This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox GGC6
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| - | NT-4, along with other growth factors including neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and nerve growth factor (NGF) have all shown to be essential for survival of neurons. <ref>PMID: 10631974, | + | NT-4, along with other growth factors including neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and nerve growth factor (NGF) have all shown to be essential for survival of neurons. <ref>PMID: 10631974</ref>, <ref>16411893</ref> These growth factors have been associated with parts of the cerebrum including the frontal lobe and limbic system because of their involvement in neurological processes like behavior, learning, and memory. <ref>PMID: 16411893</ref> |
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 14:45, 28 April 2021
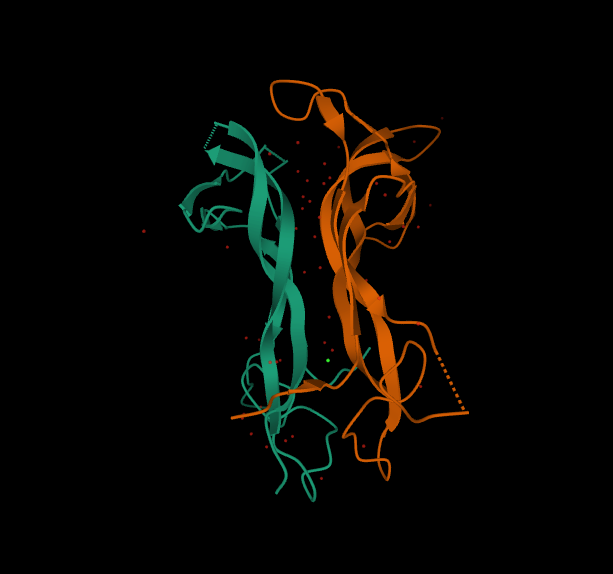
Neurotrophin-4
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Robinson RC, Radziejewski C, Spraggon G, Greenwald J, Kostura MR, Burtnick LD, Stuart DI, Choe S, Jones EY. The structures of the neurotrophin 4 homodimer and the brain-derived neurotrophic factor/neurotrophin 4 heterodimer reveal a common Trk-binding site. Protein Sci. 1999 Dec;8(12):2589-97. PMID:10631974
- ↑ 16411893
- ↑ Chao MV, Rajagopal R, Lee FS. Neurotrophin signalling in health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2006 Feb;110(2):167-73. doi: 10.1042/CS20050163. PMID:16411893 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/CS20050163