We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Maggie Stopa/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Relevance & Disease == | == Relevance & Disease == | ||
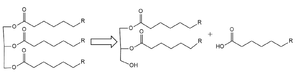
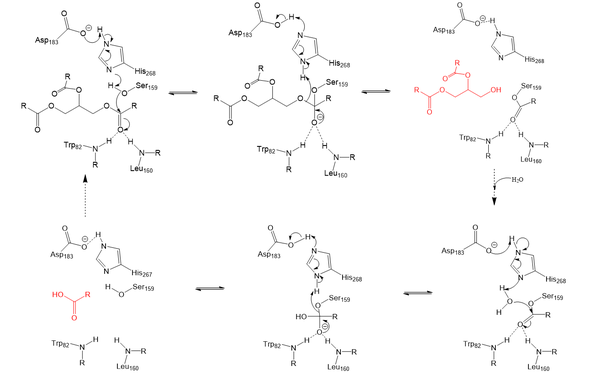
LPL is an extremely important enzyme, in that it is responsible for the proper breakdown of certain fats in the body. LPL breaks down triglycerides carried on very low-density lipoproteins ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Very_low-density_lipoprotein VLDL]), which eventually leads to the reduction of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesterol cholesterol] buildup. Cholesterol buildup is a very serious issue with regards to obesity and heart disease in the United States. In addition to this, increased plasma triglyceride levels ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertriglyceridemia hypertriglyceridemia]) is very unhealthy and is the leading cause of [https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16898-coronary-artery-disease Coronary Artery Disease] in America. LPL is an enzyme that helps combat this disease by breaking down the excess triglycerides that cause blockage in the arteries of your heart. Very similarly, [https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000405.htm Chylomicronemia], which is defined as an excess of chylomicrons in the blood, results in a buildup of triglycerides and leads to similar diseases. Chylomicrons, otherwise known as ultra-low-density lipoproteins, carry digested fats in the form of triglycerides out of the small intestine and into the bloodstream. LPL recognizes the chylomicrons, resulting in the hydrolysis of triglycerides. Without LPL in the body, triglycerides are unable to get broken down, and there is a much higher likelihood of developing coronary & metabolic (liver & pancreas) based diseases. | LPL is an extremely important enzyme, in that it is responsible for the proper breakdown of certain fats in the body. LPL breaks down triglycerides carried on very low-density lipoproteins ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Very_low-density_lipoprotein VLDL]), which eventually leads to the reduction of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cholesterol cholesterol] buildup. Cholesterol buildup is a very serious issue with regards to obesity and heart disease in the United States. In addition to this, increased plasma triglyceride levels ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertriglyceridemia hypertriglyceridemia]) is very unhealthy and is the leading cause of [https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/16898-coronary-artery-disease Coronary Artery Disease] in America. LPL is an enzyme that helps combat this disease by breaking down the excess triglycerides that cause blockage in the arteries of your heart. Very similarly, [https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000405.htm Chylomicronemia], which is defined as an excess of chylomicrons in the blood, results in a buildup of triglycerides and leads to similar diseases. Chylomicrons, otherwise known as ultra-low-density lipoproteins, carry digested fats in the form of triglycerides out of the small intestine and into the bloodstream. LPL recognizes the chylomicrons, resulting in the hydrolysis of triglycerides. Without LPL in the body, triglycerides are unable to get broken down, and there is a much higher likelihood of developing coronary & metabolic (liver & pancreas) based diseases. | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:M404_No_Mutation_copy.jpg|400 px|right|thumb|No Mutation Image]] | ||
| - | [[Image:M404ToR404Pymol_copy_2.jpg|400 px|right|thumb|Mutation Image]] | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 24: | ||
=== Calcium Ion Stabilization === | === Calcium Ion Stabilization === | ||
| - | + | <scene name='87/877513/Calcium_stabilization_-labeled/1'>calcium ion stabilization</scene> | |
=== Lid Region === | === Lid Region === | ||
| - | + | <scene name='87/877514/Lid_region_final/1'>Lid Region</scene> | |
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 15:24, 26 April 2021
Lipoprotein Lipase LPL
| |||||||||||