We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Dustin Soe/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | =Lipoprotein Lipase coupled with GPIHBP1= | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='6ob0' size='350' side='right' caption='Lipoprotein Lipase PDB' scene='87/877513/Original_scene/1'> | ||
| - | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
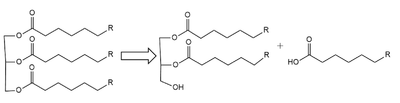
| - | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>Lipoprotein Lipase</scene>(LPL) is an important enzyme for the breakdown of triglycerides in the body (Figure 1).<ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> [[Image:Simple_mech.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1: breakdown of a triglyceride into a diglyceride and creation of one free fatty acid by LPL]] A [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipase lipase] is an enzyme that is capable of catalyzing the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysis] of fats/lipids which are consumed through oils. It is encoded by the [https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LPL p22 region in chromosome 8]. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the interstitial space in several tissues. The main site of action for <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is in the [https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/116/5/1480/F1.large.jpg capillary lumen] within muscle and adipose tissues.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> The function of this lipase is to hydrolyze [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides] of very-low-density lipoproteins ([https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-8e874e647baeb69b00203c47165247e2 VLDL]) and to aid in the delivery of lipid nutrients to vital tissues.<ref name=”Birrane”/ | + | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>Lipoprotein Lipase</scene>(LPL) is an important enzyme for the breakdown of triglycerides in the body (Figure 1).<ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> [[Image:Simple_mech.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1: breakdown of a triglyceride into a diglyceride and creation of one free fatty acid by LPL]] A [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipase lipase] is an enzyme that is capable of catalyzing the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysis] of fats/lipids which are consumed through oils. It is encoded by the [https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LPL p22 region in chromosome 8]. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the interstitial space in several tissues. The main site of action for <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is in the [https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/116/5/1480/F1.large.jpg capillary lumen] within muscle and adipose tissues.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> The function of this lipase is to hydrolyze [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides] of very-low-density lipoproteins ([https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-8e874e647baeb69b00203c47165247e2 VLDL]) and to aid in the delivery of lipid nutrients to vital tissues.<ref name=”Birrane” /> |
Revision as of 02:04, 28 April 2021
Introduction
(LPL) is an important enzyme for the breakdown of triglycerides in the body (Figure 1).[1] A lipase is an enzyme that is capable of catalyzing the hydrolysis of fats/lipids which are consumed through oils. It is encoded by the p22 region in chromosome 8. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the interstitial space in several tissues. The main site of action for is in the capillary lumen within muscle and adipose tissues.[2] The function of this lipase is to hydrolyze triglycerides of very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) and to aid in the delivery of lipid nutrients to vital tissues.Cite error: Invalid<ref> tag;
refs with no content must have a name