We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Jacob Holt/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
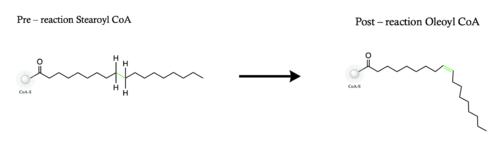
[[Image:Screenshot.png|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Overall reaction completed by the SCD1 enzyme. It introduces a double bond between carbons 9 and 10 on the ligand Stearoyl CoA, converting it into Oleoyl CoA]]Stearyol CoA Desaturase (SCD1) functions as a lipogenic enzyme which is essential for fatty acid metabolism. SCD1 desaturates the sigma bond, within the 18-carbon acyl-CoA ligand, that attaches carbons 9 and 10<ref name="Bai">PMID: 26098370 </ref>. The primary role of SCD1 is to catalyze the biosynthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) via saturated [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyl-CoA acyl-CoAs] with an acyl chain length of 14-19 carbons<ref name="Paton">PMID: 19066317 </ref><ref name="Shen">PMID: 32470559 </ref>. Variations of the monounsaturated fatty acids function as precursors for the biosynthesis of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipid phospholipids], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesteryl_ester cholesteryl esters], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides]; therefore, SCD1 is a promising candidate for drug targeting<ref name="Bai" />. | [[Image:Screenshot.png|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Overall reaction completed by the SCD1 enzyme. It introduces a double bond between carbons 9 and 10 on the ligand Stearoyl CoA, converting it into Oleoyl CoA]]Stearyol CoA Desaturase (SCD1) functions as a lipogenic enzyme which is essential for fatty acid metabolism. SCD1 desaturates the sigma bond, within the 18-carbon acyl-CoA ligand, that attaches carbons 9 and 10<ref name="Bai">PMID: 26098370 </ref>. The primary role of SCD1 is to catalyze the biosynthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) via saturated [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acyl-CoA acyl-CoAs] with an acyl chain length of 14-19 carbons<ref name="Paton">PMID: 19066317 </ref><ref name="Shen">PMID: 32470559 </ref>. Variations of the monounsaturated fatty acids function as precursors for the biosynthesis of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipid phospholipids], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesteryl_ester cholesteryl esters], and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides]; therefore, SCD1 is a promising candidate for drug targeting<ref name="Bai" />. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | == Biological Relevance == | ||
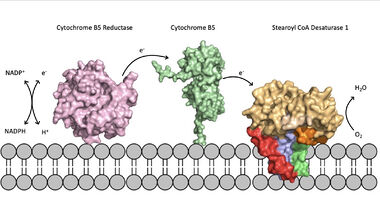
| - | [[Image:scd_in_membrane.jpeg|380 px|thumb|left|Figure 2. Position of SCD within the biological membrane. It is part of an electron transport chain involving cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome b5 to allow for the activation of the catalytic molecule coordinated by the two ions in the center of SCD.]]Absence or a deficit of SCD1 in the body is associated with obesity and insulin resistant which is a main cause of Type II diabetes [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes type 2 diabetes]<ref name="Shen" />. Cancer sites in the body tend to show a much higher expression rate of SCD1<ref name="Shen" />. Focusing on SCD1 as a drug target could lead to advancements in treatment of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic diseases<ref name="Bai" />. The ligand structure was determined by using Zn2+ metal ions and product structure was determined using Fe2+ ions<ref name="Shen" />. | ||
== Structural Overview == | == Structural Overview == | ||
| Line 43: | Line 39: | ||
The main function of SCD1 is to create the desaturated ligand that is used in the synthesis of cholesterol esters and triglycerides<ref name="Shen" />. Based on this main function it has been confirmed that insulin and carbohydrate metabolism play a major role in the regulation of SCD1<ref name="Ntambi">PMID: 7480063</ref>. Along with insulin many other hormones have shown positive regulation of the SCD1 enzyme including T3, estradiol, and dexamethasone<ref name="Ntambi" />. The carbohydrate metabolism can be altered by eating a fat-free, high carbohydrate diet with an increased intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids<ref name="Ntambi" />. The will negatively regulate the mRNA expression of the SCD1 enzyme in the liver because high amounts of carbohydrates and polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease/inhibit the activity of the SCD1 enzyme<ref name="Ntambi" />. | The main function of SCD1 is to create the desaturated ligand that is used in the synthesis of cholesterol esters and triglycerides<ref name="Shen" />. Based on this main function it has been confirmed that insulin and carbohydrate metabolism play a major role in the regulation of SCD1<ref name="Ntambi">PMID: 7480063</ref>. Along with insulin many other hormones have shown positive regulation of the SCD1 enzyme including T3, estradiol, and dexamethasone<ref name="Ntambi" />. The carbohydrate metabolism can be altered by eating a fat-free, high carbohydrate diet with an increased intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids<ref name="Ntambi" />. The will negatively regulate the mRNA expression of the SCD1 enzyme in the liver because high amounts of carbohydrates and polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease/inhibit the activity of the SCD1 enzyme<ref name="Ntambi" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Biological Relevance == | ||
| + | [[Image:scd_in_membrane.jpeg|380 px|thumb|left|Figure 2. Position of SCD within the biological membrane. It is part of an electron transport chain involving cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome b5 to allow for the activation of the catalytic molecule coordinated by the two ions in the center of SCD.]]Absence or a deficit of SCD1 in the body is associated with obesity and insulin resistant which is a main cause of Type II diabetes [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Type_2_diabetes type 2 diabetes]<ref name="Shen" />. Cancer sites in the body tend to show a much higher expression rate of SCD1<ref name="Shen" />. Focusing on SCD1 as a drug target could lead to advancements in treatment of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic diseases<ref name="Bai" />. The ligand structure was determined by using Zn2+ metal ions and product structure was determined using Fe2+ ions<ref name="Shen" />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 21:03, 23 April 2021
Desaturation of Fatty Acids using Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 Enzyme
| |||||||||||
Student Contributions
Carson Maris, Jess Kersey, Jacob Holt