We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox GGC17
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
KRT 4 gene is going to provide enough information to create the protein Keratin 4. Keratins are the main groups for tough fibrous proteins that will form the framework of epithelial cells. Epithelial cells line up the surfaces and cavities intended for the body. Keratin 4 is usually found within the moist lining of your mouth, nose, esophagus, anus, and gentitals. | KRT 4 gene is going to provide enough information to create the protein Keratin 4. Keratins are the main groups for tough fibrous proteins that will form the framework of epithelial cells. Epithelial cells line up the surfaces and cavities intended for the body. Keratin 4 is usually found within the moist lining of your mouth, nose, esophagus, anus, and gentitals. | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
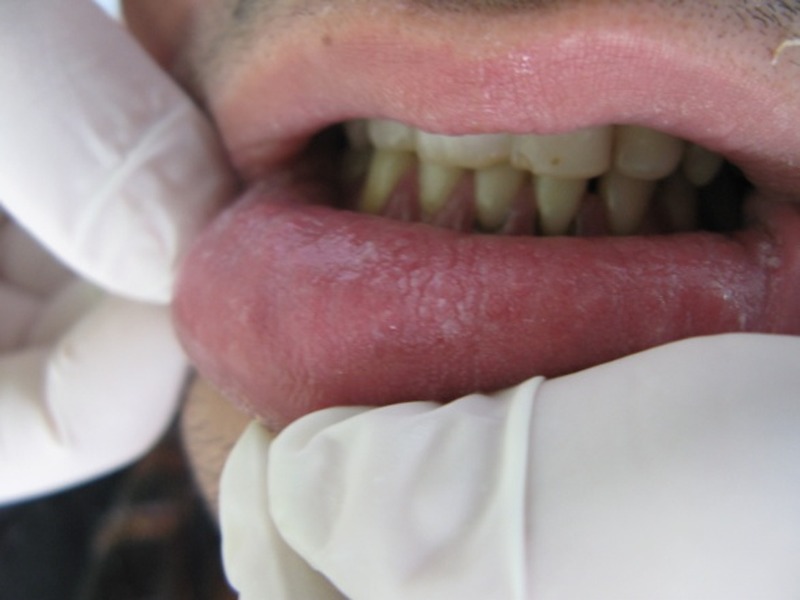
| - | The disease that Keratin 4 causes is white sponge nevus. White sponge nevus is an autosomal dominant disease which is caused by amutation of a certain keratin genes. White sponge nevus is going to be a main componenet for a group of inherited diseases that are going to provide a white bilateral, keratinized apperance typically appearing on the buccal mucosa. [[Image:joddd-3-70- | + | The disease that Keratin 4 causes is white sponge nevus. White sponge nevus is an autosomal dominant disease which is caused by amutation of a certain keratin genes. White sponge nevus is going to be a main componenet for a group of inherited diseases that are going to provide a white bilateral, keratinized apperance typically appearing on the buccal mucosa. [[Image:joddd-3-70-g001.jpg]] |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
The two way parallel beta-sheet is where the C-terminal strand of one monomer is being positioned and anti-parallel to the N-terminal strand of the main adjacent monomer and this arrangement is not seen so far in any of the homologous structures. This is the <scene name='87/874949/00rainbow_ribbon/1'>Keratin 4 protein</scene>. | The two way parallel beta-sheet is where the C-terminal strand of one monomer is being positioned and anti-parallel to the N-terminal strand of the main adjacent monomer and this arrangement is not seen so far in any of the homologous structures. This is the <scene name='87/874949/00rainbow_ribbon/1'>Keratin 4 protein</scene>. | ||
Revision as of 18:27, 26 April 2021
Keratin 4
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.201412048
- ↑ Moore PS, Hierholzer J, DeWitt W, Gouan K, Djore D, Lippeveld T, Plikaytis B, Broome CV. Respiratory viruses and mycoplasma as cofactors for epidemic group A meningococcal meningitis. JAMA. 1990 Sep 12;264(10):1271-5. PMID:2117679