User:Hannah Wright/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
====Mechanism==== | ====Mechanism==== | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:mech426.png|200 px|]] |
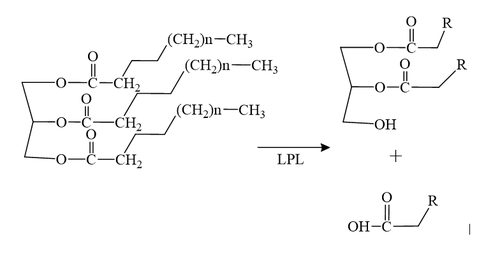
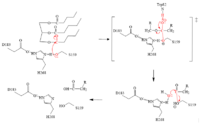
# The triglyceride binds to LPL’s lipid-binding region in an open lid conformation. | # The triglyceride binds to LPL’s lipid-binding region in an open lid conformation. | ||
| - | # The oxygen on S159 is made more nucleophilic. This happens via histidine hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen on S159’s alcohol group. | + | # The oxygen on S159 is made more [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nucleophile nucleophilic]. This happens via [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histidine histidine] hydrogen bonding with the hydrogen on S159’s alcohol group. |
| - | # The nucleophilic oxygen attacks the carbonyl carbon of one of the fatty acid chains. | + | # The nucleophilic oxygen attacks the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbonyl_group carbonyl carbon] of one of the fatty acid chains. |
| - | # This pushes electrons up onto the carbonyl oxygen, creating a tetrahedral intermediate. This is the oxyanion hole which is stabilized by main chain nitrogen atoms of W82 and L160. | + | # This pushes electrons up onto the carbonyl oxygen, creating a [http://www.chem.ucla.edu/~harding/IGOC/T/tetrahedral_intermediate.html tetrahedral intermediate]. This is the oxyanion hole which is stabilized by main chain nitrogen atoms of W82 and L160. |
# One of the lone pairs of the oxygen (in the oxyanion hole) creates a double bond carbon. | # One of the lone pairs of the oxygen (in the oxyanion hole) creates a double bond carbon. | ||
| - | # The oxygen-carbon bond between the single fatty acid chain and the diglyceride is cleaved. | + | # The oxygen-carbon bond between the single fatty acid chain and the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diglyceride diglyceride] is cleaved. |
# H268 hydrogen bonds water, making the oxygen a better nucleophile. Water attacks the carbonyl carbon. | # H268 hydrogen bonds water, making the oxygen a better nucleophile. Water attacks the carbonyl carbon. | ||
| - | # The carboxylic acid is formed and the S159 bond is cleaved and re-protonated via H268. | + | # The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carboxylic_acid carboxylic acid] is formed and the S159 bond is cleaved and re-protonated via H268. |
# The active site is now back in its original state. | # The active site is now back in its original state. | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
===Mutations=== | ===Mutations=== | ||
====D201V==== | ====D201V==== | ||
| - | <scene name='87/877636/D201_mutation/10'>D201V</scene> is a mutation that is found to cause chylomicronemia. Chylomicronemia is when the body cannot break down lipids properly. This leads to their build-up in the body causing high levels of triglycerides in the body. The carboxyl side chain of aspartate 201 is one of the coordination sites for the calcium ion of LPL. The mutation to hydrophobic valine means the loss of this coordination site<ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. This mutation adversely affects the folding of LPL and thus affects the secretion of LPL, overall decreasing the activity of LPL<ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. | + | <scene name='87/877636/D201_mutation/10'>D201V</scene> is a mutation that is found to cause [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipoprotein_lipase_deficiency chylomicronemia]. Chylomicronemia is when the body cannot break down lipids properly. This leads to their build-up in the body causing high levels of triglycerides in the body. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aspartic_acid carboxyl side chain of aspartate] 201 is one of the coordination sites for the calcium ion of LPL. The mutation to hydrophobic [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Valine valine] means the loss of this coordination site<ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. This mutation adversely affects the folding of LPL and thus affects the secretion of LPL, overall decreasing the activity of LPL<ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. |
====M404R==== | ====M404R==== | ||
| - | <scene name='87/877636/M404r_1/2'>M404R</scene> is a mutation found within LPL that caused chylomicronemia in patients. The hydrophobic methionine is mutated to the larger and charged side chain of arginine. Originally it was thought to impact LPL secretion from cells. It was found that the M404R does not affect LPL secretion <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. M404R interacts with the hydrophobic pocket of GPIHBP1’s finger 3 of its 3 fingered domain (V121, E122, T124, V126). The large, charged arginine repelled the hydrophobic pocket and does not fit well. This prevents proper binding and formation of the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. | + | <scene name='87/877636/M404r_1/2'>M404R</scene> is a mutation found within LPL that caused [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipoprotein_lipase_deficiency chylomicronemia] in patients. The hydrophobic [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Methionine methionine] is mutated to the larger and charged side chain of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arginine arginine]. Originally it was thought to impact LPL secretion from cells. It was found that the M404R does not affect LPL secretion <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. M404R interacts with the hydrophobic pocket of GPIHBP1’s finger 3 of its 3 fingered domain (V121, E122, T124, V126). The large, charged arginine repelled the hydrophobic pocket and does not fit well. This prevents proper binding and formation of the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. |
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 21:57, 26 April 2021
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) complexed with GPIHBP1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Arora R, Nimonkar AV, Baird D, Wang C, Chiu CH, Horton PA, Hanrahan S, Cubbon R, Weldon S, Tschantz WR, Mueller S, Brunner R, Lehr P, Meier P, Ottl J, Voznesensky A, Pandey P, Smith TM, Stojanovic A, Flyer A, Benson TE, Romanowski MJ, Trauger JW. Structure of lipoprotein lipase in complex with GPIHBP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 21;116(21):10360-10365. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1820171116. Epub 2019 May 9. PMID:31072929 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820171116
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Birrane G, Beigneux AP, Dwyer B, Strack-Logue B, Kristensen KK, Francone OL, Fong LG, Mertens HDT, Pan CQ, Ploug M, Young SG, Meiyappan M. Structure of the lipoprotein lipase-GPIHBP1 complex that mediates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 17. pii: 1817984116. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1817984116. PMID:30559189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1817984116
Student/Contributors
- Ashrey Burely
- Allison Welz
- Hannah Wright