage within the cell. [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesterol Cholesterol] is a type of membrane lipid that is responsible for controlling the fluidity and integrity of the membrane, along with other important biological processes. When there are high concentrations of cholesterol in the cell, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesteryl_ester cholesteryl esters] can be formed for storage within the membrane.<ref name="Guan" /> |
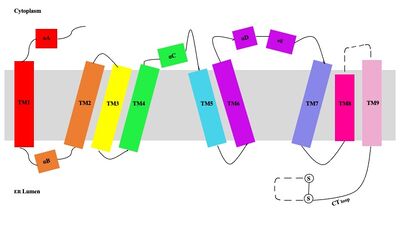
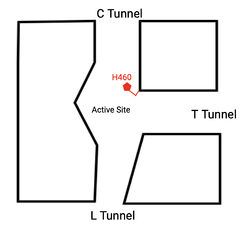
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
Revision as of 03:18, 23 April 2021
Human Sterol O-acyltransferase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bhattacharyya R, Kovacs DM. ACAT inhibition and amyloid beta reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1801(8):960-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.04.003. , Epub 2010 Apr 14. PMID:20398792 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.04.003
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Huttunen HJ, Kovacs DM. ACAT as a drug target for Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegener Dis. 2008;5(3-4):212-4. doi: 10.1159/000113705. Epub 2008 Mar 6. PMID:18322393 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000113705
- ↑ Chang C, Dong R, Miyazaki A, Sakashita N, Zhang Y, Liu J, Guo M, Li BL, Chang TY. Human acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) and its potential as a target for pharmaceutical intervention against atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2006 Mar;38(3):151-6. doi:, 10.1111/j.1745-7270.2006.00154.x. PMID:16518538 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2006.00154.x
- ↑ Ayyagari VN, Wang X, Diaz-Sylvester PL, Groesch K, Brard L. Assessment of acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT-1) role in ovarian cancer progression-An in vitro study. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0228024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228024., eCollection 2020. PMID:31978092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228024
Student Contributors
- Kylie Pfeifer
- Stephanie Pellegrino
- Kaitlyn Roberts