Introduction
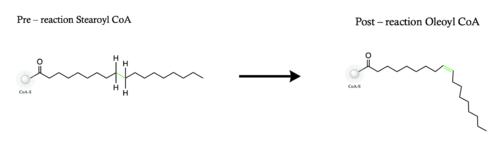
Figure 1. Overall reaction completed by the SCD1 enzyme. It introduces a double bond between carbons 9 and 10 on the ligand Stearoyl CoA, converting it into Oleoyl CoA
Stearyol CoA Desaturase (SCD1) functions as a lipogenic enzyme which is essential for fatty acid metabolism. SCD1 desaturates the sigma bond, within the 18-carbon acyl-CoA ligand, that attaches carbons 9 and 10
[1]. The primary role of SCD1 is to catalyze the biosynthesis of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) via saturated
acyl-CoAs with an acyl chain length of 14-19 carbons
[2][3]. Variations of the monounsaturated fatty acids function as precursors for the biosynthesis of
phospholipids,
cholesteryl esters, and
triglycerides; therefore, SCD1 is a promising candidate for drug targeting
[1].
Structural Overview
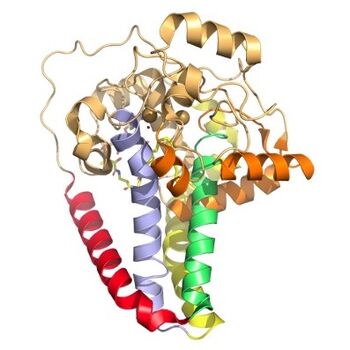
Figure 3. Hydrophobicity of each of the 12 helices found in SCD. red, blue, yellow, and green represent helices found in the transmembrane region. Orange helices represent helices found on the surface of the membrane. Pale yellow helices represent the hydrophilic helices.
SCD1 is a
protein transmembrane protein (4 helices in membrane, 8 helices in cytoplasm, shown in figures 2 and 3) that acquires electrons via an electron transport chain which includes
cytochrome b5 reductase and
cytochrome b5. The electrons are transferred via a ternary complex and accepted by SCD1 by the iron metal ions
[3]. SCD1 has 8 helices that are hydrophobic, 4 helices that are hydrophilic, and 3 helices that are amphipathic
[1][3](figure 2).There are two Fe+2 metal ions within the structure of SCD1 that were determined by x-ray fluorescence chromatography
x-ray fluorescense[3]. These ions are believed to be the activators of the catalytic molecule to allow for the desaturation reaction to occur within the enzyme.

Figure 2. Colored helices based on hydrophobicity. Red, green, yellow, and blue represent the transmembrane helices. Orange represents the helices found on the surface of the membrane, and tan represents the helices found in the cytoplasm.
Ligand Binding Pocket and Histidine Coordination
The ligand binding pocket is a narrow tunnel that extends approximately 24 Å into the mostly hydrophobic interior of the protein. The ligand is stabilized by bending into a kinked conformation which creates a tight fit in the binding pocket tunnel, and by a hydrogen bond that occurs between the side chain and the acyl carbonyl[1]. The kink in the tunnel is formed by the conserved residues, which are stabilized by the hydrogen bond shared with Q143[1]. There are that interact with the substrate; the Fe2+ ions are coordinated by 9 histidine residues. One metal ion is coordinated by 4 histidines residues and a water molecule, and the other metal ion is coordinated by 5 histidine residues[1]. the ligand is seen to be in a eclipsed position, indicating it is in its post-reaction form. The histidine residues position the metal ions 6.4 Å apart[1].
Desaturation Site
The ligand is desaturated at carbons 9 and 10[3]. The desaturation site of the ligand takes place inside the active site tunnel which enforces correct positioning of the substrate[1]. Before the reaction occurs, the ligand is in a gauche conformation at the desaturation site. This was determined by accidental usage of which allowed for binding of the substrate but prevented the reaction[3]. The product is in a cis conformation post-reaction. The product structure was determined using Fe2+ metal ions which allowed for the full reaction to take place[3]. The difference between the is the creation of a double bond, and the positioning of carbon 9 and 10 into a eclipsed position
Active Site Cap
The two conserved residues of the active site cap are . These two residues form a hydrogen bond creating a ridged barrier at the end of the active site to keep the ligand from moving during the reaction[1]. The active site cap is also used in determining the substrate length when entering the active site[1].
Catalytic Molecule
The of the SCD1 enzyme is a water molecule, coordinated by via hydrogen bonding[1]. The water molecule is 2.2 Å away from the Fe2+ metal ion molecule[1]. It interacts with the Fe2+ ion to make highly reactive radicals that are able to desaturate the highly stable carbon chain[4]. It is through the coordination of these ions by the histidines that the are able to be positioned within the vicinity of carbons 9 and 10 of the ligand[4].
Substrate Entering and Leaving
The substrate enters the active site through the active site tunnel and undergoes a to conform to the kinked shape of the tunnel[1]. Upon the substrate being converted to its final form, the product is laterally released from the protein due to a lateral egress of H1 and H2 caused by the deformation in the hydrogen bonding of the residues N 143 and T 257[1].
Proposed Mechanism
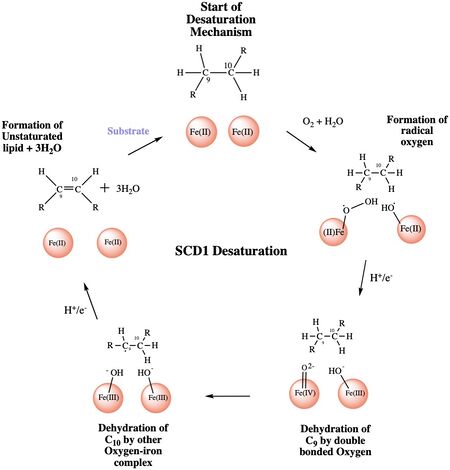
Figure 4: A proposed mechanism for SCD1 desaturase. The catalytic water molecule reacts with Fe2+ and O2 to create oxygen radicals on the iron ions. Electrons are brought in via an electron transport chain; this lowers the oxidation state of the iron ions and forms the reactive species. The first hydrogen is abstracted creating a radical intermediate that is then deprotonated again to make the final desaturated product. Electrons are transferred in again to allow for the iron ions to go back to their original oxidation state because enzymes must end a reaction in the same state, they started it. Figure was a modification of scheme 1 proposed by Yu M. and Chen S.5
The mechanism used by the SCD1 enzyme is different than most desaturase enzymes because it does not use an oxo-bridge. This was confirmed based on the distance between the metal ions (~6.4Å) and the lack of electron density that should be present with two oxygens[3]. There have been multiple proposed mechanisms, but the mechanism shown below is a shortened version of the mechanism that is the most accurate[4].
Step 1: Addition of O2 and H2O which react with the Fe2+ ions to create oxygen radicals on
the iron ions (Figure 4).
Step 2: Electron/proton pair is brought in via the electron transport chain; this increases the oxidation of both iron ions, gets rid of the radicals, and creates an active Fe-oxyl molecule (Figure).5 Fe-oxyl molecule is reactive enough, due to the change in the oxidation state, to pull off the first hydrogen on carbon 9 (figure 4).
Step 3: An unstable radical intermediate of the 18-carbon acyl-CoA ligand is formed which reacts with the other Fe-O molecule, in the +3 state, to pull of the second hydrogen and form the final product (figure 4)[4].
Step 4: Another electron/proton pair is brought in to create three H2O molecules and to take the Fe ions back down to their original oxidation state of +2 (Figure 4)[4].
Biological Relevance
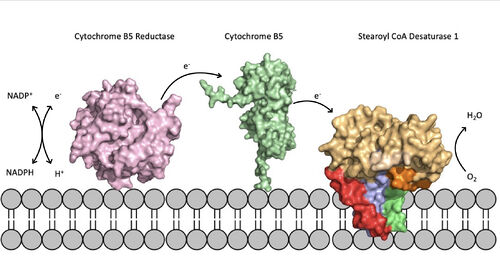
Figure 5. Position of SCD within the biological membrane. It is part of an electron transport chain involving cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome b5 to allow for the activation of the catalytic molecule coordinated by the two ions in the center of SCD
The electron transport chain allows for the mechanism of SCD1 to be carried out by providing electrons via either a Cytochrome B5 electron shuttle or an exchange through a ternary complex
ternary complex[3]. The electrons will be shuttled from complex to complex and then eventually be accepted by the SCD1 enzyme which will allow for activation of the catalytic molecule (Figure 5). The placement of SCD1 in the ER membrane is believed to prevent inhibition by allowing better flow of products/side products to their later pathways
[3].
Absence or a deficit of SCD1 in the body is associated with obesity and insulin resistant which is a main cause of type 2 diabetes[3]. Cancer sites in the body tend to show a much higher expression rate of SCD1[3]. Focusing on SCD1 as a drug target could lead to advancements in treatment of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic diseases[1].
The SCD1 enzyme can be down regulated or slightly inhibited by low-carbohydrate diets, low glucose levels, low insulin levels, and a low cholesterol diet. SCD1 is also regulated by leptin leptin; a protein that is created by fat cells[5]. When the leptin signaling pathway is fully functioning, the SCD1 enzyme is regulated in its ability to create MUFAs. SCD1 being associated with obesity could directly be tied to errors in the signaling pathways of the leptin protein[5].
Regulation of Enzyme
The main function of SCD1 is to create the desaturated ligand that is used in the synthesis of cholesterol esters and triglycerides[3]. Based on this main function it has been confirmed that insulin and carbohydrate metabolism play a major role in the regulation of SCD1[5]. Along with insulin many other hormones have shown positive regulation of the SCD1 enzyme including T3, estradiol, and dexamethasone[5]. The carbohydrate metabolism can be altered by eating a fat-free, high carbohydrate diet with an increased intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids[5]. The will negatively regulate the mRNA expression of the SCD1 enzyme in the liver because high amounts of carbohydrates and polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease/inhibit the activity of the SCD1 enzyme[5].
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 Bai Y, McCoy JG, Levin EJ, Sobrado P, Rajashankar KR, Fox BG, Zhou M. X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Nature. 2015 Jun 22. doi: 10.1038/nature14549. PMID:26098370 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14549
- ↑ Paton CM, Ntambi JM. Biochemical and physiological function of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jul;297(1):E28-37. doi:, 10.1152/ajpendo.90897.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 9. PMID:19066317 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.90897.2008
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 Shen J, Wu G, Tsai AL, Zhou M. Structure and Mechanism of a Unique Diiron Center in Mammalian Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. J Mol Biol. 2020 May 27. pii: S0022-2836(20)30367-3. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017. PMID:32470559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b00456
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Ntambi JM. The regulation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD). Prog Lipid Res. 1995;34(2):139-50. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(94)00010-j. PMID:7480063 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0163-7827(94)00010-j





