User:Giselle Flores/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | Giselle’s Edit Box | ||
=Lipoprotein Lipase coupled with GPIHBP1= | =Lipoprotein Lipase coupled with GPIHBP1= | ||
<StructureSection load='6ob0' size='350' side='right' caption='Lipoprotein Lipase PDB' scene='87/877513/Original_scene/1'> | <StructureSection load='6ob0' size='350' side='right' caption='Lipoprotein Lipase PDB' scene='87/877513/Original_scene/1'> | ||
| - | + | It should be noted that the PDB: 6OB0 was used to synthesize the following images. | |
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
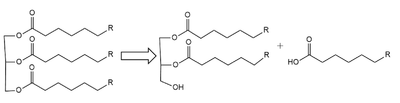
| - | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>Lipoprotein Lipase</scene>(LPL) is an important enzyme for the breakdown of triglycerides in the body (Figure 1).<ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> [[Image:Simple_mech.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1: breakdown of a triglyceride into a diglyceride and creation of one free fatty acid by LPL]] A [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipase lipase] is an enzyme that is capable of catalyzing the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysis] of fats/lipids which are consumed through oils. It is encoded by the [https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LPL p22 region in chromosome 8]. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the interstitial space in several tissues. The main site of action for <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is in the [https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/116/5/1480/F1.large.jpg capillary lumen] within muscle and adipose tissues.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> The function of this lipase is to hydrolyze [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides] of very-low-density lipoproteins ([https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-8e874e647baeb69b00203c47165247e2 VLDL]) and to aid in the delivery of lipid nutrients to vital tissues.<ref name=”Birrane” /> The enzyme is commonly found on the surface of cells that line blood capillaries. Two different lipoproteins are essential to break down triglycerides. One of the lipoproteins is utilized to transport fat into the bloodstream from different organs.<ref name=”Arora” /> The lipoproteins essential, in the transport of fat from the intestine are referred to as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chylomicron chylomicrons]. VLDL are utilized in carrying triglycerides from the liver into the bloodstream. The hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase results in fat molecules being used by the body as energy or stored in fatty tissue. <ref name=”Arora” /><ref name=”Mead”>PMID:12483461</ref> | + | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>Lipoprotein Lipase</scene>(LPL) is an important enzyme for the breakdown of triglycerides in the body (Figure 1).<ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> [[Image:Simple_mech.png|400 px|right|thumb|Figure 1: breakdown of a triglyceride into a diglyceride and creation of one free fatty acid by LPL]] A [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lipase lipase] is an enzyme that is capable of catalyzing the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysis] of fats/lipids which are consumed through oils. It is encoded by the [https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LPL p22 region in chromosome 8]. Once synthesized, it is secreted into the interstitial space in several tissues. The main site of action for <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is in the [https://www.pnas.org/content/pnas/116/5/1480/F1.large.jpg capillary lumen] within muscle and adipose tissues.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> The function of this lipase is to hydrolyze [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triglyceride triglycerides] of very-low-density lipoproteins ([https://qph.fs.quoracdn.net/main-qimg-8e874e647baeb69b00203c47165247e2 VLDL]) and to aid in the delivery of lipid nutrients to vital tissues.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> The enzyme is commonly found on the surface of cells that line blood capillaries. Two different lipoproteins are essential to break down triglycerides. One of the lipoproteins is utilized to transport fat into the bloodstream from different organs.<ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> The lipoproteins essential, in the transport of fat from the intestine are referred to as [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chylomicron chylomicrons]. VLDL are utilized in carrying triglycerides from the liver into the bloodstream. The hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoprotein lipase results in fat molecules being used by the body as energy or stored in fatty tissue. <ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref><ref name=”Mead”>PMID:12483461</ref> |
==Structural Overview== | ==Structural Overview== | ||
===LPL=== | ===LPL=== | ||
| - | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is assumed to only be active as a <scene name='87/877513/Lpl_dimer/5'>tetramer</scene> composed of two LPL-GPIHBP1 heterodimers, however, previous studies have argued that the lipase can be active in its <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>single heterodimeric form</scene>.<ref name=”Arora” /><ref name=”Beigneux”>PMID:30850549</ref>The N-terminal domain of lipoprotein lipase is known to consist of an alpha/beta hydrolase domain, which is composed of six alpha helices and ten beta strands. This domain creates an <scene name='87/877513/Alpha-beta_hydrolase_domain_1/3'>alpha beta hydrolase fold</scene>. The C-terminal domain of lipoprotein lipase is composed of twelve beta strands which form a "<scene name='87/877513/Just_barrel_domain_1/1'>barrel domain</scene>".<ref name=”Arora” /> | + | |
| + | <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene> is assumed to only be active as a <scene name='87/877513/Lpl_dimer/5'>tetramer</scene> composed of two LPL-GPIHBP1 heterodimers, however, previous studies have argued that the lipase can be active in its <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>single heterodimeric form</scene>.<ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref><ref name=”Beigneux”>PMID:30850549</ref>The N-terminal domain of lipoprotein lipase is known to consist of an alpha/beta hydrolase domain, which is composed of six alpha helices and ten beta strands. This domain creates an <scene name='87/877513/Alpha-beta_hydrolase_domain_1/3'>alpha beta hydrolase fold</scene>. The C-terminal domain of lipoprotein lipase is composed of twelve beta strands which form a "<scene name='87/877513/Just_barrel_domain_1/1'>barrel domain</scene>".<ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> | ||
=== GPIHBP1 === | === GPIHBP1 === | ||
| - | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPIHBP1 GPIHBP1]) is a secondary domain that is critical to the stabilization, function, and movement of <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene>.<ref name=”Birrane” /> The GPIHBP1’s highly acidic and intrinsically disordered N-terminal domain are essential to the binding of LPL’s C-terminal Domain. It has been shown that GPIHBP1 has a “three fingered domain”, which holds it tightly to LPL by <scene name='87/877513/Hydrophobic_interface-labeled/3'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>.<ref name=”Birrane” /> The importance of GPIBP1’s affinity to LPL was analyzed by Birrane et al.<ref name=”Birrane” />, and it was found that missense mutations of critical residues resulted in high amounts of impairments. It was also concluded that these impairments caused hypertriglyceridemia (chylomicronemia).<ref name=”Birrane” /> | + | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored high density lipoprotein-binding protein 1 ([https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPIHBP1 GPIHBP1]) is a secondary domain that is critical to the stabilization, function, and movement of <scene name='87/877513/Original_scene/1'>LPL</scene>.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> The GPIHBP1’s highly acidic and intrinsically disordered N-terminal domain are essential to the binding of LPL’s C-terminal Domain. It has been shown that GPIHBP1 has a “three fingered domain”, which holds it tightly to LPL by <scene name='87/877513/Hydrophobic_interface-labeled/3'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> The importance of GPIBP1’s affinity to LPL was analyzed by Birrane et al.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref>, and it was found that missense mutations of critical residues resulted in high amounts of impairments. It was also concluded that these impairments caused hypertriglyceridemia (chylomicronemia).<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> |
== Structural Highlights == | == Structural Highlights == | ||
=== Calcium Ion Stabilization === | === Calcium Ion Stabilization === | ||
| - | Ions are widely used in proteins and mechanistic stabilization in many areas of biochemistry. LPL’s tertiary folding is stabilized by a Calcium (Ca2+) ion. The calcium ion shares electron density with surrounding residues in order to orient the protein in its formal state.<ref name=”Birrane” /> The <scene name='87/877513/Calcium_stabilization_-labeled/3'>calcium ion stabilization</scene> is achieved by the calcium ion’s interactions with the following of LPL’s residues: Ala194, Arg197, Ser199, Asp201, and Asp202.<ref name=”Birrane” /> | + | Ions are widely used in proteins and mechanistic stabilization in many areas of biochemistry. LPL’s tertiary folding is stabilized by a Calcium (Ca2+) ion. The calcium ion shares electron density with surrounding residues in order to orient the protein in its formal state.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> The <scene name='87/877513/Calcium_stabilization_-labeled/3'>calcium ion stabilization</scene> is achieved by the calcium ion’s interactions with the following of LPL’s residues: Ala194, Arg197, Ser199, Asp201, and Asp202.<ref name=”Birrane”>PMID:30559189</ref> |
=== Lid and Lipid Binding Region === | === Lid and Lipid Binding Region === | ||
| - | In the presence of the GPIHBP1 inhibitor, the <scene name='87/ | + | In the presence of the GPIHBP1 inhibitor, the <scene name='87/877513/Lid_region_final/2'>lid region</scene> and <scene name='87/877516/Inhibitorsbound/1'>lipid-binding region</scene> become visible within the structure. As displayed through a study conducted by Arora et. al, in 2019, the lipid-binding region of LPL actively interacts with the known inhibitor in the heterodimeric form. <ref name=”Arora”>PMID:31072929</ref> This was established to be the only time that the heterodimeric form was shown as an active lipase. The lid region residues Ile245, Ile249, V251, Ile252, Leu257, Val260, Leu263, and Val264, are found as an open conformation which is composed of two small alpha helices that reach out and away from the protein. The lid and lipid-binding region create hydrophobic patches on the surface of lipoprotein lipase which are essential for <scene name='87/877513/Lipid_binding_and_lid/1'>ligand binding</scene> by LPL. |
[[Image:Inhibiting.png|300 px|right|thumb|The novel inhibitor bound between the lipid-binding region of one LPL and the catalytic site of the other LPL of the tetramer.]] | [[Image:Inhibiting.png|300 px|right|thumb|The novel inhibitor bound between the lipid-binding region of one LPL and the catalytic site of the other LPL of the tetramer.]] | ||
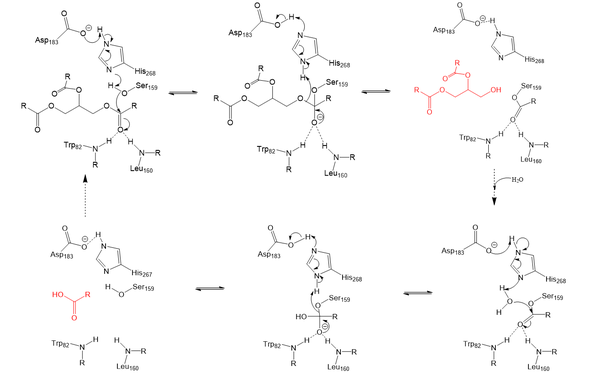
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 37: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Revision as of 02:26, 28 April 2021
Giselle’s Edit Box
Lipoprotein Lipase coupled with GPIHBP1
| |||||||||||