User:Maggie Stopa/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
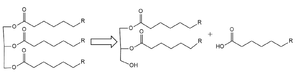
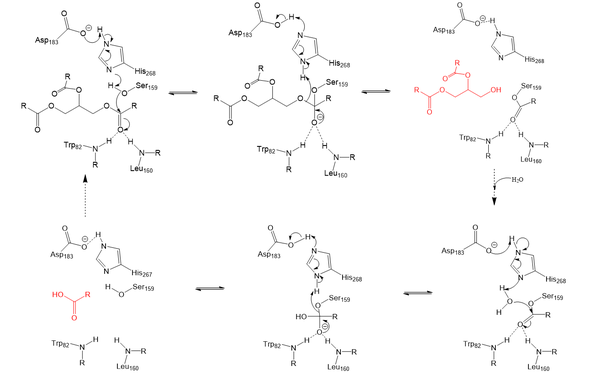
| - | Lipoprotein Lipase functions to catalyze the hydrolysis of one [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ester ester bond] of triglycerides in order to remove one fatty acid tail and turn the triglyceride into a diglyceride. It does this by utilizing a simple [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serine_hydrolase serine hydrolase] mechanism, in which it uses a <scene name='87/877513/Catalytic_triad-1/5'>catalytic triad</scene> composed of Asp183, His268, and Ser159 to catalyze the hydrolysis. His268 serves as a base catalyst by deprotonation of Ser159, which can then serve as the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophile]. The transition state of the catalysis is stabilized by the backbone of Trp82 and Leu160 residues, forming the <scene name='87/877513/Oxyanion_hole_-_labeled/ | + | Lipoprotein Lipase functions to catalyze the hydrolysis of one [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ester ester bond] of triglycerides in order to remove one fatty acid tail and turn the triglyceride into a diglyceride. It does this by utilizing a simple [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serine_hydrolase serine hydrolase] mechanism, in which it uses a <scene name='87/877513/Catalytic_triad-1/5'>catalytic triad</scene> composed of Asp183, His268, and Ser159 to catalyze the hydrolysis. His268 serves as a base catalyst by deprotonation of Ser159, which can then serve as the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophile]. The transition state of the catalysis is stabilized by the backbone of Trp82 and Leu160 residues, forming the <scene name='87/877513/Oxyanion_hole_-_labeled/6'>oxyanion hole</scene>. The hydrolysis results in the formation of one free fatty acid and a glycerol with two fatty acid tails. |
[[Image:LPL_final_Mechanism.png|600 px|center|thumb|Serine hydrolase mechanism utilized by LPL to catalyze the breakdown of one ester bond of a triglyceride. Compounds colored red are the products of the hydrolysis.]] | [[Image:LPL_final_Mechanism.png|600 px|center|thumb|Serine hydrolase mechanism utilized by LPL to catalyze the breakdown of one ester bond of a triglyceride. Compounds colored red are the products of the hydrolysis.]] | ||
Revision as of 19:28, 26 April 2021
Lipoprotein Lipase LPL
| |||||||||||