We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Betsy Johns/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
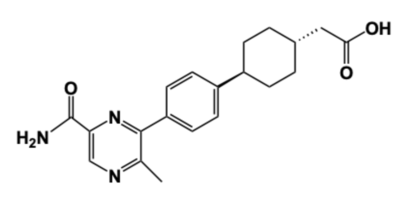
[[Image:DGAT_INHIBITOR.png|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 4: DGAT1 Inhibitor AZD7687''' Shown is the structure of AZD7687, a known inhibitor of DGAT1.]] | [[Image:DGAT_INHIBITOR.png|400 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 4: DGAT1 Inhibitor AZD7687''' Shown is the structure of AZD7687, a known inhibitor of DGAT1.]] | ||
| - | Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease ([https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567 NAFLD]) result from an accumulation of triacylglycerides within the body. Recently, DGAT1 has become a therapeutic target for obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in order to reduce triacylglyceride storage within the body <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref>. Different inhibitors have been created, such as AstraZeneca’s direct inhibitor [https://www.apexbt.com/azd7687.html AZD7687], shown in Figure 4 <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref>. AZD7687 has an EC50 value 0.44 µmol/L, showing that it binds with high affinity at a low concentration of DGAT1 <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref>. However, while triacylglyceride accumulation decreased, negative side effects did occur, such as diarrhea and other adverse GI symptoms <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref>. | + | Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease ([https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567 NAFLD]) result from an accumulation of triacylglycerides within the body. Recently, DGAT1 has become a therapeutic target for obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in order to reduce triacylglyceride storage within the body <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref>,ref name="Villanueva">PMID: 19472314</ref>. Different inhibitors have been created, such as AstraZeneca’s direct inhibitor [https://www.apexbt.com/azd7687.html AZD7687], shown in Figure 4 <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref>. AZD7687 has an EC50 value 0.44 µmol/L, showing that it binds with high affinity at a low concentration of DGAT1 <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref>. However, while triacylglyceride accumulation decreased, negative side effects did occur, such as diarrhea and other adverse GI symptoms <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref>. |
===Congenital Protein-Losing Enteropathy=== | ===Congenital Protein-Losing Enteropathy=== | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
<ref name="Stephen">PMID: 26883093</ref> | <ref name="Stephen">PMID: 26883093</ref> | ||
<ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref> | <ref name="Denison">PMID: 24118885</ref> | ||
| - | <ref name= | + | <ref name="Ma">PMID: 30283133</ref> |
| - | + | <ref name="Villanueva">PMID: 19472314</ref> | |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 19:56, 26 April 2021
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1, DGAT1, synthesizes triacylglycerides
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Wang L, Qian H, Nian Y, Han Y, Ren Z, Zhang H, Hu L, Prasad BVV, Laganowsky A, Yan N, Zhou M. Structure and mechanism of human diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):329-332. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433610 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2280-2
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 Sui X, Wang K, Gluchowski NL, Elliott SD, Liao M, Walther TC, Farese RV Jr. Structure and catalytic mechanism of a human triacylglycerol-synthesis enzyme. Nature. 2020 May;581(7808):323-328. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6. Epub 2020 May, 13. PMID:32433611 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2289-6
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Ma D, Wang Z, Merrikh CN, Lang KS, Lu P, Li X, Merrikh H, Rao Z, Xu W. Crystal structure of a membrane-bound O-acyltransferase. Nature. 2018 Oct;562(7726):286-290. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0568-2. Epub 2018 Oct, 3. PMID:30283133 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0568-2
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Denison H, Nilsson C, Lofgren L, Himmelmann A, Martensson G, Knutsson M, Al-Shurbaji A, Tornqvist H, Eriksson JW. Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 inhibition with AZD7687 alters lipid handling and hormone secretion in the gut with intolerable side effects: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Apr;16(4):334-43. doi: 10.1111/dom.12221. Epub 2013 Oct, 31. PMID:24118885 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dom.12221
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Stephen J, Vilboux T, Haberman Y, Pri-Chen H, Pode-Shakked B, Mazaheri S, Marek-Yagel D, Barel O, Di Segni A, Eyal E, Hout-Siloni G, Lahad A, Shalem T, Rechavi G, Malicdan MC, Weiss B, Gahl WA, Anikster Y. Congenital protein losing enteropathy: an inborn error of lipid metabolism due to DGAT1 mutations. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016 Aug;24(9):1268-73. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2016.5. Epub 2016 Feb , 17. PMID:26883093 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.5
- ↑ Villanueva CJ, Monetti M, Shih M, Zhou P, Watkins SM, Bhanot S, Farese RV Jr. Specific role for acyl CoA:Diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 (Dgat1) in hepatic steatosis due to exogenous fatty acids. Hepatology. 2009 Aug;50(2):434-42. doi: 10.1002/hep.22980. PMID:19472314 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hep.22980
Student Contributors
- Betsy Johns
- Elise Wang
- Tyler Bihasa