User:Sarah Maarouf/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
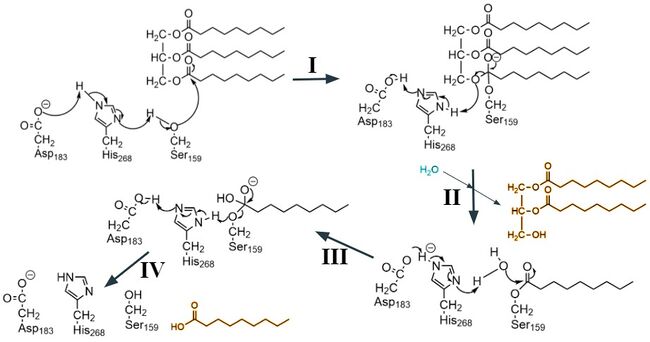
<scene name='87/877554/Lpl_w_gpihbp1/4'>Lipoprotein lipase (LPL)</scene> is an enzyme synthesized and secreted primarily by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myocyte myocytes] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocyte adipocytes] into interstitial spaces.<ref name = "Fong">PMID: 27185325</ref> It is located on the surface of capillaries where it is bound to a glycolipid-anchored protein expressed by capillary endothelial cells. This protein is called glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1, or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPIHBP1 GPIHBP1].<ref name="Voss">PMID:21518912</ref>. LPL is an essential enzyme for triglyceride metabolism and utilization, however it is susceptible to unfolding in its catalytic domain and thus must be bound to GPIHBP1 to prevent loss of enzymatic activity. When LPL is not bound to GPIHBP1 its enzymatic activity is relatively low and declines until it has lost all function, but when bound to GPIHBP1 it is able to maintain its maximum enzymatic activity.<ref name="Arora">PMID:31072929</ref> In addition, binding to GPIHBP1 is required for adhesion of [https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/triglyceride-rich-lipoprotein#:~:text=Triglyceride%2Drich%20lipoproteins%20are%20secreted,phospholipid%20monolayer%20with%20associated%20apolipoproteins triglyceride rich lipoproteins (TRLs)] to LPL and transport of LPL to its site of action in the capillary lumen. Once it has reached the site of action the enzyme is able to produce a monoglyceride and two fatty acids from the triglyceride substrate (Figure 1).<ref name="Young">PMID:31269429</ref> | <scene name='87/877554/Lpl_w_gpihbp1/4'>Lipoprotein lipase (LPL)</scene> is an enzyme synthesized and secreted primarily by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Myocyte myocytes] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adipocyte adipocytes] into interstitial spaces.<ref name = "Fong">PMID: 27185325</ref> It is located on the surface of capillaries where it is bound to a glycolipid-anchored protein expressed by capillary endothelial cells. This protein is called glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1, or [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPIHBP1 GPIHBP1].<ref name="Voss">PMID:21518912</ref>. LPL is an essential enzyme for triglyceride metabolism and utilization, however it is susceptible to unfolding in its catalytic domain and thus must be bound to GPIHBP1 to prevent loss of enzymatic activity. When LPL is not bound to GPIHBP1 its enzymatic activity is relatively low and declines until it has lost all function, but when bound to GPIHBP1 it is able to maintain its maximum enzymatic activity.<ref name="Arora">PMID:31072929</ref> In addition, binding to GPIHBP1 is required for adhesion of [https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/triglyceride-rich-lipoprotein#:~:text=Triglyceride%2Drich%20lipoproteins%20are%20secreted,phospholipid%20monolayer%20with%20associated%20apolipoproteins triglyceride rich lipoproteins (TRLs)] to LPL and transport of LPL to its site of action in the capillary lumen. Once it has reached the site of action the enzyme is able to produce a monoglyceride and two fatty acids from the triglyceride substrate (Figure 1).<ref name="Young">PMID:31269429</ref> | ||
| - | |||
Revision as of 17:44, 23 April 2021
H. sapiens Lipoprotein Lipase in complex with GPIHBP1 and triglyceride metabolism
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Fong LG, Young SG, Beigneux AP, Bensadoun A, Oberer M, Jiang H, Ploug M. GPIHBP1 and Plasma Triglyceride Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Jul;27(7):455-469. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.04.013. , Epub 2016 May 14. PMID:27185325 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2016.04.013
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Voss CV, Davies BS, Tat S, Gin P, Fong LG, Pelletier C, Mottler CD, Bensadoun A, Beigneux AP, Young SG. Mutations in lipoprotein lipase that block binding to the endothelial cell transporter GPIHBP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 10;108(19):7980-4. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1100992108. Epub 2011 Apr 25. PMID:21518912 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1100992108
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Arora R, Nimonkar AV, Baird D, Wang C, Chiu CH, Horton PA, Hanrahan S, Cubbon R, Weldon S, Tschantz WR, Mueller S, Brunner R, Lehr P, Meier P, Ottl J, Voznesensky A, Pandey P, Smith TM, Stojanovic A, Flyer A, Benson TE, Romanowski MJ, Trauger JW. Structure of lipoprotein lipase in complex with GPIHBP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 21;116(21):10360-10365. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1820171116. Epub 2019 May 9. PMID:31072929 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820171116
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Young SG, Fong LG, Beigneux AP, Allan CM, He C, Jiang H, Nakajima K, Meiyappan M, Birrane G, Ploug M. GPIHBP1 and Lipoprotein Lipase, Partners in Plasma Triglyceride Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2019 Jul 2;30(1):51-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.05.023. PMID:31269429 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.05.023
- ↑ Olivecrona G. Role of lipoprotein lipase in lipid metabolism. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2016 Jun;27(3):233-41. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000297. PMID:27031275 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MOL.0000000000000297
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Birrane G, Beigneux AP, Dwyer B, Strack-Logue B, Kristensen KK, Francone OL, Fong LG, Mertens HDT, Pan CQ, Ploug M, Young SG, Meiyappan M. Structure of the lipoprotein lipase-GPIHBP1 complex that mediates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 17. pii: 1817984116. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1817984116. PMID:30559189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1817984116
Student Contributors
- Aniyah Coles
- Sarah Maarouf
- Audrey Marjamaa

![Figure 2. A cartoon representation of GPIHBP1's N-terminal intrinsically disordered region (IDR) colored green and an surface representation of LPL with electrostatic coloring [acidic (red), neutral (white), basic (blue)] to show how GPIHBP1's N-terminal domain interacts with LPL's basic patch to stabilize LPL structure and activity.](/wiki/images/thumb/7/72/Electro.jpg/250px-Electro.jpg)