Introduction
LPL, lipoprotein lipase, is an enzyme that affects the breakdown of triglycerides which are carried from various organs to the blood by molecules called lipoproteins. LPL is found on the surface of cells lining the capillaries within muscles and fatty tissue.
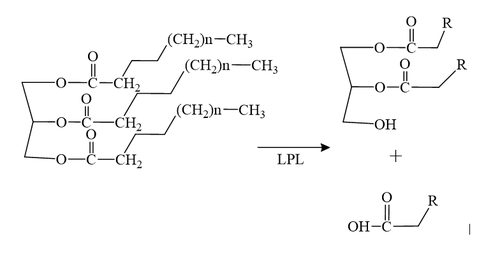
Figure 1: Conversion of triglyceride to diglyceride by LPL.
LPL was identified more than 60 years ago and studied by biochemists and physiologists intensely since. It wasn’t until recently that LPL’s detailed structure was determined due to LPL’s hydrolase domain susceptibility to unfolding. LMF1 and GPIHBP1, glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein–binding protein 1 ,were discovered to be required for proper folding and enzymatic activity of LPL. LMF1, lipase maturation factor 1, is a chaperone protein that is responsible for proper folding and secretion of LPL. Through the use of X-ray crystallography it was also discovered that LPL is a monomer rather than the previously believed homodimer.
Function
LPL is located within the interstitial space independently and remains stranded there if not acted upon by GPIHBP1. GPIHBP1 then captures LPL in the interstitial spaces and shuttles it across endothelial cells into the capillary lumen. Once in the capillaries, the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex catalyzes the breakdown of triglycerides in the blood. In doing so, it prevents high levels of triglycerides in the plasma to provide nutrients for vital tissues.
Significance
Lipoprotein lipase deficiency leads to hypertriglyceridemia (elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood) also known as chylomicronemia. This can go on to increase insulin resistance and risk of obesity.
Structure
Overall Structure
Overall, LPL is a monomer but biologically it is paired with another monomer. These are often referred two as . Chain A (shown as slate blue) and Chain B (shown as magenta) are identical besides orientation. Chain A and B are oriented head to tail. LPL is also complexed with GPIHBP1 (shown as cyan) and is essential for LPL to remain stable and avoid denaturation
LPL
LPL has two main domains, the larger N-terminus domain containing the active site and the smaller C-terminus domain. These two domains are connected via a peptide linker hinge. LPL also contains a large basic patch and a single calcium ion. Additionally, LPL consists of two N-linked glycans (N70, N386) which likely contribute to the correct folding of LPL due to the attached oligosaccharides. Five disulfide bonds contribute to the stabilization throughout LPL’s structure. Lastly, the active site in the larger N-terminus domain is lined with hydrophobic residues.
GPIHBP1
GPIHBP1 (glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high-density lipoprotein-binding protein 1) is a LU (Ly6/uPAR) domain. GPIHBP1 is stabilized by five disulfide bonds and is also known for its N-terminal intrinsically disordered acidic domain.
LPL GPIHBP1 complex
N-terminus of LPL
The N-terminus of LPL is made up of 6 α-helices and 10 β-strands known as the . Additionally, α/β hydrolase harbors the catalytic triad.
C-terminus of LPL
The C-terminus of LPL consists of 12 β-sheets and is known as the . The β-sheets are interacting giving a shape that resembles an elongated cylinder or barrel.
Interaction of LPL and GPIHBP1
GPIHBP1’s LU domain interacts with LPL’s C-terminal domain via . This is largely due to the hydrophobic effect and stabilization. The acidic N-terminal domain of GPIHBP1 (residues 21–61) is disordered and not visible in the structure, which is presumably due to dynamic interaction with the large basic patch on the LPL.
Calcium Ion Coordination
The calcium ion has been shown to convert inactive LPL to the active dimer form. The calcium ion is coordinated by residues A194, R197, S199, D201, and D202. Mutations in the side chain of D201, for example, can give rise to detrimental metabolic diseases. The crystal structures of LPL revealed that the carboxylic acid side chain of D201 significantly aids in the coordination of LPL with the calcium ion. If D201 is mutated to a valine, for example, LPL can no longer fold correctly, and thus, LPL secretion from cells is inhibited due to the loss of the carboxylic acid side chain.
Active Site
The of LPL is composed of multiple pieces. The to the binding site outlines the general structure and provides considerable stability to the active site. The is also an important component of the active site, occupying residues 243-266, which is vital for the recognition of substrates. The are H268, S159, and D183 which catalyze the reaction of the typical substrate of LPL, triglycerides. The oxyanion hole, consisting of residues L160, and W82, aids in the overall stability of the active site and the transition state of substrates. The main chain nitrogens stabilize the tetrahedral intermediate.
Mechanism
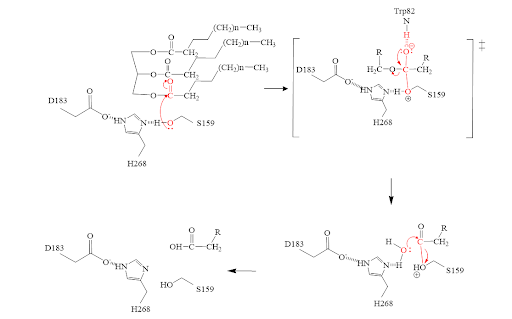
- The triglyceride binds to LPL’s lipid-binding region in an open lid conformation.
- The oxygen on S159 is made more nucleophilic. This happens via histidine hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen on S159’s alcohol group.
- The nucleophilic oxygen attacks the carbonyl carbon of one of the fatty acid chains.
- This pushes electrons up onto the carbonyl oxygen, creating a tetrahedral intermediate. This is the oxyanion hole which is stabilized by main chain nitrogen atoms of W82 and L160.
- One of the lone pairs of the oxygen (in the oxyanion hole) creates a double bond carbon.
- The oxygen-carbon bond between the single fatty acid chain and the diglyceride is cleaved.
- H268 hydrogen bonds water, making the oxygen a better nucleophile. Water attacks the carbonyl carbon.
- The carboxylic acid is formed and the S159 bond is cleaved and re-protonated via H268.
- The active site is now back in its original state.
Inhibitors
This , M3D shown in a peach color, was a vital piece in unraveling the correct structure of LPL. With the inhibitor bound, LPL’s active site and lid region become visible and crystallizable, thus this inhibitor is what allowed the first complete crystal structure of LPL to come into existence. This inhibitor also revealed the correct orientation of H268, a residue involved in the catalytic triad. Originally, the hydrogen bonding did not align with substrates in the original crystal structure; however, when this inhibitor was bound, the H268 was flipped, thus aligning the hydrogen bonds in the correct orientation.
Disease
Mutations
D201V
is a mutation that is found to cause chylomicronemia. Chylomicronemia is when the body cannot break down lipids properly. This leads to their build-up in the body causing high levels of triglycerides in the body. The carboxyl side chain of aspartate 201 is one of the coordination sites for the calcium ion of LPL. The mutation to hydrophobic valine means the loss of this coordination site[1]. This mutation adversely affects the folding of LPL and thus affects the secretion of LPL, overall decreasing the activity of LPL[1].
M404R
is a mutation found within LPL that caused chylomicronemia in patients. The hydrophobic methionine is mutated to the larger and charged side chain of arginine. Originally it was thought to impact LPL secretion from cells. It was found that the M404R does not affect LPL secretion [1]. M404R interacts with the hydrophobic pocket of GPIHBP1’s finger 3 of its 3 fingered domain (V121, E122, T124, V126). The large, charged arginine repelled the hydrophobic pocket and does not fit well. This prevents proper binding and formation of the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex [1].
Relevance
Hypertriglycerademia


