We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Hannah Wright/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
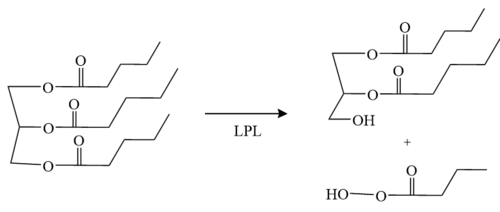
LPL is located within the interstitial space independently and remains stranded there if not acted upon by GPIHBP1. GPIHBP1 then captures LPL in the interstitial spaces and shuttles it across [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endothelium endothelial cells] into the capillary lumen. Once in the capillaries, the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex catalyzes the breakdown of triglycerides in the blood. In doing so, it prevents high levels of triglycerides in the plasma to provide nutrients for vital tissues <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. | LPL is located within the interstitial space independently and remains stranded there if not acted upon by GPIHBP1. GPIHBP1 then captures LPL in the interstitial spaces and shuttles it across [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endothelium endothelial cells] into the capillary lumen. Once in the capillaries, the LPL-GPIHBP1 complex catalyzes the breakdown of triglycerides in the blood. In doing so, it prevents high levels of triglycerides in the plasma to provide nutrients for vital tissues <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. | ||
===Significance=== | ===Significance=== | ||
| - | Lipoprotein lipase deficiency leads to [http://.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertriglyceridemia hypertriglyceridemia] (elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood) also known as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipoprotein_lipase_deficiency chylomicronemia]. This can go on to increase [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistance insulin resistance] and the risk of [ | + | Lipoprotein lipase deficiency leads to [http://.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hypertriglyceridemia hypertriglyceridemia] (elevated levels of triglycerides in the blood) also known as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipoprotein_lipase_deficiency chylomicronemia]. This can go on to increase [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin_resistance insulin resistance] and the risk of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Obesity obesity]. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
===Overall Structure=== | ===Overall Structure=== | ||
| - | Overall, LPL is a monomer but biologically it is paired with another monomer. These are often referred two as <scene name='87/877603/Chain_a_and_chain_b/4'>Chain A and Chain B</scene>. Chain A (shown as slate blue) and Chain B (shown as magenta) are identical besides orientation. Chain A and B are oriented head to tail. LPL is also complexed with GPIHBP1 (shown as cyan) and is essential for LPL to remain stable and avoid [ | + | Overall, LPL is a monomer but biologically it is paired with another monomer. These are often referred two as <scene name='87/877603/Chain_a_and_chain_b/4'>Chain A and Chain B</scene>. Chain A (shown as slate blue) and Chain B (shown as magenta) are identical besides orientation. Chain A and B are oriented head to tail. LPL is also complexed with GPIHBP1 (shown as cyan) and is essential for LPL to remain stable and avoid [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Denaturation_(biochemistry) denaturation]. |
===LPL=== | ===LPL=== | ||
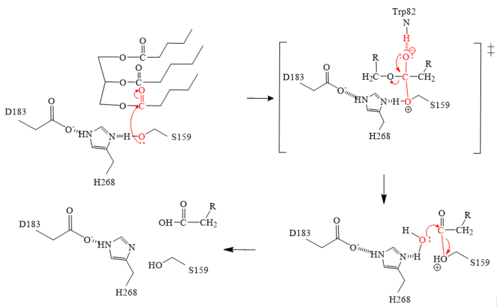
LPL has two main domains, the larger N-terminus domain containing the active site and the smaller C-terminus domain. These two domains are connected via a peptide linker hinge. LPL also contains a large basic patch and a single calcium ion. Additionally, LPL consists of two N-linked glycans (N70, N386) which likely contribute to the correct folding of LPL due to the attached oligosaccharides. Five disulfide bonds contribute to the stabilization throughout LPL’s structure. Lastly, the active site in the larger N-terminus domain is lined with hydrophobic residues <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. | LPL has two main domains, the larger N-terminus domain containing the active site and the smaller C-terminus domain. These two domains are connected via a peptide linker hinge. LPL also contains a large basic patch and a single calcium ion. Additionally, LPL consists of two N-linked glycans (N70, N386) which likely contribute to the correct folding of LPL due to the attached oligosaccharides. Five disulfide bonds contribute to the stabilization throughout LPL’s structure. Lastly, the active site in the larger N-terminus domain is lined with hydrophobic residues <ref name="Birrane">PMID:30559189</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 16:04, 27 April 2021
Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) complexed with GPIHBP1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 Birrane G, Beigneux AP, Dwyer B, Strack-Logue B, Kristensen KK, Francone OL, Fong LG, Mertens HDT, Pan CQ, Ploug M, Young SG, Meiyappan M. Structure of the lipoprotein lipase-GPIHBP1 complex that mediates plasma triglyceride hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 17. pii: 1817984116. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1817984116. PMID:30559189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1817984116
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wong H, Davis RC, Thuren T, Goers JW, Nikazy J, Waite M, Schotz MC. Lipoprotein lipase domain function. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10319-23. PMID:8144612
- ↑ Arora R, Nimonkar AV, Baird D, Wang C, Chiu CH, Horton PA, Hanrahan S, Cubbon R, Weldon S, Tschantz WR, Mueller S, Brunner R, Lehr P, Meier P, Ottl J, Voznesensky A, Pandey P, Smith TM, Stojanovic A, Flyer A, Benson TE, Romanowski MJ, Trauger JW. Structure of lipoprotein lipase in complex with GPIHBP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 21;116(21):10360-10365. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1820171116. Epub 2019 May 9. PMID:31072929 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1820171116
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Falko JM. Familial Chylomicronemia Syndrome: A Clinical Guide For Endocrinologists. Endocr Pract. 2018 Aug;24(8):756-763. doi: 10.4158/EP-2018-0157. PMID:30183397 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4158/EP-2018-0157
Student/Contributors
- Ashrey Burley
- Allison Welz
- Hannah Wright