We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox GGC6
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Depletion and/or unavailable receptor binding sites are also being studied to further understand these mechanisms. | Depletion and/or unavailable receptor binding sites are also being studied to further understand these mechanisms. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
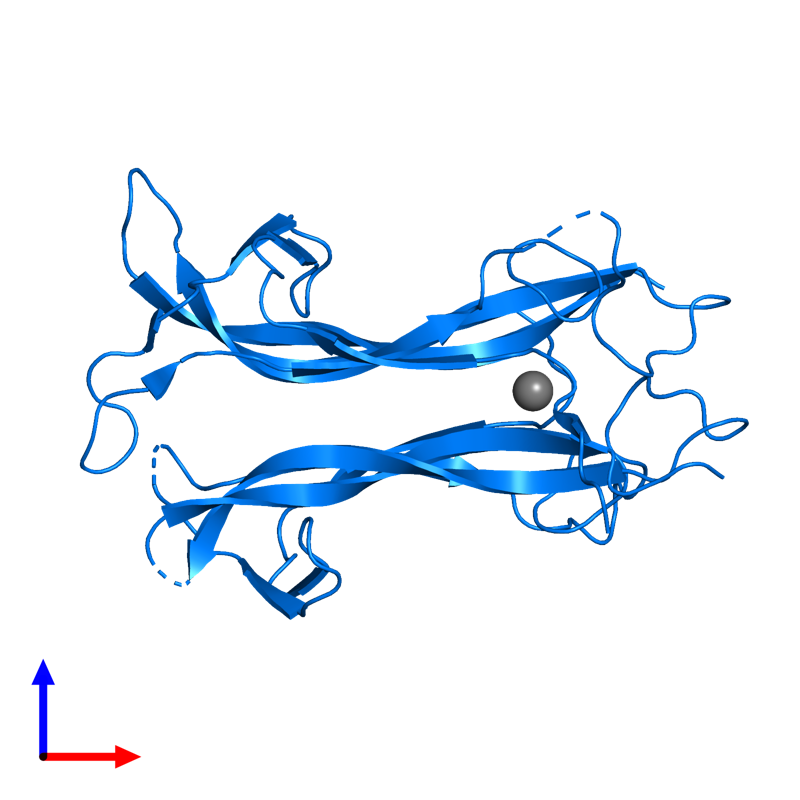
| - | NT-4 is a homodimer; Its structure includes 2 Neurotrophin-4 factors bound with a chloride ion. NT-4 is 130 amino acids in length. This chloride ion is a ligand that binds to nerve growth factor receptors. | + | NT-4 is a homodimer; Its <scene name='78/781192/Protein-ligand/1'>structure</scene> includes 2 Neurotrophin-4 factors bound with a chloride ion. NT-4 is 130 amino acids in length. This chloride ion is a ligand that binds to nerve growth factor receptors. |
<scene name='78/781192/N_to_c_rainbow/1'>N to C sequence</scene> | <scene name='78/781192/N_to_c_rainbow/1'>N to C sequence</scene> | ||
{{Template:ColorKey_N52C3Rainbow}} | {{Template:ColorKey_N52C3Rainbow}} | ||
Current revision
Neurotrophin-4
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Chao MV, Rajagopal R, Lee FS. Neurotrophin signalling in health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2006 Feb;110(2):167-73. doi: 10.1042/CS20050163. PMID:16411893 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/CS20050163
- ↑ Robinson RC, Radziejewski C, Spraggon G, Greenwald J, Kostura MR, Burtnick LD, Stuart DI, Choe S, Jones EY. The structures of the neurotrophin 4 homodimer and the brain-derived neurotrophic factor/neurotrophin 4 heterodimer reveal a common Trk-binding site. Protein Sci. 1999 Dec;8(12):2589-97. PMID:10631974
- ↑ Liebl DJ, Klesse LJ, Tessarollo L, Wohlman T, Parada LF. Loss of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent neural crest-derived sensory neurons in neurotrophin-4 mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Feb 29;97(5):2297-302. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.040562597. PMID:10681461 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.040562597
- ↑ Gaudet P, Livstone MS, Lewis SE, Thomas PD. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform. 2011 Sep;12(5):449-62. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbr042. Epub 2011 Aug, 27. PMID:21873635 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbr042
- ↑ Liebl DJ, Klesse LJ, Tessarollo L, Wohlman T, Parada LF. Loss of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent neural crest-derived sensory neurons in neurotrophin-4 mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Feb 29;97(5):2297-302. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.040562597. PMID:10681461 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.040562597
- ↑ Botchkarev VA, Botchkareva NV, Welker P, Metz M, Lewin GR, Subramaniam A, Bulfone-Paus S, Hagen E, Braun A, Lommatzsch M, Renz H, Paus AR. A new role for neurotrophins: involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-4 in hair cycle control. FASEB J. 1999 Feb;13(2):395-410. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.13.2.395. PMID:9973328 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.13.2.395
- ↑ Xie CW, Sayah D, Chen QS, Wei WZ, Smith D, Liu X. Deficient long-term memory and long-lasting long-term potentiation in mice with a targeted deletion of neurotrophin-4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jul 5;97(14):8116-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.140204597. PMID:10869436 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.140204597
- ↑ Gaudet P, Livstone MS, Lewis SE, Thomas PD. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform. 2011 Sep;12(5):449-62. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbr042. Epub 2011 Aug, 27. PMID:21873635 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbr042
- ↑ Gaudet P, Livstone MS, Lewis SE, Thomas PD. Phylogenetic-based propagation of functional annotations within the Gene Ontology consortium. Brief Bioinform. 2011 Sep;12(5):449-62. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbr042. Epub 2011 Aug, 27. PMID:21873635 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbr042
- ↑ Sofroniew MV, Howe CL, Mobley WC. Nerve growth factor signaling, neuroprotection, and neural repair. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:1217-81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.1217. PMID:11520933 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.1217
- ↑ Liebl DJ, Mbiene JP, Parada LF. NT4/5 mutant mice have deficiency in gustatory papillae and taste bud formation. Dev Biol. 1999 Sep 15;213(2):378-89. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9385. PMID:10479455 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/dbio.1999.9385
- ↑ Robinson RC, Radziejewski C, Spraggon G, Greenwald J, Kostura MR, Burtnick LD, Stuart DI, Choe S, Jones EY. The structures of the neurotrophin 4 homodimer and the brain-derived neurotrophic factor/neurotrophin 4 heterodimer reveal a common Trk-binding site. Protein Sci. 1999 Dec;8(12):2589-97. PMID:10631974
- ↑ Chao MV, Rajagopal R, Lee FS. Neurotrophin signalling in health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2006 Feb;110(2):167-73. doi: 10.1042/CS20050163. PMID:16411893 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/CS20050163
- ↑ Chao MV, Rajagopal R, Lee FS. Neurotrophin signalling in health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2006 Feb;110(2):167-73. doi: 10.1042/CS20050163. PMID:16411893 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/CS20050163
- ↑ Chao MV, Rajagopal R, Lee FS. Neurotrophin signalling in health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2006 Feb;110(2):167-73. doi: 10.1042/CS20050163. PMID:16411893 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/CS20050163
- ↑ Serum neurotrophin concentrations in autism and mental retardation: a pilot study Miyazaki, Kaoru et al. Brain and Development, Volume 26, Issue 5, 292 - 295