We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Jacob Holt/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Biological Relevance == | == Biological Relevance == | ||
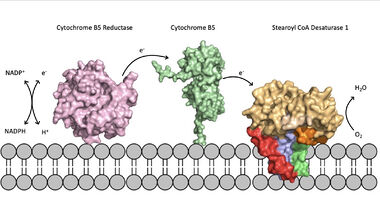
| - | [[Image:scd_in_membrane.jpeg|380 px|thumb|left|Figure 2. Position of SCD within the biological membrane. It is part of an electron transport chain involving cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome b5 to allow for the activation of the catalytic molecule coordinated by the two ions in the center of SCD.]] | + | [[Image:scd_in_membrane.jpeg|380 px|thumb|left|Figure 2. Position of SCD within the biological membrane. It is part of an electron transport chain involving cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome b5 to allow for the activation of the catalytic molecule coordinated by the two ions in the center of SCD.]]Absence or a deficit of SCD1 in the body is associated with obesity and insulin resistant which is a main cause of Type II diabetes [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes type 2 diabetes]<ref name="Shen" />. Cancer sites in the body tend to show a much higher expression rate of SCD1<ref name="Shen" />. Focusing on SCD1 as a drug target could lead to advancements in treatment of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic diseases<ref name="Bai" />. The ligand structure was determined by using Zn2+ metal ions and product structure was determined using Fe2+ ions<ref name="Shen" />. |
| - | Absence or a deficit of SCD1 in the body is associated with obesity and insulin resistant which is a main cause of Type II diabetes [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes type 2 diabetes]<ref name="Shen" />. Cancer sites in the body tend to show a much higher expression rate of SCD1<ref name="Shen" />. Focusing on SCD1 as a drug target could lead to advancements in treatment of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic diseases<ref name="Bai" />. The ligand structure was determined by using Zn2+ metal ions and product structure was determined using Fe2+ ions<ref name="Shen" />. | + | |
== Structural Overview == | == Structural Overview == | ||
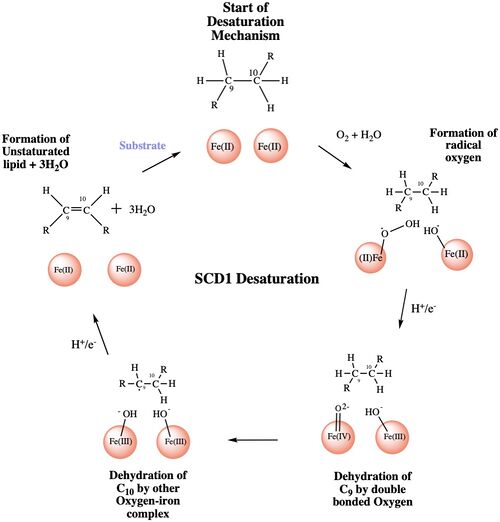
| - | SCD1 is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmembrane protein transmembrane protein] (4 helices in membrane, 8 helices in cytoplasm) that acquires electrons via an electron transport chain which includes [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytochrome_b5_reductase cytochrome b5 reductase] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytochrome_b5 cytochrome b5] . The electrons are transferred via a ternary complex and accepted by SCD1 by the iron metal ions<ref name="Shen" />. SCD1 has 8 helices that are hydrophobic, 4 helices that are hydrophilic, and 3 helices that are amphipathic<ref name="Bai" /><ref name="Shen" />. There are two Fe+2 metal ions within the structure of SCD1 that were determined by x-ray fluorescence chromatography [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_fluorescence x-ray fluorescense]<ref name="Shen" />. | ||
| - | [[Image:colorful2.jpg|200 px|thumb|left|Figure 3. Hydrophobicity of each of the 12 helices found in SCD. red, blue, yellow, and green represent helices found in the transmembrane region. Orange helices represent helices found on the surface of the membrane. Pale yellow helices represent the hydrophilic helices.]] [[Image:colored_helices.jpg|420 px|right|thumb|Figure 4. Colored helices based on hydrophobicity. Red, green, yellow, and blue represent the transmembrane helices. Orange represents the helices found on the surface of the membrane, and tan represents the helices found in the cytoplasm.]] | + | SCD1 is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmembrane protein transmembrane protein] (4 helices in membrane, 8 helices in cytoplasm) that acquires electrons via an electron transport chain which includes [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytochrome_b5_reductase cytochrome b5 reductase] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytochrome_b5 cytochrome b5] . The electrons are transferred via a ternary complex and accepted by SCD1 by the iron metal ions<ref name="Shen" />. SCD1 has 8 helices that are hydrophobic, 4 helices that are hydrophilic, and 3 helices that are amphipathic<ref name="Bai" /><ref name="Shen" />. There are two Fe+2 metal ions within the structure of SCD1 that were determined by x-ray fluorescence chromatography [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X-ray_fluorescence x-ray fluorescense]<ref name="Shen" />. [[Image:colorful2.jpg|200 px|thumb|left|Figure 3. Hydrophobicity of each of the 12 helices found in SCD. red, blue, yellow, and green represent helices found in the transmembrane region. Orange helices represent helices found on the surface of the membrane. Pale yellow helices represent the hydrophilic helices.]] [[Image:colored_helices.jpg|420 px|right|thumb|Figure 4. Colored helices based on hydrophobicity. Red, green, yellow, and blue represent the transmembrane helices. Orange represents the helices found on the surface of the membrane, and tan represents the helices found in the cytoplasm.]] |
=== Ligand Binding Pocket === | === Ligand Binding Pocket === | ||
Revision as of 21:01, 23 April 2021
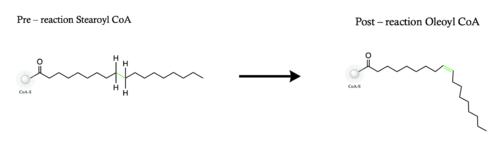
Desaturation of Fatty Acids using Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 Enzyme
| |||||||||||
Student Contributions
Carson Maris, Jess Kersey, Jacob Holt