We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Kaitlyn Roberts/Sandbox 2
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Inhibitors == | == Inhibitors == | ||
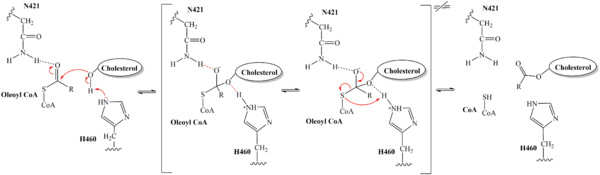
| - | SOAT activity is inhibited by CI-976, depending on the concentration and exposure of the inhibitor to the SOAT enzyme. When exposed, CI-976 locks itself in the <scene name='87/877559/Active_site_overview/1'>catalytic center</scene> of the enzyme. The trimethoxyphenyl head can be found interacting with the catalytic residues <scene name='87/877559/Residues_and_inhibitor/17'>H460, W420, and N421</scene>. The interactions with these residues as well as the location of the trimethoxyphenol head indicate that CI-976 inhibits the SOAT enzyme in a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Competitive_inhibition competitive manner]by preventing the | + | SOAT activity is inhibited by CI-976, depending on the concentration and exposure of the inhibitor to the SOAT enzyme. When exposed, CI-976 locks itself in the <scene name='87/877559/Active_site_overview/1'>catalytic center</scene> of the enzyme. The trimethoxyphenyl head can be found interacting with the catalytic residues <scene name='87/877559/Residues_and_inhibitor/17'>H460, W420, and N421</scene>. The interactions with these residues as well as the location of the trimethoxyphenol head indicate that CI-976 inhibits the SOAT enzyme in a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Competitive_inhibition competitive manner]by preventing the substrates from entering the catalytic center via the tunnel system. Similar to the interactions with the substrates, mutating those key catalytic residues, N421A, H460A, and H460N, result in a smaller effect of the inhibitor on the thermostability of the enzyme. <ref name="Guan" /> |
== Biological Relevance == | == Biological Relevance == | ||
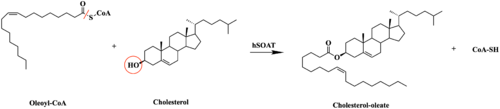
SOAT can actually use multiple sterols as substrates and activators. Because of its functional importance, SOAT is a potential drug target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer%27s_disease Alzheimer’s disease], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atherosclerosis atherosclerosis], and several types of cancers. | SOAT can actually use multiple sterols as substrates and activators. Because of its functional importance, SOAT is a potential drug target for [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alzheimer%27s_disease Alzheimer’s disease], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atherosclerosis atherosclerosis], and several types of cancers. | ||
| - | Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive disease that severely hinders a person’s memory and other cognitive functions. AD is the result of a significant increase in beta-amyloid (Aβ) peptide concentration. <ref name="Bhattacharyya">PMID:20398792</ref> Previous studies have found that the amount and distribution of intracellular cholesterol plays an important role in regulating Aβ production.<ref name="Huttunen">PMID:18322393</ref> Therefore, SOAT inhibition could be an effective therapy for treating AD because it would reduce cholesteryl ester formation in the brain and help lower Aβ generation as well. <ref name="Bhattacharyya" /> <ref name="Huttunen" /> | + | Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive disease that severely hinders a person’s memory and other cognitive functions. AD is the result of a significant increase in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amyloid_beta beta-amyloid] (Aβ) peptide concentration. <ref name="Bhattacharyya">PMID:20398792</ref> Previous studies have found that the amount and distribution of intracellular cholesterol plays an important role in regulating Aβ production.<ref name="Huttunen">PMID:18322393</ref> Therefore, SOAT inhibition could be an effective therapy for treating AD because it would reduce cholesteryl ester formation in the brain and help lower Aβ generation as well. <ref name="Bhattacharyya" /> <ref name="Huttunen" /> |
Another disease SOAT inhibition could help treat is atherosclerosis. Buildup of cholesteryl esters from SOAT catalysis has been shown to be partially responsible for foam cell formation, one of the major indicators of atherosclerosis. Consequently, SOAT inhibitors have been studied as potential drug targets for this disease.<ref name="Chang">PMID:16518538</ref> | Another disease SOAT inhibition could help treat is atherosclerosis. Buildup of cholesteryl esters from SOAT catalysis has been shown to be partially responsible for foam cell formation, one of the major indicators of atherosclerosis. Consequently, SOAT inhibitors have been studied as potential drug targets for this disease.<ref name="Chang">PMID:16518538</ref> | ||
Increased expression of SOAT and abnormal accumulation of cholesteryl esters has also been found in multiple cancers including ovarian cancer. Therefore, inhibiting SOAT and exhausting cholesteryl ester concentrations has shown to have anti-tumor effects in terms of monitoring apoptosis, cell proliferation, and migration and invasion properties. Therapies that target SOAT regulation and expression levels could thus lead to potential treatments for ovarian and other types of cancer.<ref name="Ayyagari">PMID:31978092</ref> | Increased expression of SOAT and abnormal accumulation of cholesteryl esters has also been found in multiple cancers including ovarian cancer. Therefore, inhibiting SOAT and exhausting cholesteryl ester concentrations has shown to have anti-tumor effects in terms of monitoring apoptosis, cell proliferation, and migration and invasion properties. Therapies that target SOAT regulation and expression levels could thus lead to potential treatments for ovarian and other types of cancer.<ref name="Ayyagari">PMID:31978092</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 25 April 2021
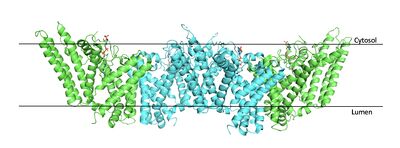
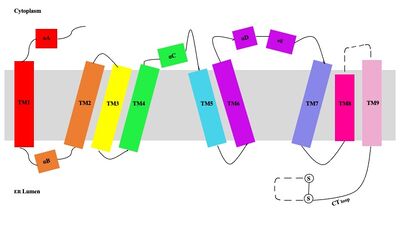
Human Sterol O-acyltransferase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Guan C, Niu Y, Chen SC, Kang Y, Wu JX, Nishi K, Chang CCY, Chang TY, Luo T, Chen L. Structural insights into the inhibition mechanism of human sterol O-acyltransferase 1 by a competitive inhibitor. Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2478. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4. PMID:32424158 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-16288-4
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Qian H, Zhao X, Yan R, Yao X, Gao S, Sun X, Du X, Yang H, Wong CCL, Yan N. Structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of human ACAT1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):333-338. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433614 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2290-0
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Bhattacharyya R, Kovacs DM. ACAT inhibition and amyloid beta reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1801(8):960-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.04.003. , Epub 2010 Apr 14. PMID:20398792 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.04.003
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Huttunen HJ, Kovacs DM. ACAT as a drug target for Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegener Dis. 2008;5(3-4):212-4. doi: 10.1159/000113705. Epub 2008 Mar 6. PMID:18322393 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1159/000113705
- ↑ Chang C, Dong R, Miyazaki A, Sakashita N, Zhang Y, Liu J, Guo M, Li BL, Chang TY. Human acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) and its potential as a target for pharmaceutical intervention against atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2006 Mar;38(3):151-6. doi:, 10.1111/j.1745-7270.2006.00154.x. PMID:16518538 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2006.00154.x
- ↑ Ayyagari VN, Wang X, Diaz-Sylvester PL, Groesch K, Brard L. Assessment of acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT-1) role in ovarian cancer progression-An in vitro study. PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0228024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228024., eCollection 2020. PMID:31978092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0228024
Student Contributors
- Kylie Pfeifer
- Stephanie Pellegrino
- Kaitlyn Roberts